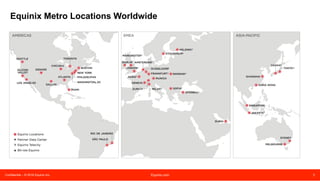
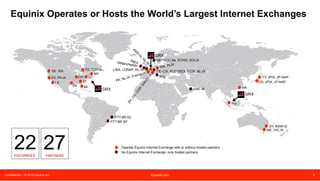
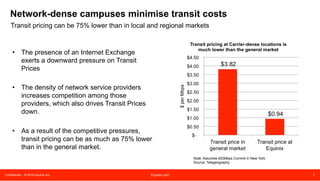
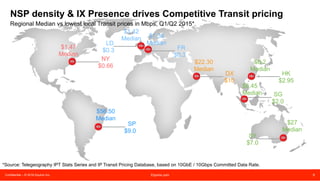
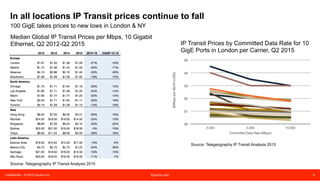
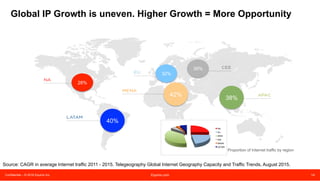
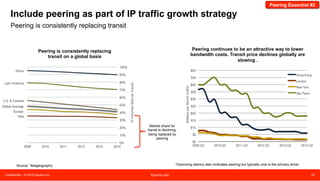
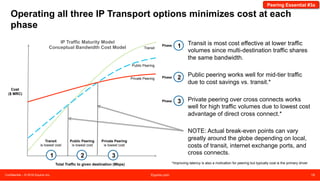
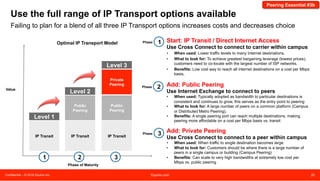
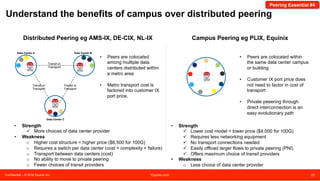
The document discusses peering strategies and options at Equinix. It recommends planning for 20%+ annual traffic growth, including peering as part of the IP traffic growth strategy, and using a blend of transit, public peering, and private peering according to traffic volumes. It also recommends understanding the cost and flexibility implications of campus versus distributed peering, and planning for private peering traffic to outgrow public peering traffic over time. The document provides an overview of peering essentials and options available at Equinix locations worldwide.