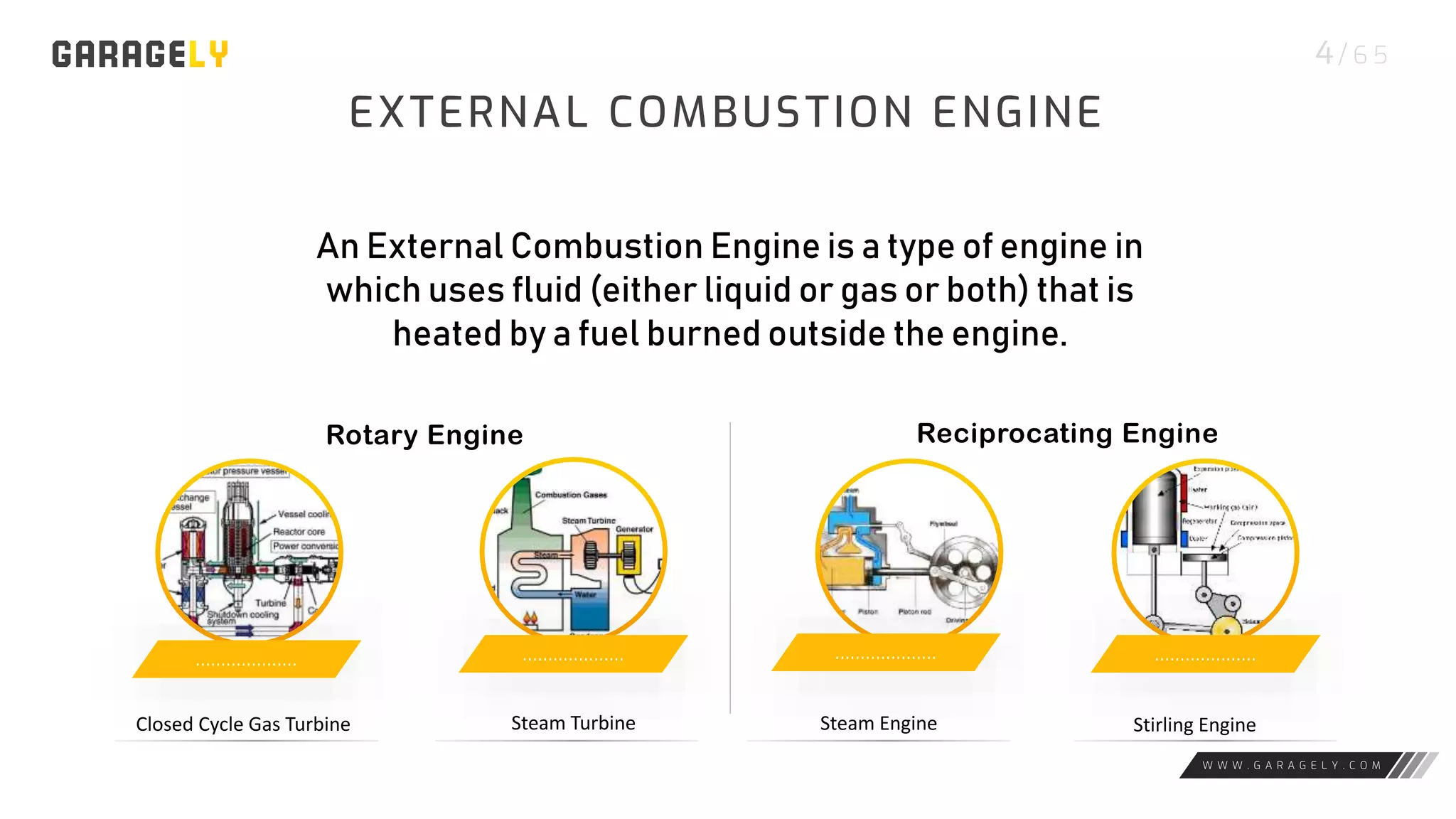
