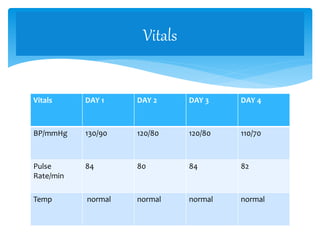
- The patient presented with erythrodermic psoriasis, a severe form of psoriasis affecting most of the body surface. Symptoms included redness, scaling, and itching all over the body.
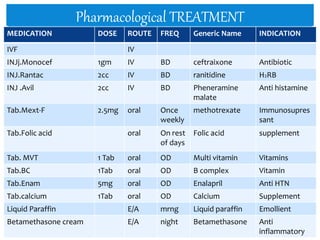
- A skin biopsy confirmed psoriatic erythroderma. The patient was started on methotrexate and folic acid for immunosuppression along with antibiotics, antihistamines, emollients and corticosteroids to treat symptoms.
- The patient was counseled on lifestyle modifications including avoiding smoking and alcohol, taking oatmeal baths, moisturizing skin, and minimizing sun exposure to manage their condition.