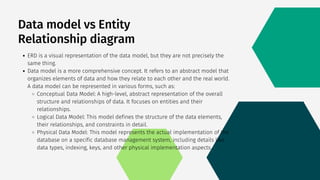
The document explains entity-relationship diagrams (ERDs), which visually represent entities, attributes, and relationships in database design, crucial for understanding structures and ensuring data integrity. It covers the importance of ERDs in normalization, planning, and scalability, and distinguishes between ERDs and data models, which encompass broader concepts. Key components of ERDs include entities, attributes, relationships, and cardinality, which define how different entities interact within a database.