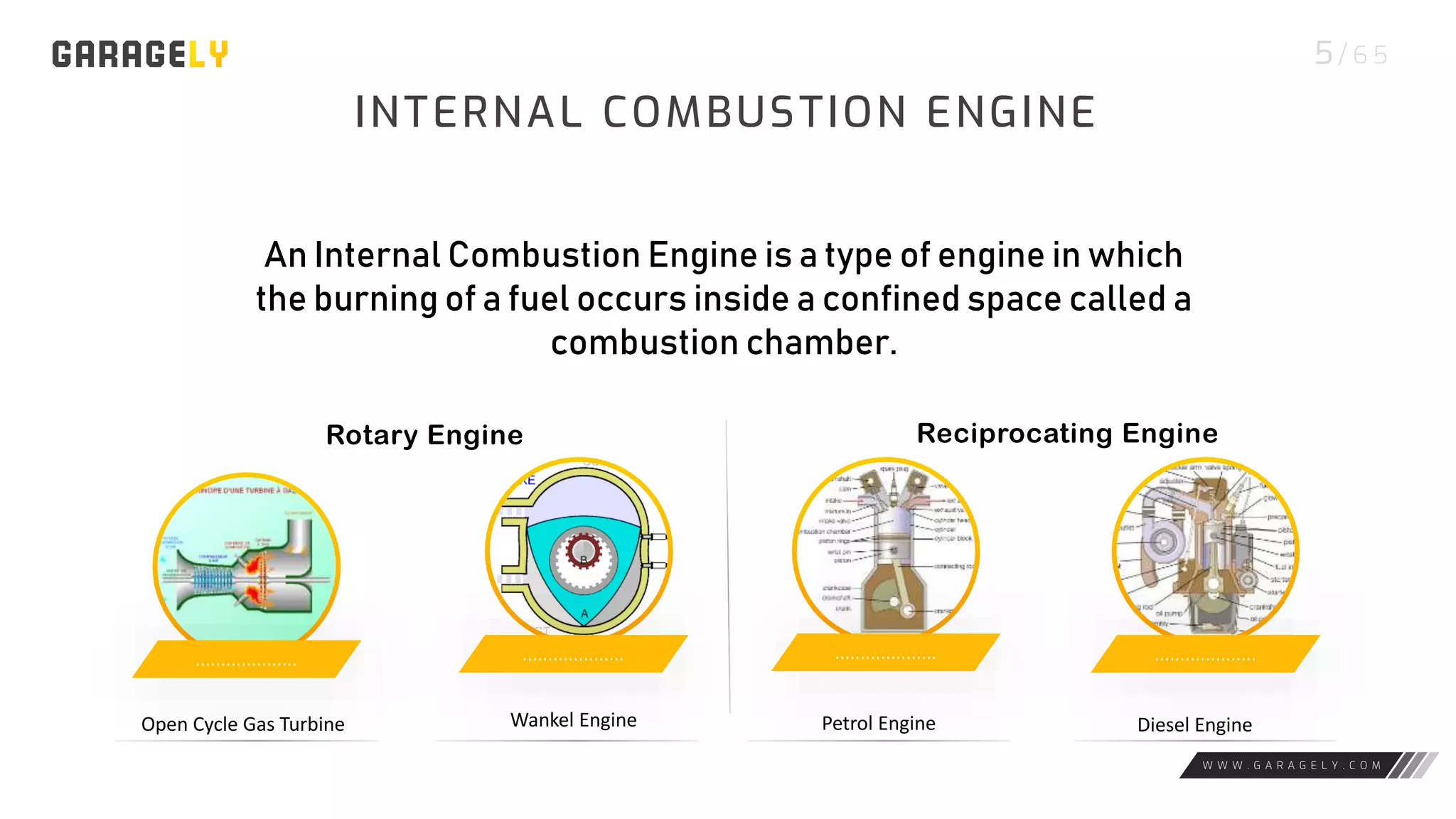
