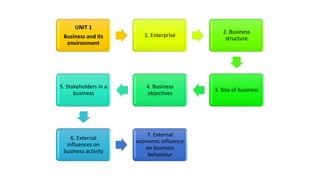
The document outlines the fundamentals of business and its environment, covering topics such as enterprise, business structures, objectives, and the role of entrepreneurs. It emphasizes the importance of adding value, common types of entrepreneurial businesses, and challenges faced by entrepreneurs, including failures and their impacts on the economy. Additionally, it discusses social enterprises and their objectives, focusing on the triple bottom line of economic, social, and environmental goals.