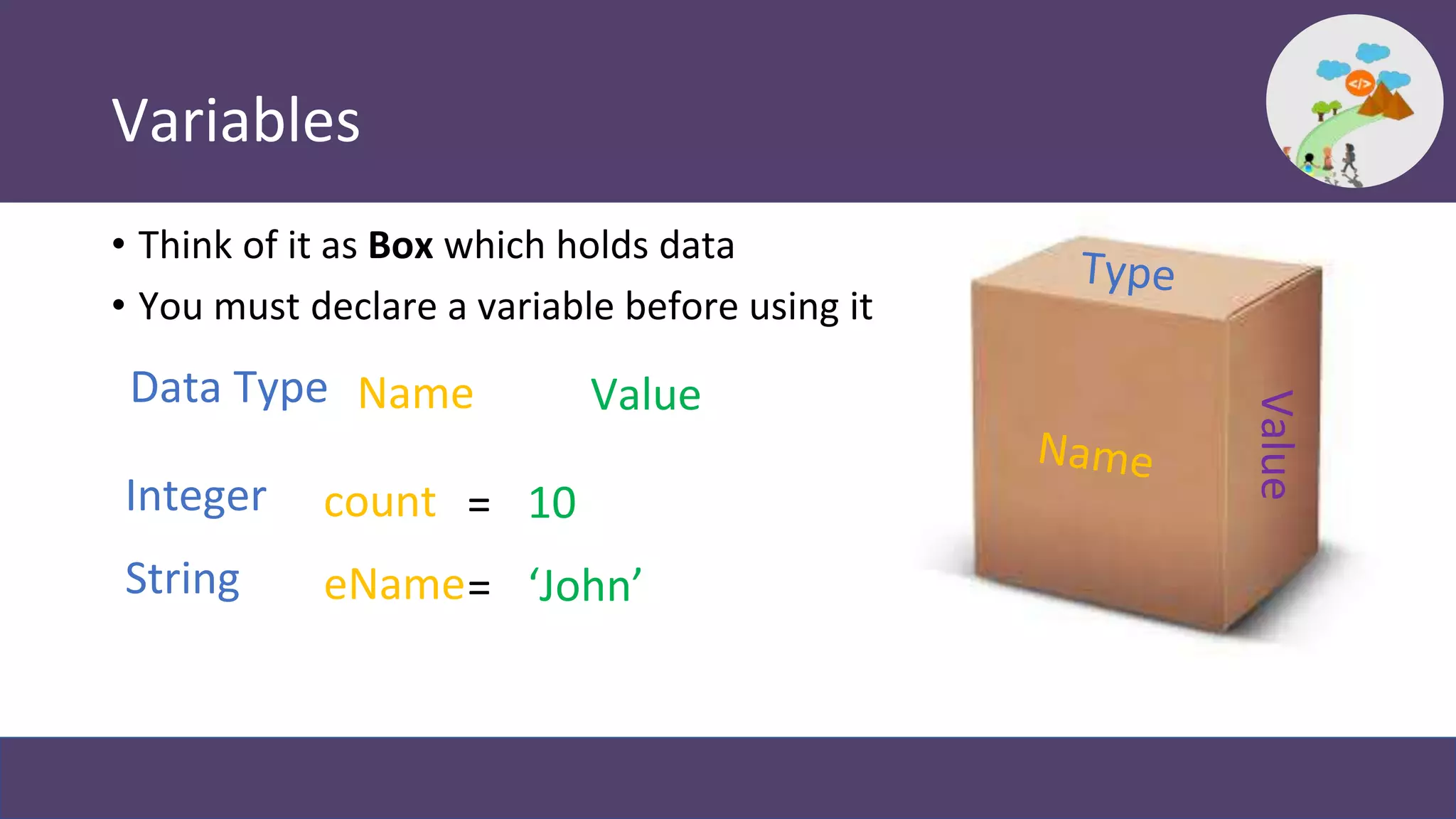
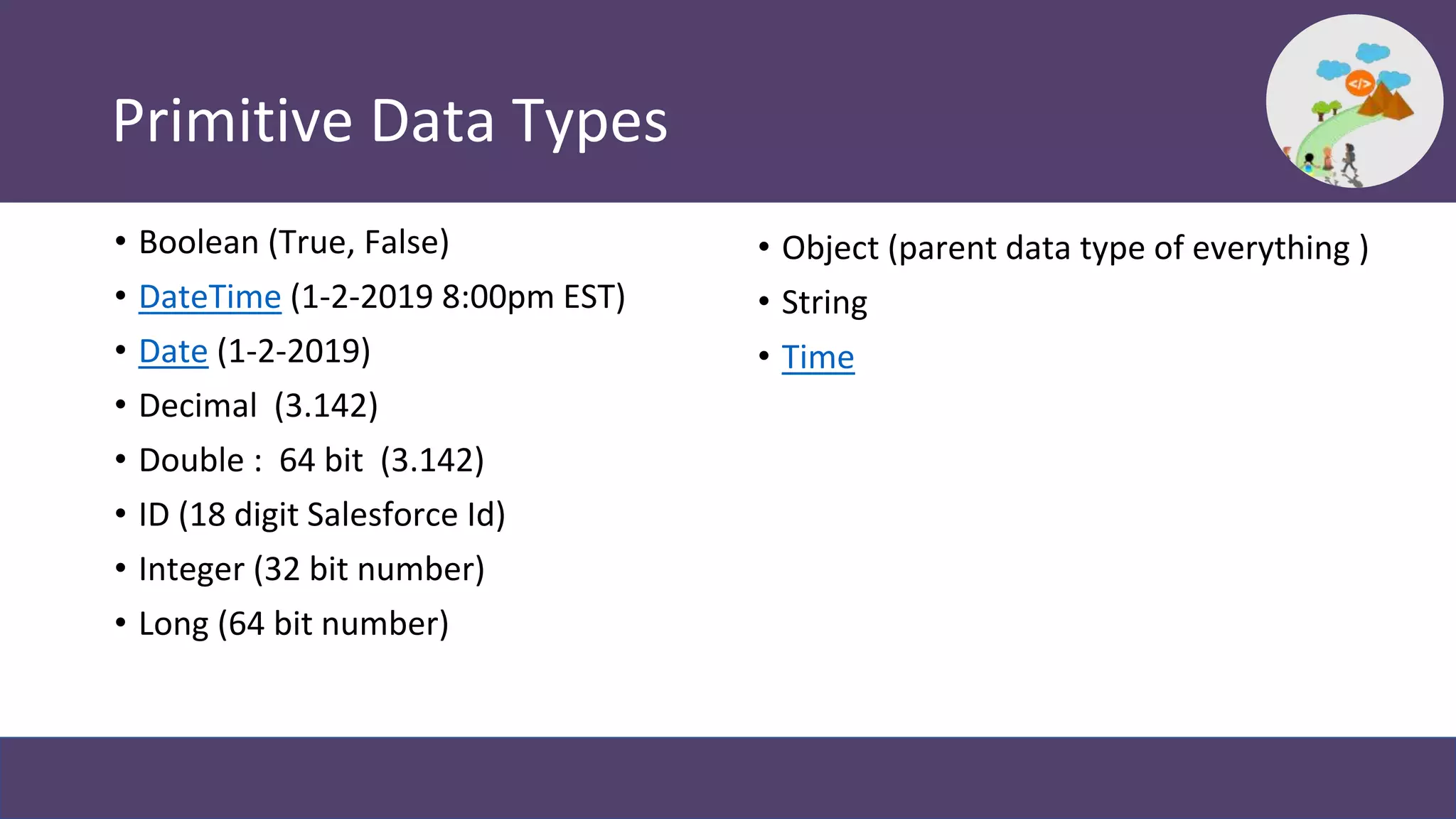
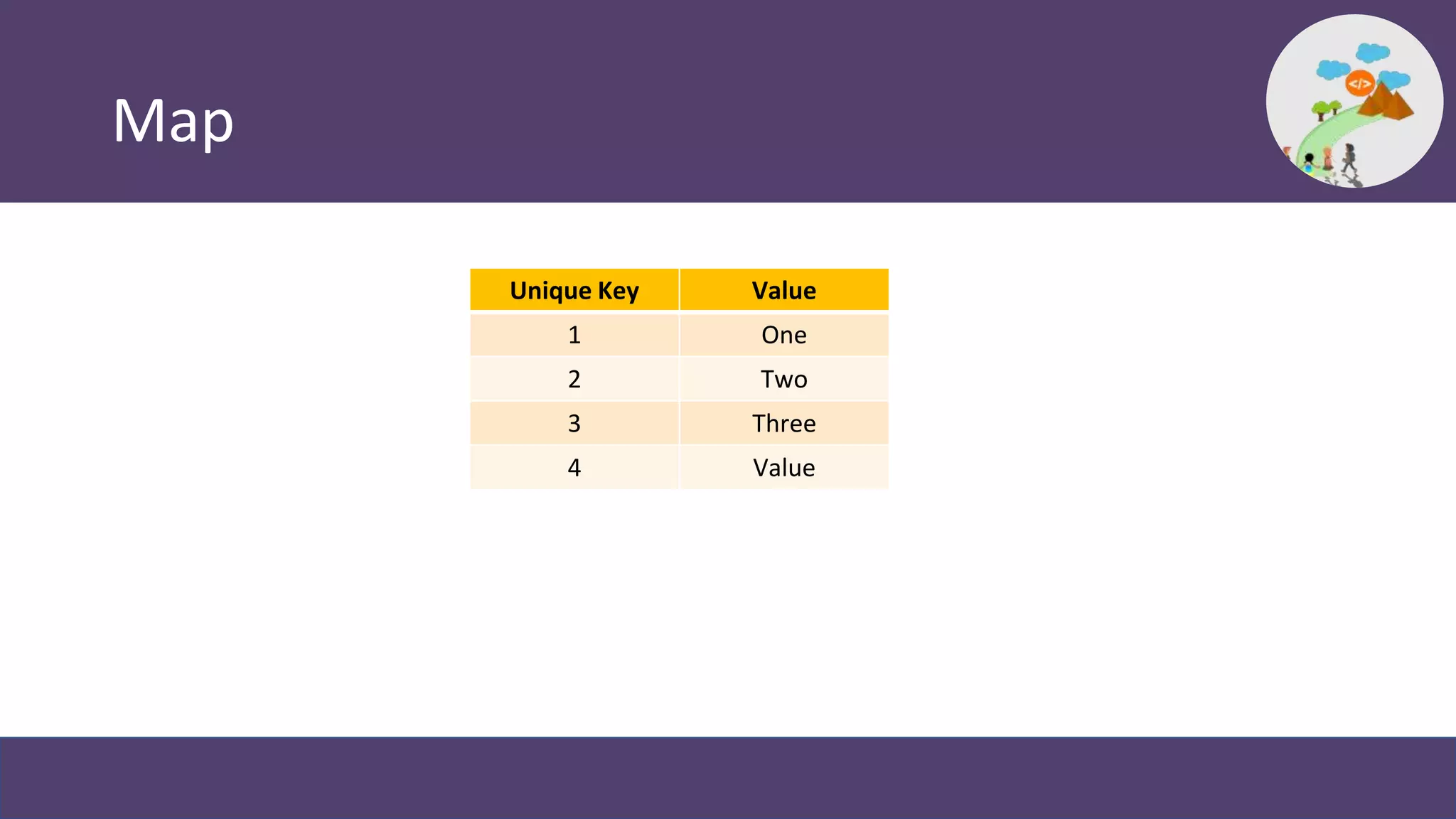
