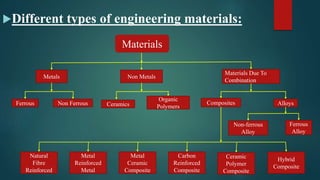
The document discusses engineering materials, their properties, classification, structure, and recent advances. It covers the historical evolution of materials from the Stone Age to modern times. Key topics include the properties of metals, ceramics, polymers and composites and how their microstructure influences characteristics. Recent advances like nanotechnology, smart materials, and shape memory alloys are transforming applications in biomedical, aerospace and other fields. Selection of materials depends on factors like strength, corrosion resistance, cost, and the operating environment.