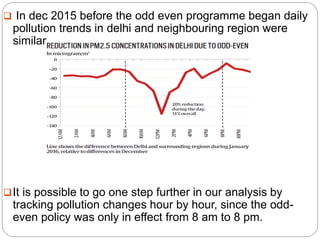
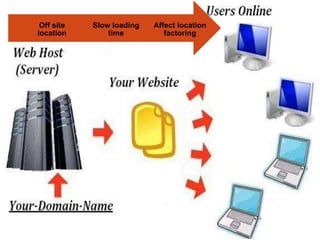
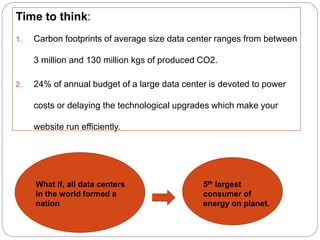
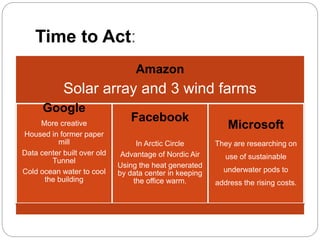
The Environment Protection Act of 1986 was enacted in India to provide a framework for the protection and improvement of the environment, particularly in response to the Bhopal gas tragedy. It includes provisions for the prevention and control of environmental pollution, outlines the powers of the central government, and establishes penalties for violations. The act has faced challenges such as legal disputes over plastic bans and highlights the need for awareness and community participation in environmental issues.