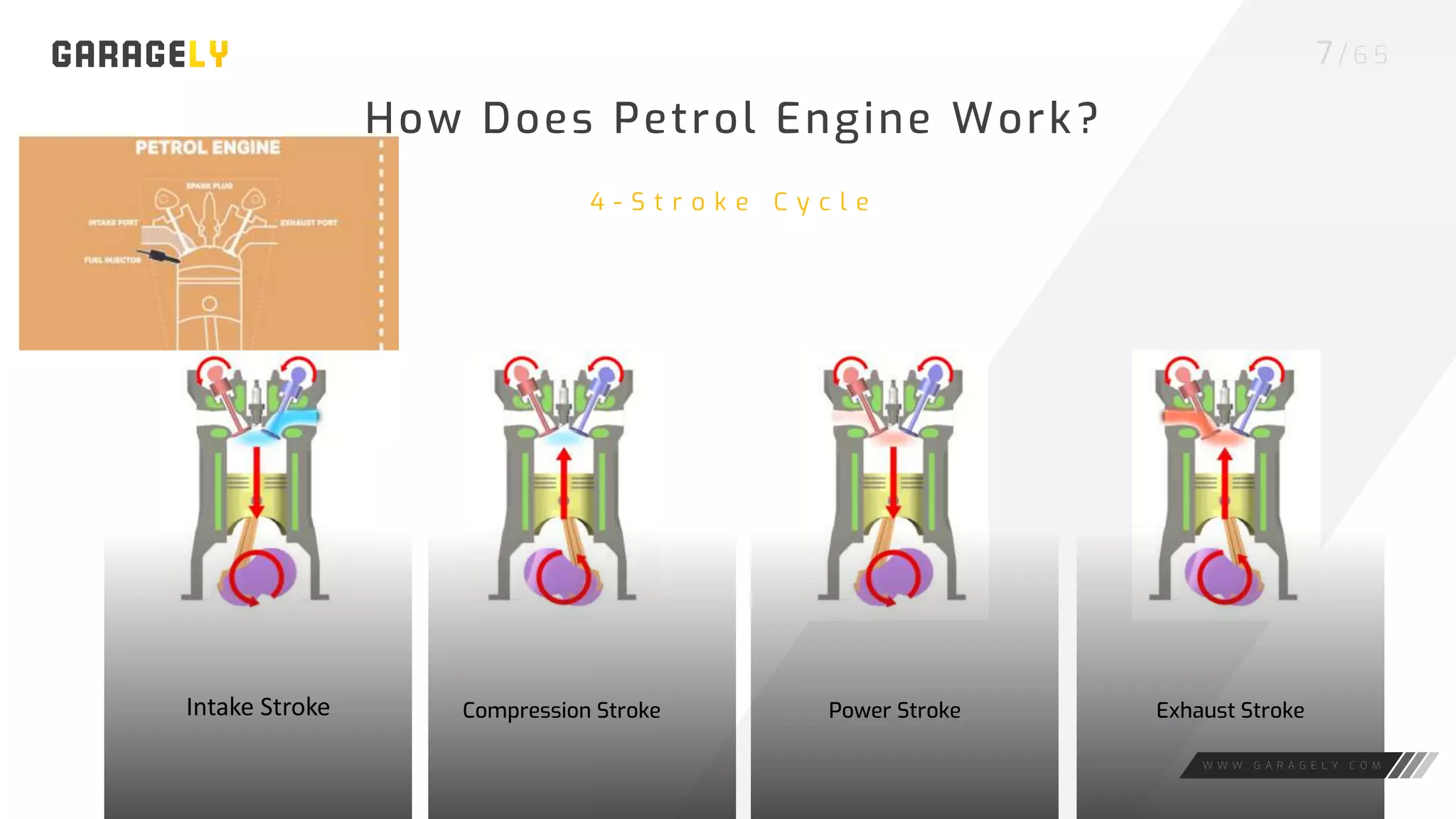
