This document is an introduction to Claude Shannon's seminal 1948 paper "A Mathematical Theory of Communication". It provides an overview of communication systems and introduces Shannon's concept of using a logarithmic measure to quantify information. Specifically:
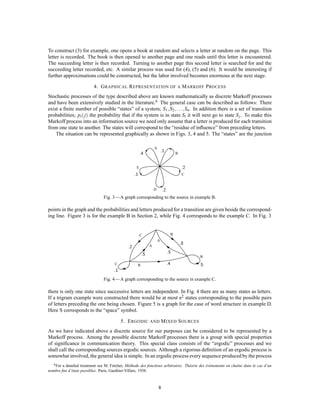
1) It defines the key components of a general communication system including an information source, transmitter, channel, receiver, and destination.
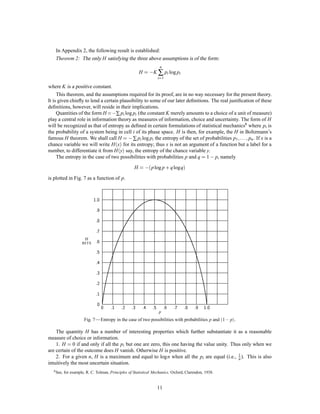
2) It explains Shannon's proposal to use a logarithmic measure (typically base 2, resulting in units called "bits") to quantify the information content of messages. This provides a convenient way to measure the capacity of communication channels.
3) It outlines Shannon's plan to develop a mathematical theory of communication by modeling different types of systems - discrete, continuous,