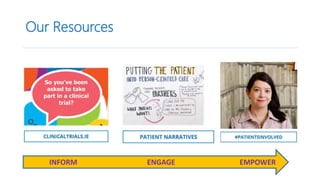
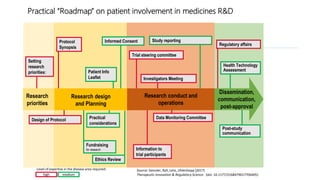
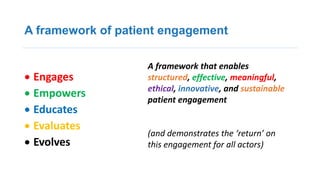
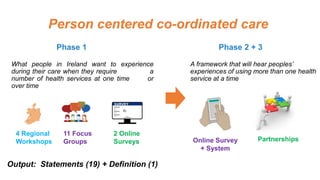
Derick Mitchell gave a talk on sustaining patient engagement resources through public-private platforms. Some key points:
1. He discussed IPPOSI, a patient-led organization that advocates for patient involvement in health innovation and research.
2. Patient organizations and industry can interact by moving past compliance and instead measuring the value of their interactions through trust and transparency.
3. Generating patient-based evidence through patient registries, mobile apps, and other tools can provide cost-effective, patient-relevant data to inform decision making.