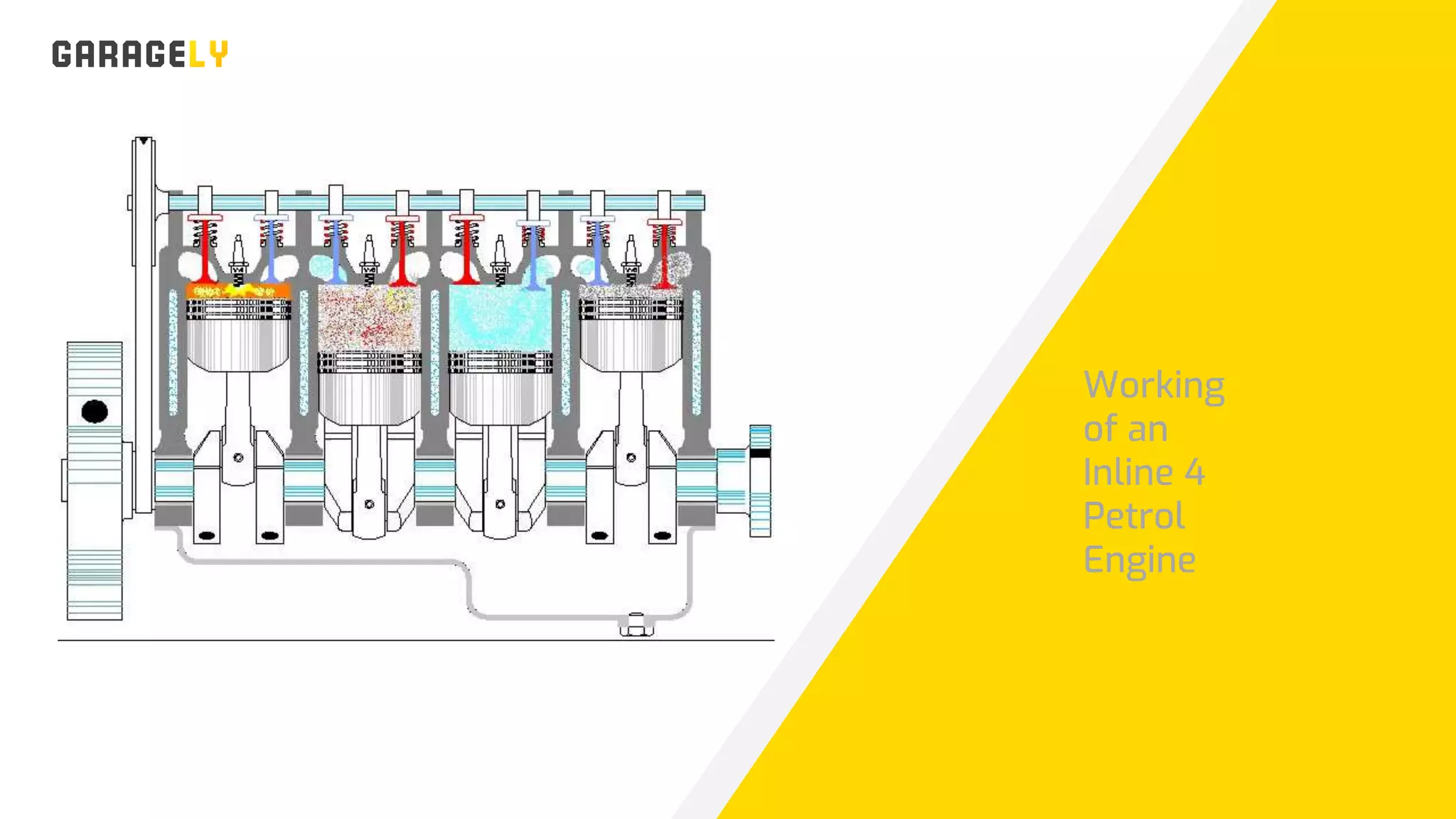
