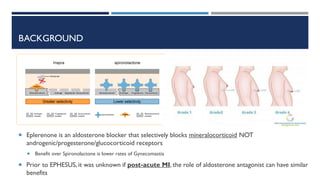
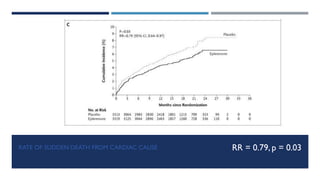
- The EPHESUS trial randomized over 6,000 patients who had a myocardial infarction with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (<40%) within 3-14 days to eplerenone or placebo in addition to standard therapy.
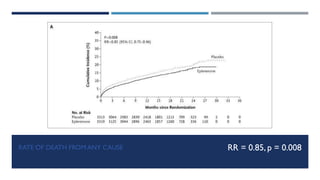
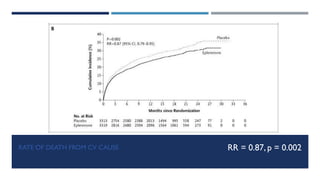
- At 16 months follow up, eplerenone reduced the risk of death from any cause by 15% and death from cardiovascular causes by 13% compared to placebo.
- Eplerenone was generally well tolerated but increased the risk of hyperkalemia compared to placebo.