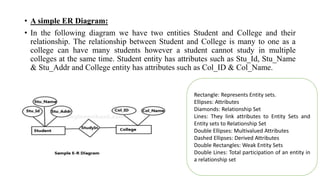
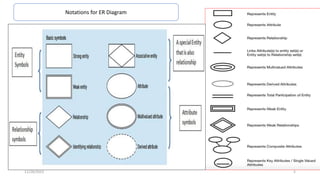
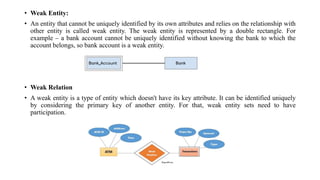
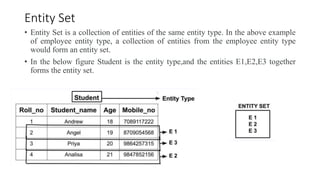
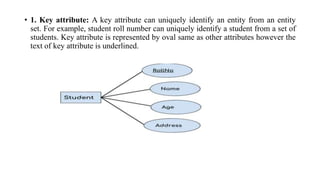
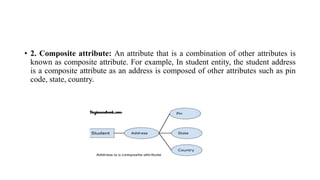
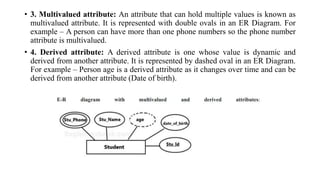
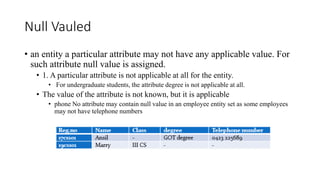
The document discusses the components of an Entity Relationship (ER) diagram including entities, attributes, and relationships. It provides examples of each component and their notations in an ER diagram. Specifically, it defines entities as objects or data components, attributes as properties of entities, and relationships as associations between entities. It also describes different types of attributes like key, composite, multivalued, and derived attributes.