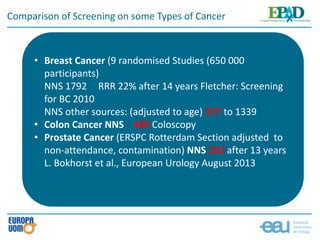
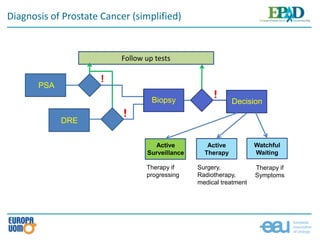
The document discusses prostate cancer screening from a patient's perspective, emphasizing the importance of early detection to reduce mortality and advanced disease risk. It highlights the controversy surrounding screening due to issues like over-diagnosis and overtreatment. The author encourages awareness and discussion around the benefits and risks of screening and early detection, aligned with the latest EAU guidelines.