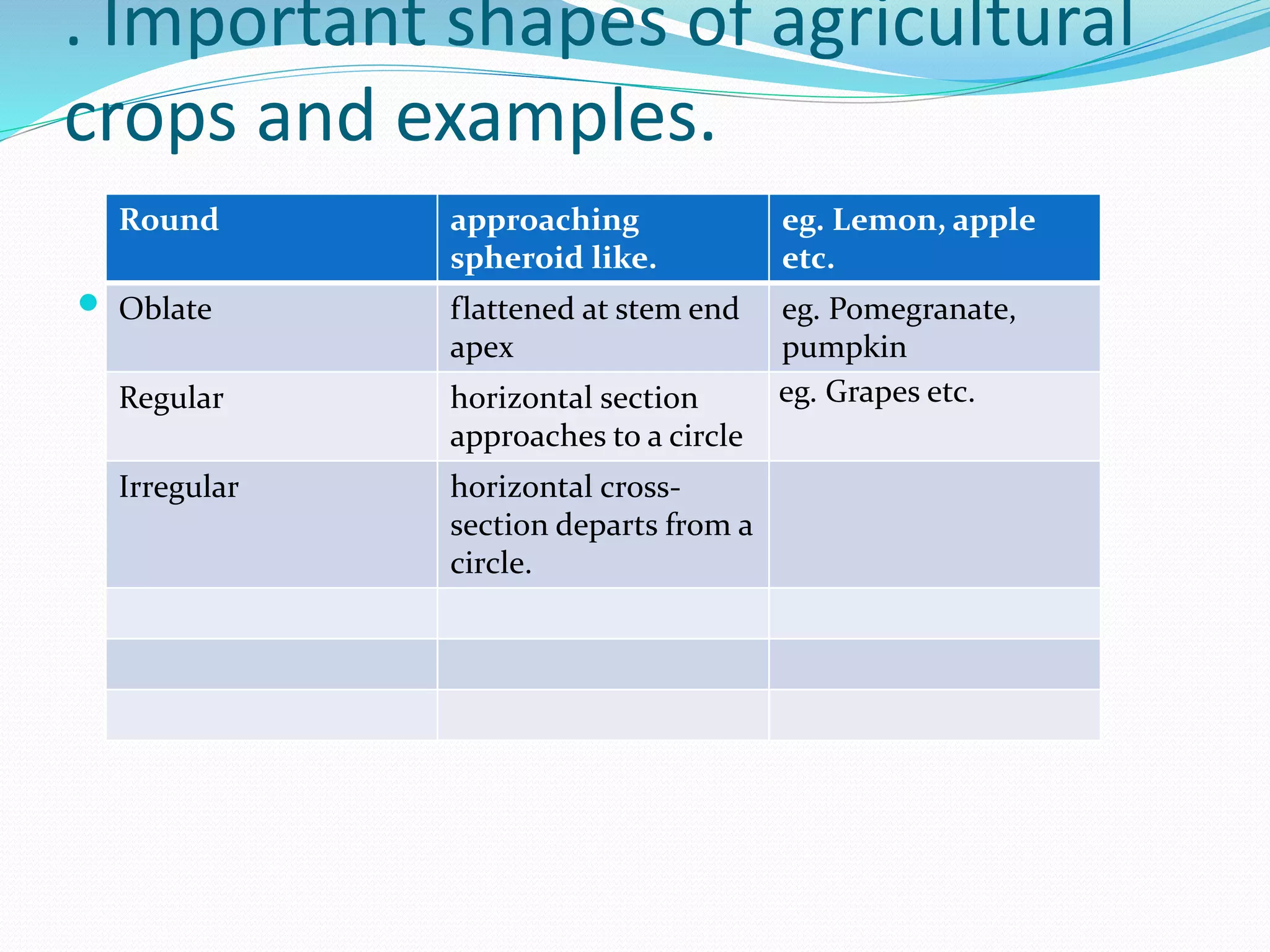
This document discusses various physical properties of agricultural crops including size, shape, volume, density, roundness, sphericity, and porosity. Size is measured using tools like calipers and microscopes. Shape can be round, oblate, or irregular and influences packaging and sorting. Volume is measured by water displacement. Density is the ratio of mass to volume. Roundness and sphericity quantify how close a shape is to a perfect sphere. Porosity measures empty space between grains. Physical properties provide important information about crops.