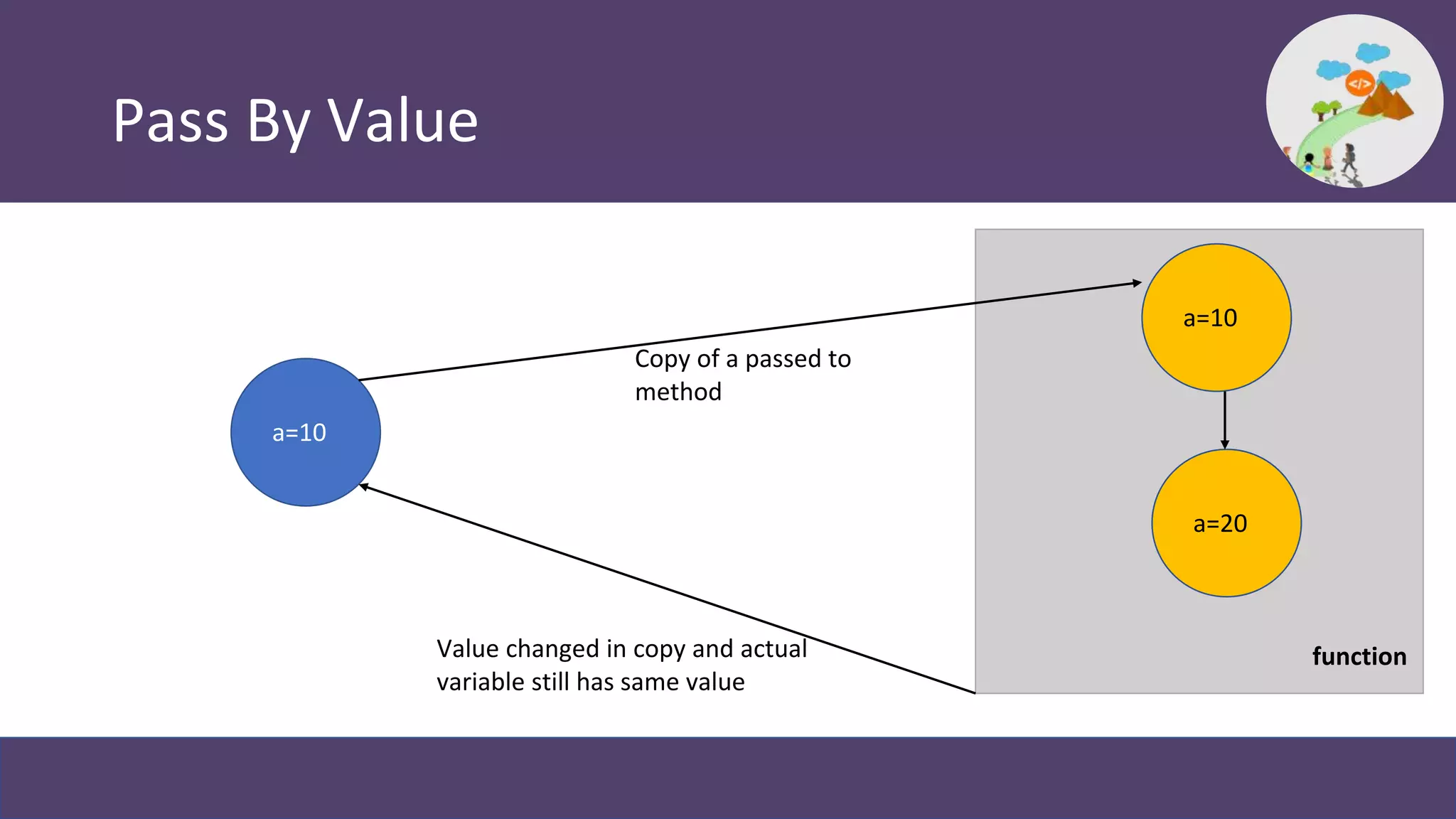
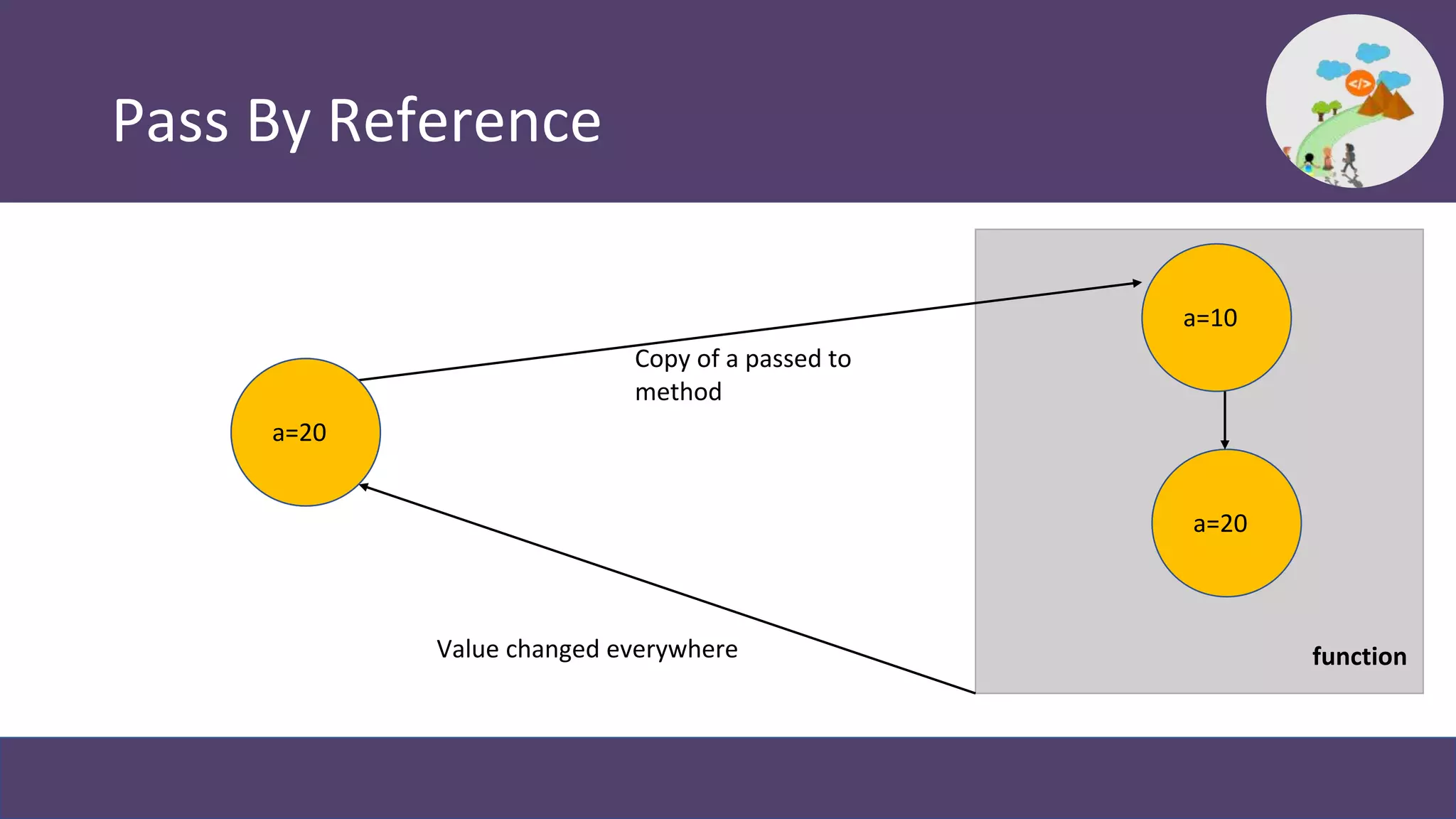
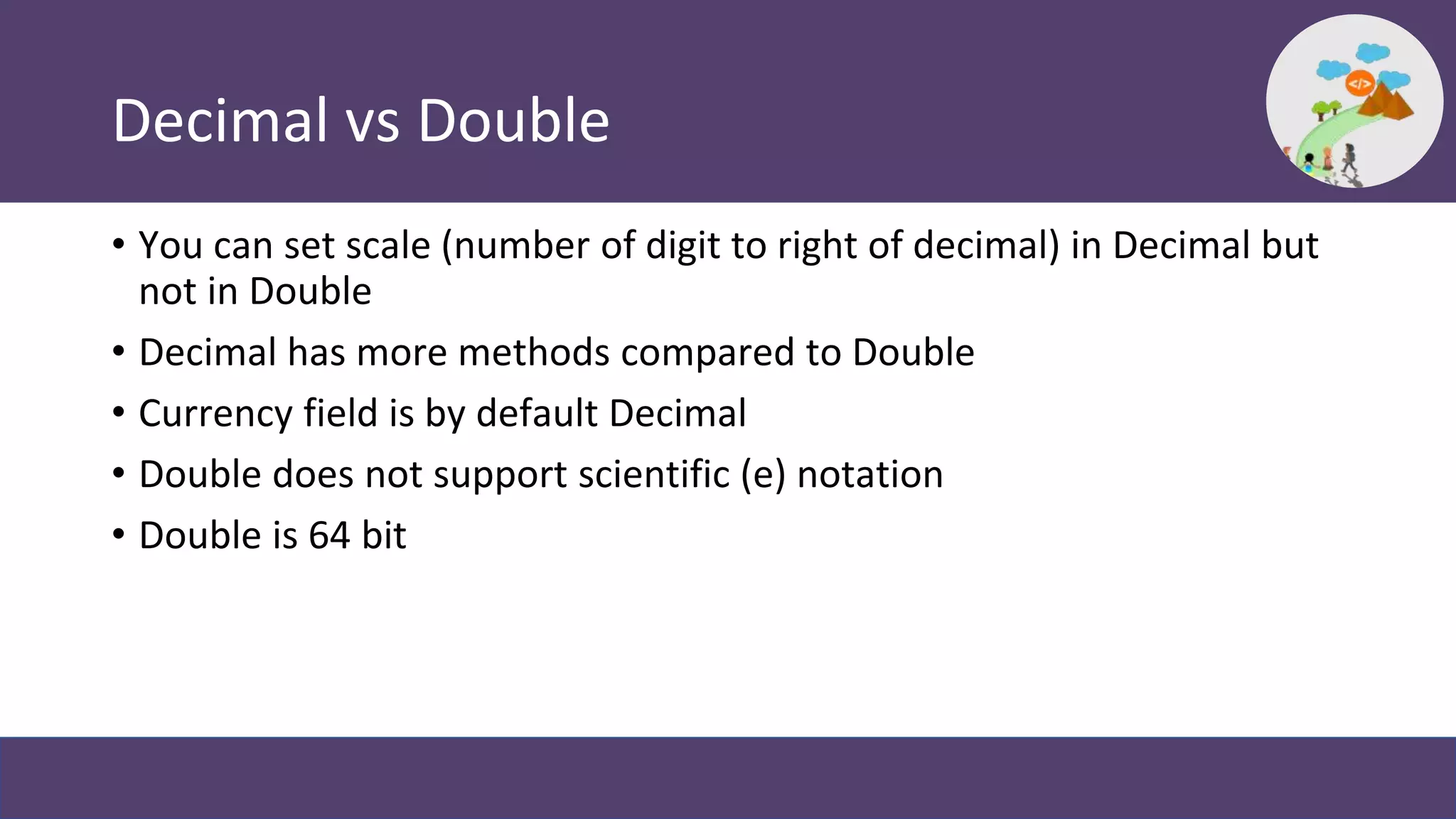
This document provides an overview and introduction to coding in Salesforce, including why coding is needed, the developer console, naming conventions, data types, collections, pass by value vs reference, and Trailhead modules to get started. It discusses primitive data types like Boolean, Date, Decimal, and String, as well as collections like Lists, Maps, and Sets. It also covers naming conventions like camel case and pascal case.