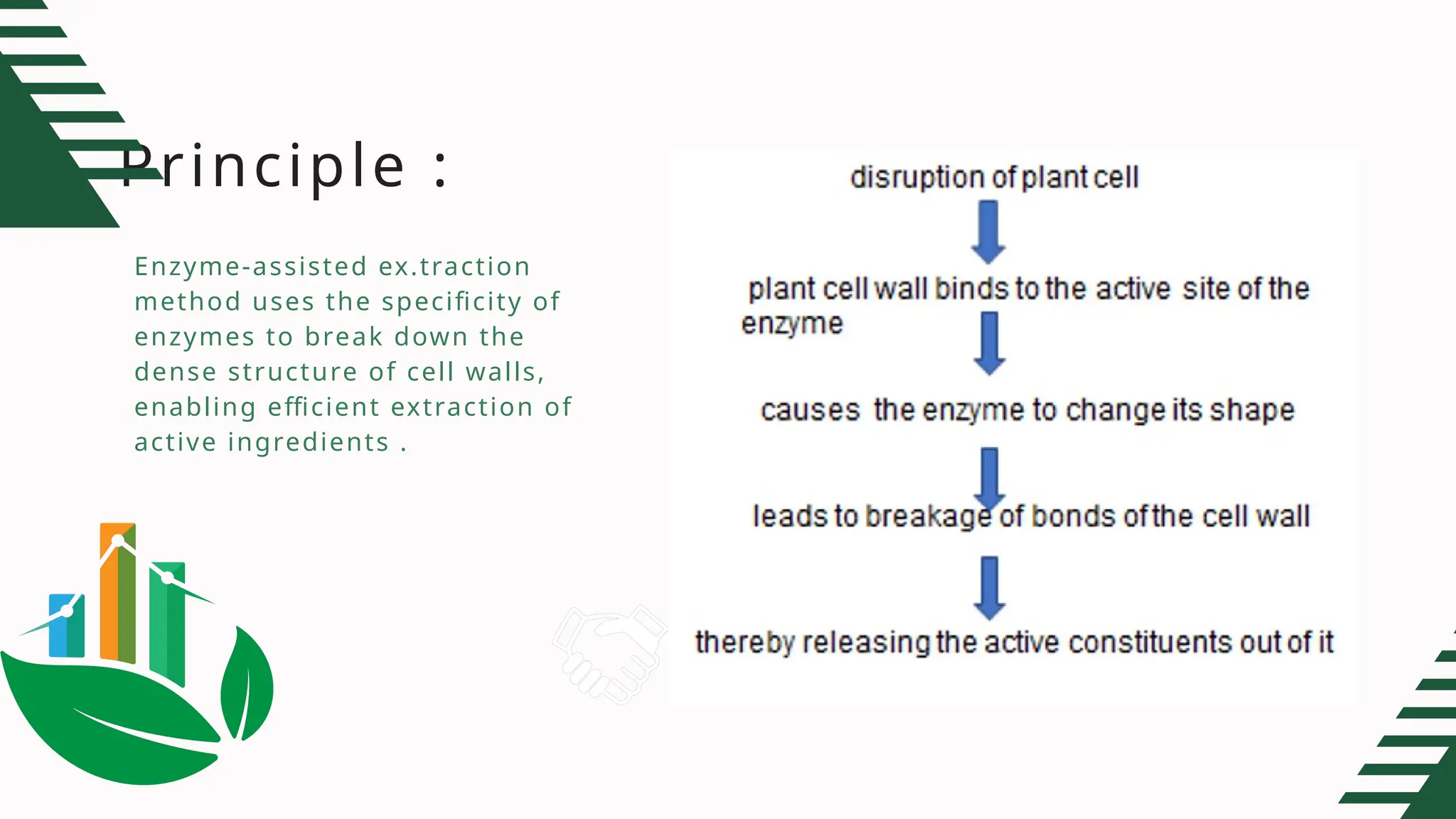
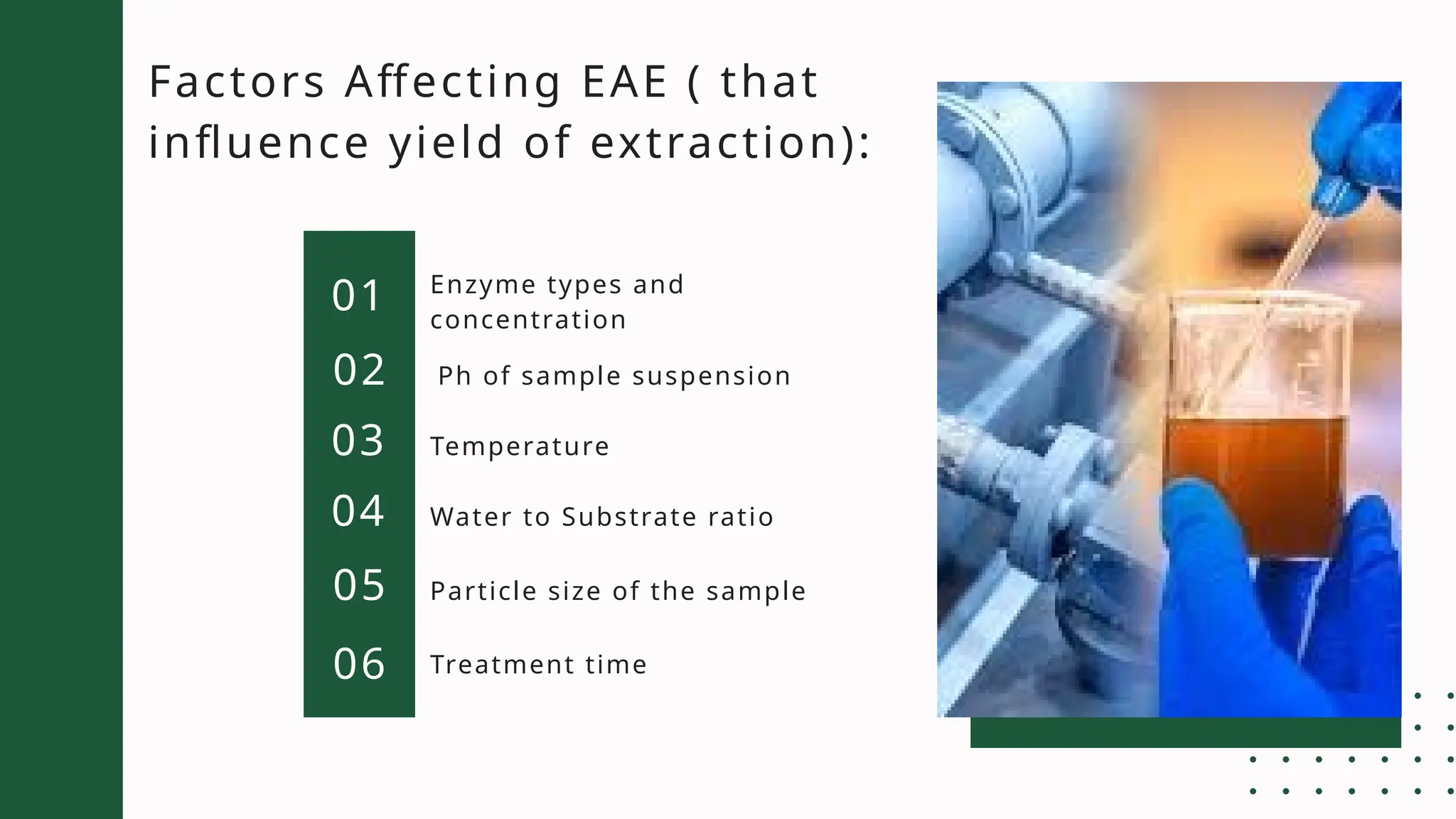
Enzyme-assisted extraction (EAE) is an eco-friendly technique that utilizes specific enzymes to break down plant cell walls, facilitating the release of bioactive components like phenolic compounds. The process can be divided into enzyme-assisted cold processing extraction (EACP) and enzyme-assisted aqueous extraction (EAAE), emphasizing oil extraction from seeds. While EAE offers high yields and reduced solvents, its effectiveness can be influenced by various factors and may be limited by high costs.