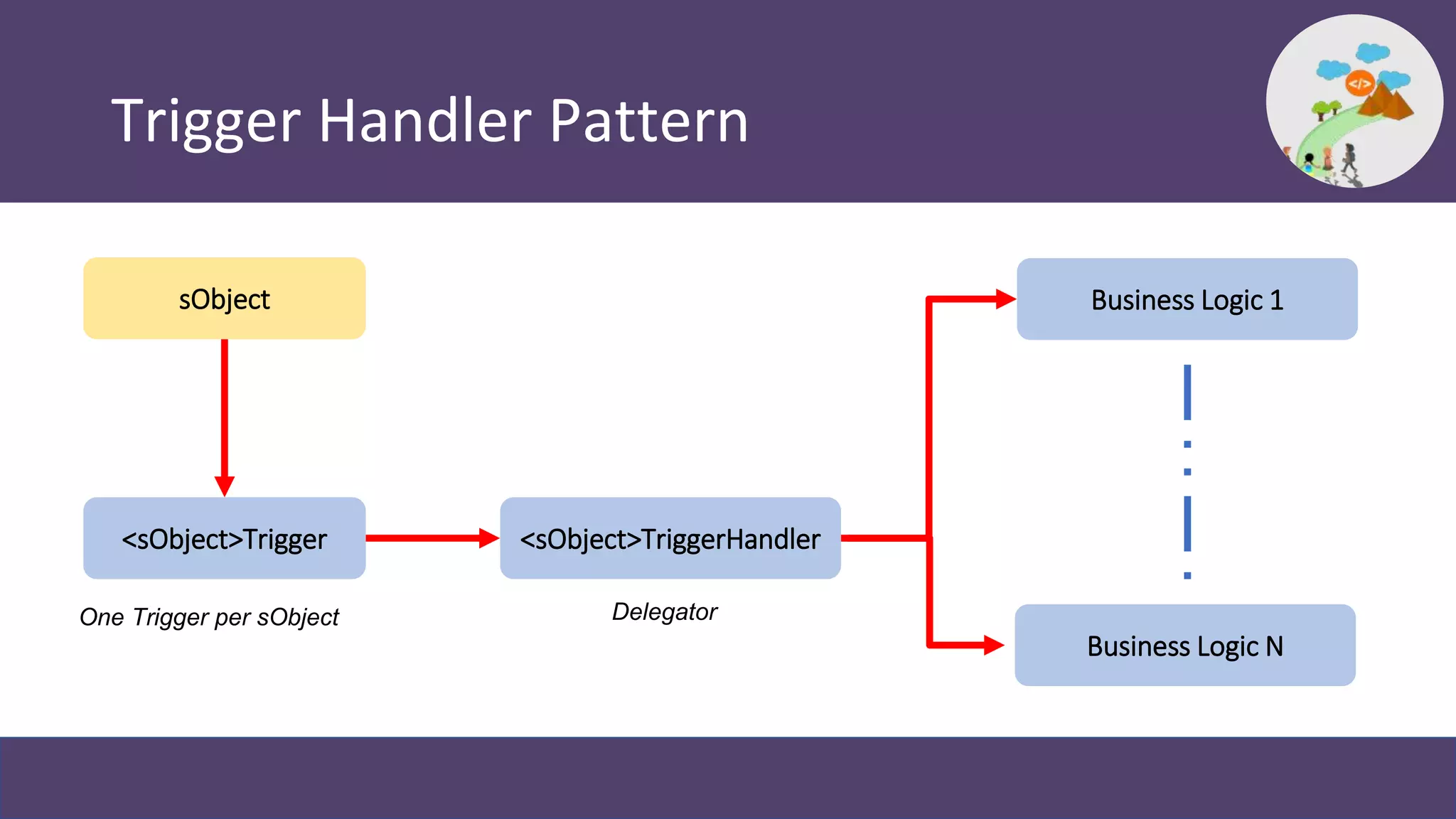
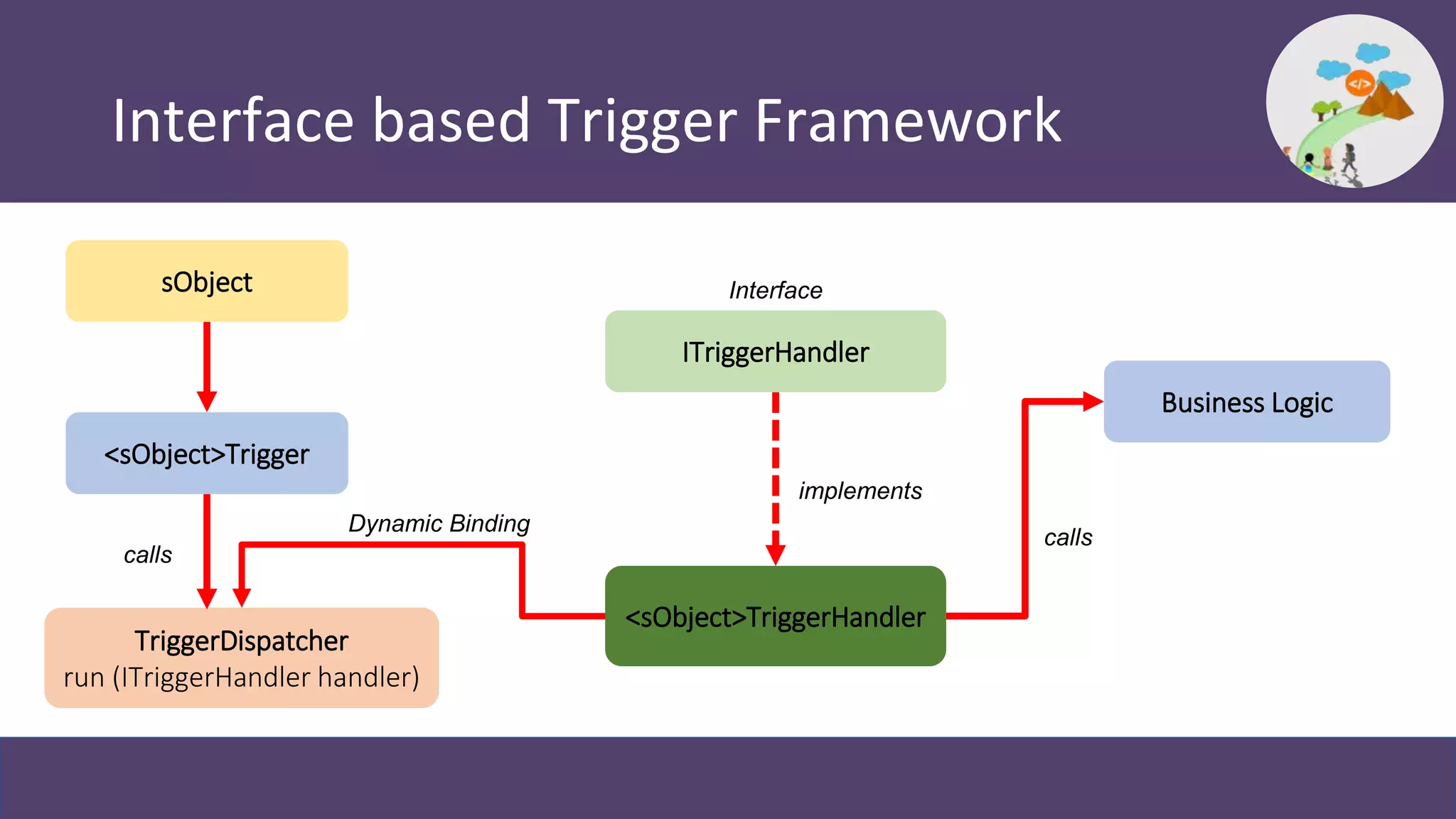
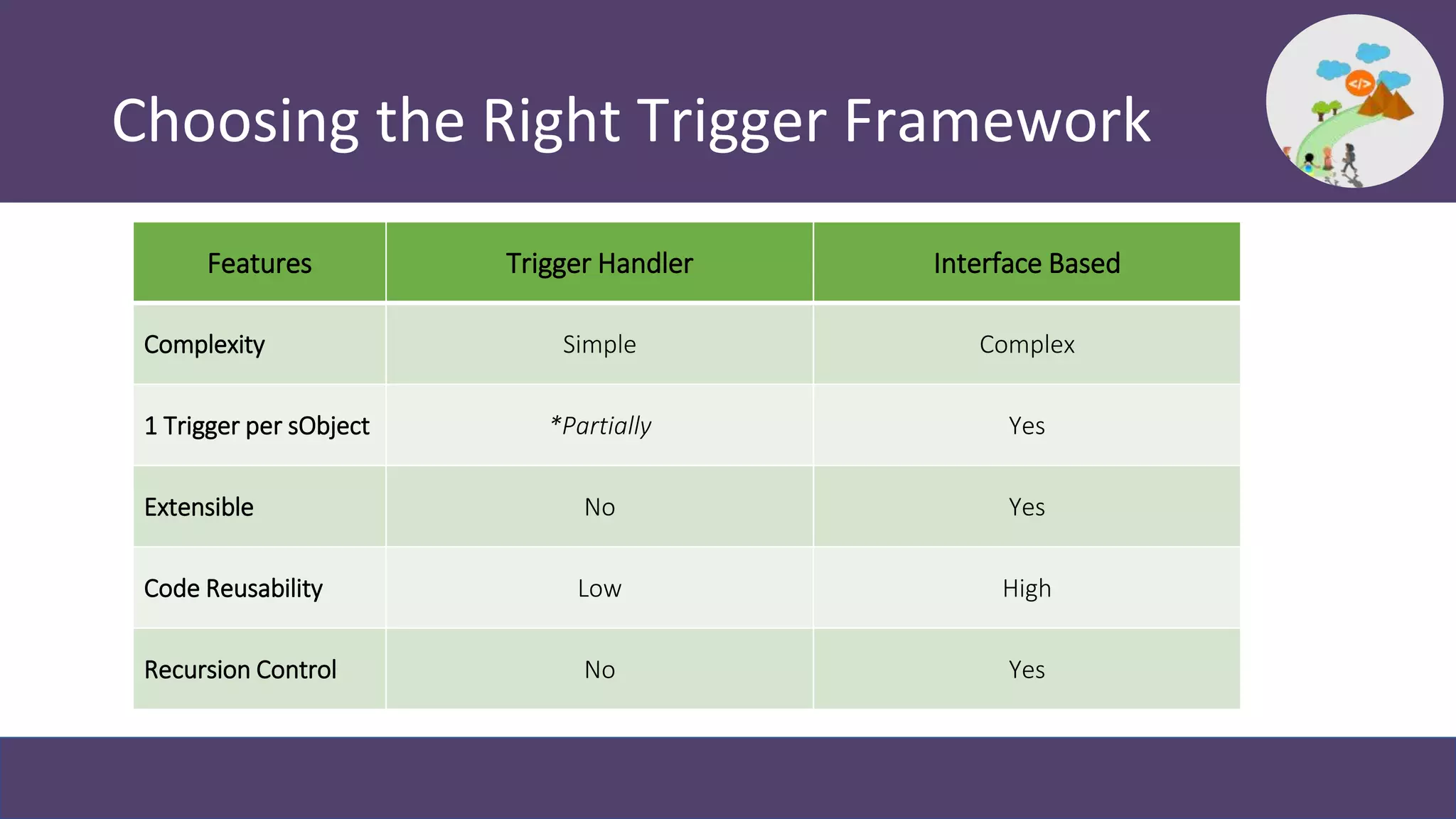
This document discusses trigger frameworks in Salesforce and their benefits. It provides an overview of trigger execution order and common patterns for writing trigger frameworks, including the trigger handler and interface-based patterns. The document demonstrates examples using these patterns. Trigger frameworks provide benefits like consistent execution, preventing recursion, improved testability and maintainability. Choosing the right framework depends on factors like complexity, extensibility and code reusability. Resources for learning more about trigger frameworks are also provided.