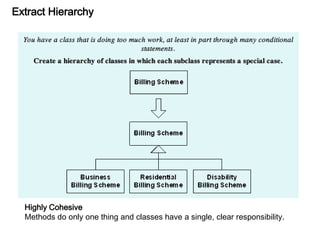
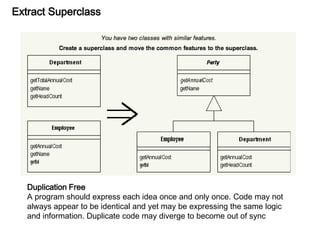
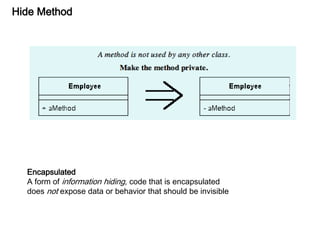
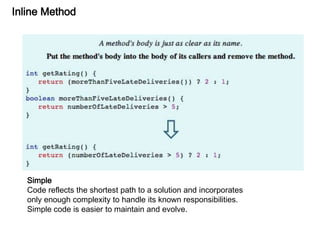
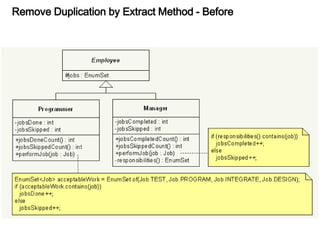
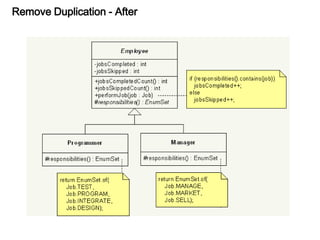
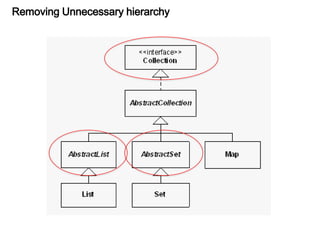
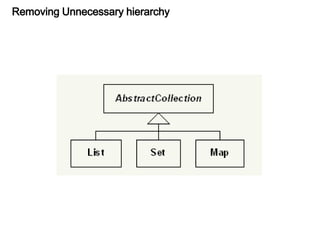
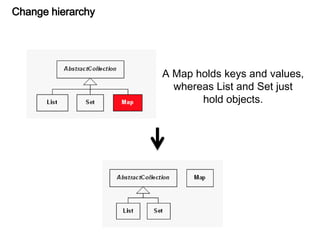
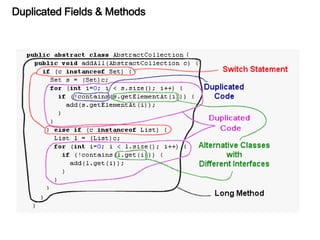
This document discusses refactoring, which involves restructuring existing code without changing its external behavior or functionality. It provides definitions of refactoring and describes best practices for refactoring code, such as taking small, incremental steps and verifying that automated tests still pass after each change. Specific refactoring techniques are also explained, like extracting duplicate code into methods, removing unnecessary complexity or duplication, and consolidating conditional expressions for clarity. The document cautions against fixing bugs during refactoring and emphasizes making changes in a way that simplifies the code and removes code smells.