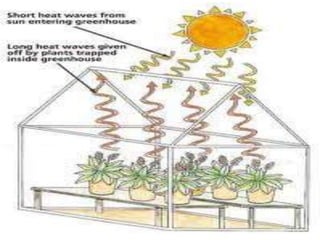
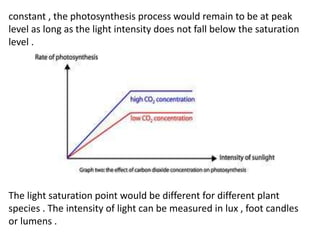
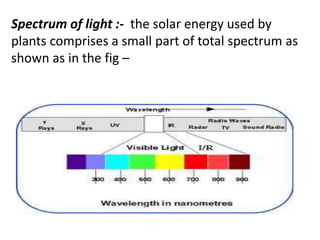
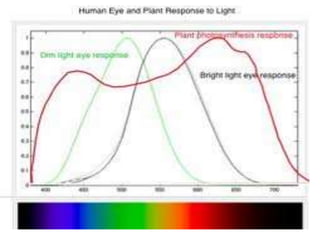
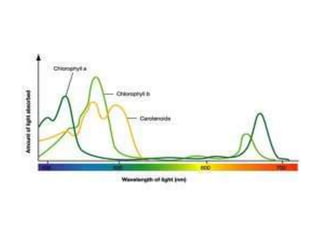
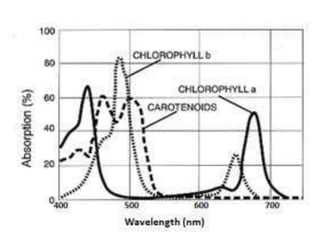
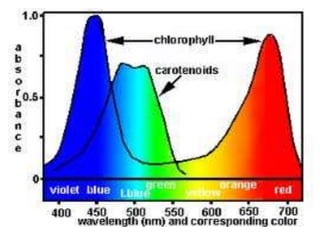
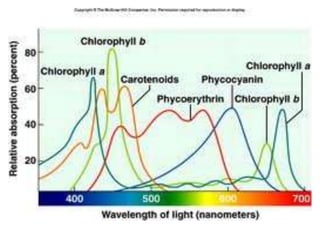
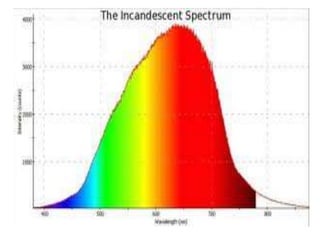
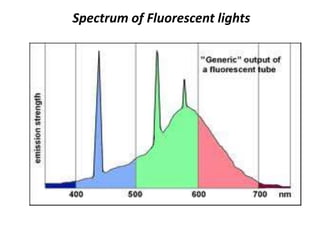
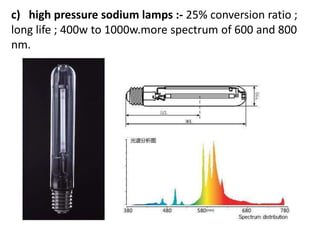
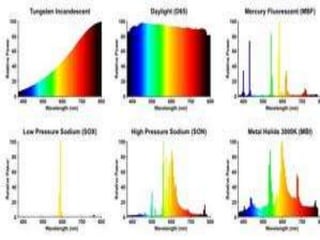
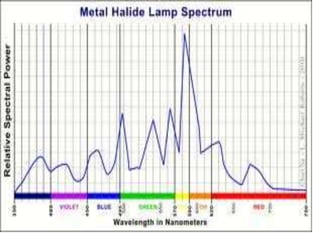
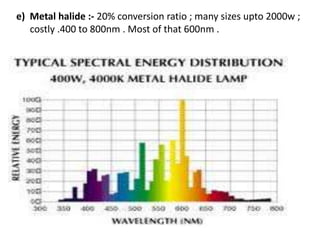
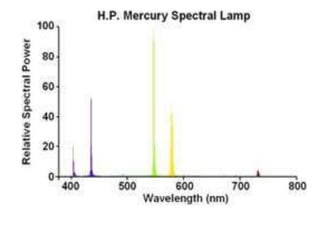
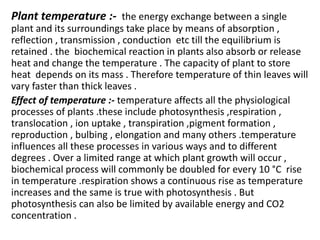
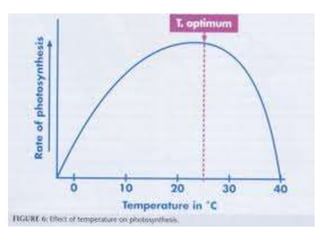
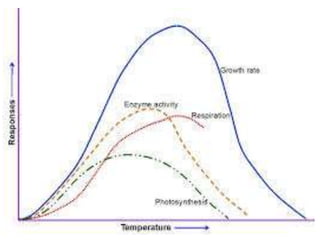
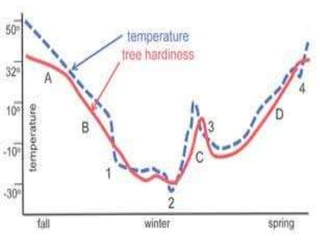
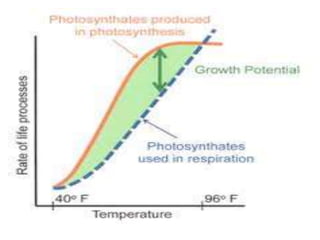
