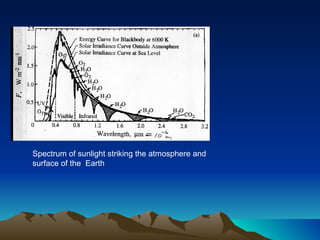
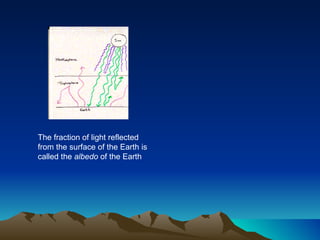
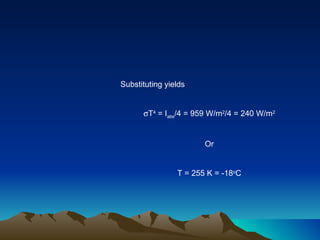
The document discusses the equilibrium temperature of the Earth using concepts from the electromagnetic spectrum and solar energy absorption. It calculates the absorbed solar intensity and the equilibrium temperature, concluding that the Earth's temperature is approximately 255 K (-18 °C). The albedo effect, the solar constant, and the Stefan-Boltzmann law are key components of this analysis.