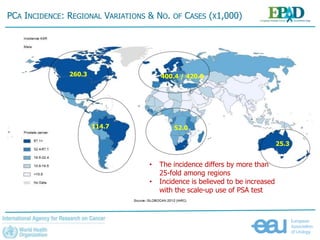
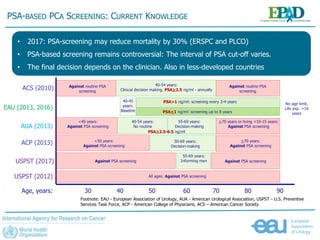
The document discusses the global landscape of prostate cancer (PCA), focusing on the increase in incidence and mortality projected by 2035 due to demographic changes and varying geographical factors. It highlights the disparities in PCA detection and treatment between high-income and low- to middle-income countries, emphasizing the need for improved screening methods and preventive strategies. The document calls for further research on risk factors and cost-effective prevention approaches to address this critical public health issue.