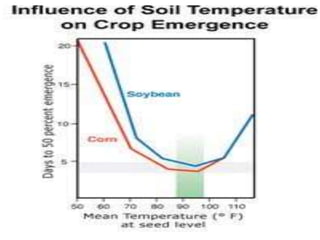
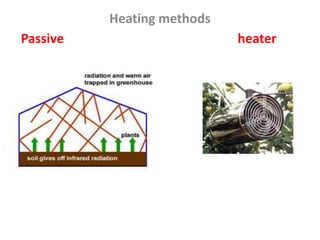
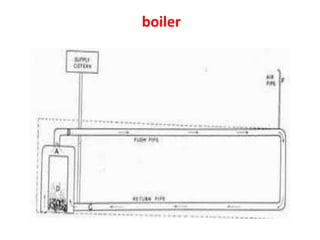
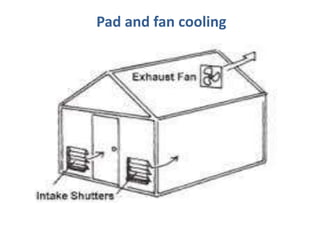
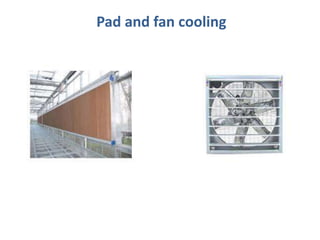
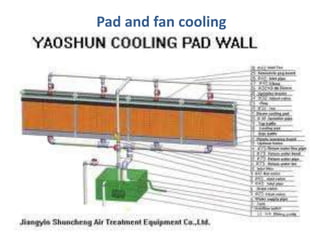
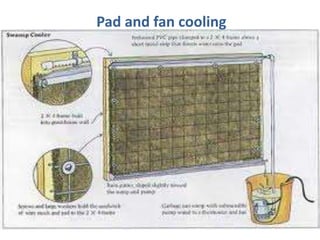
This document discusses environmental parameters that affect plant growth in greenhouses, including light, temperature, and air composition. It describes how light intensity, spectrum, and photoperiod impact photosynthesis and plant development. It also explains different lighting options and methods for controlling temperature, such as active heating/cooling systems or passive techniques like water storage and shading. Optimum temperatures ranges for plant growth are discussed along with the effects of temperature on physiological processes.