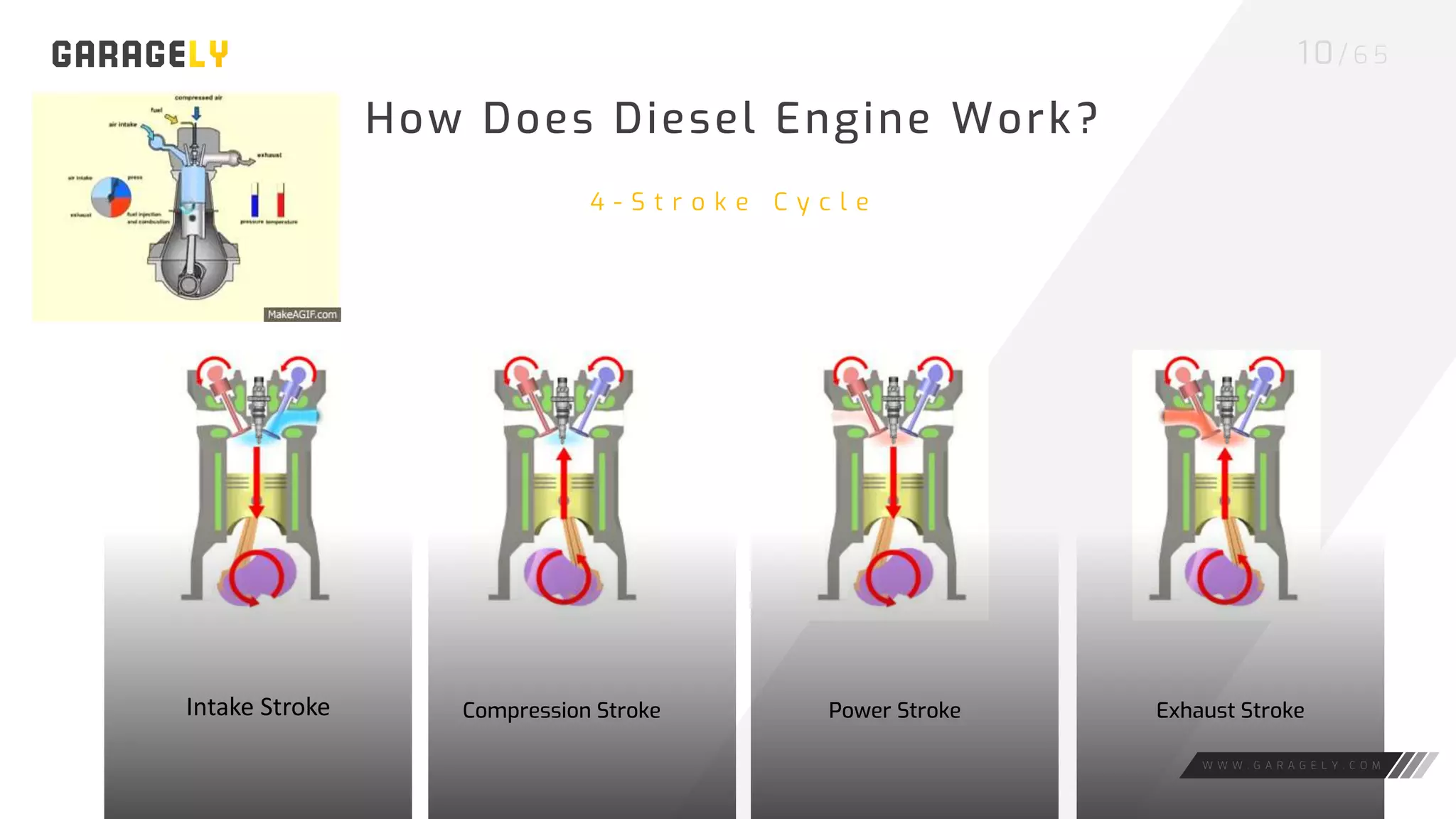
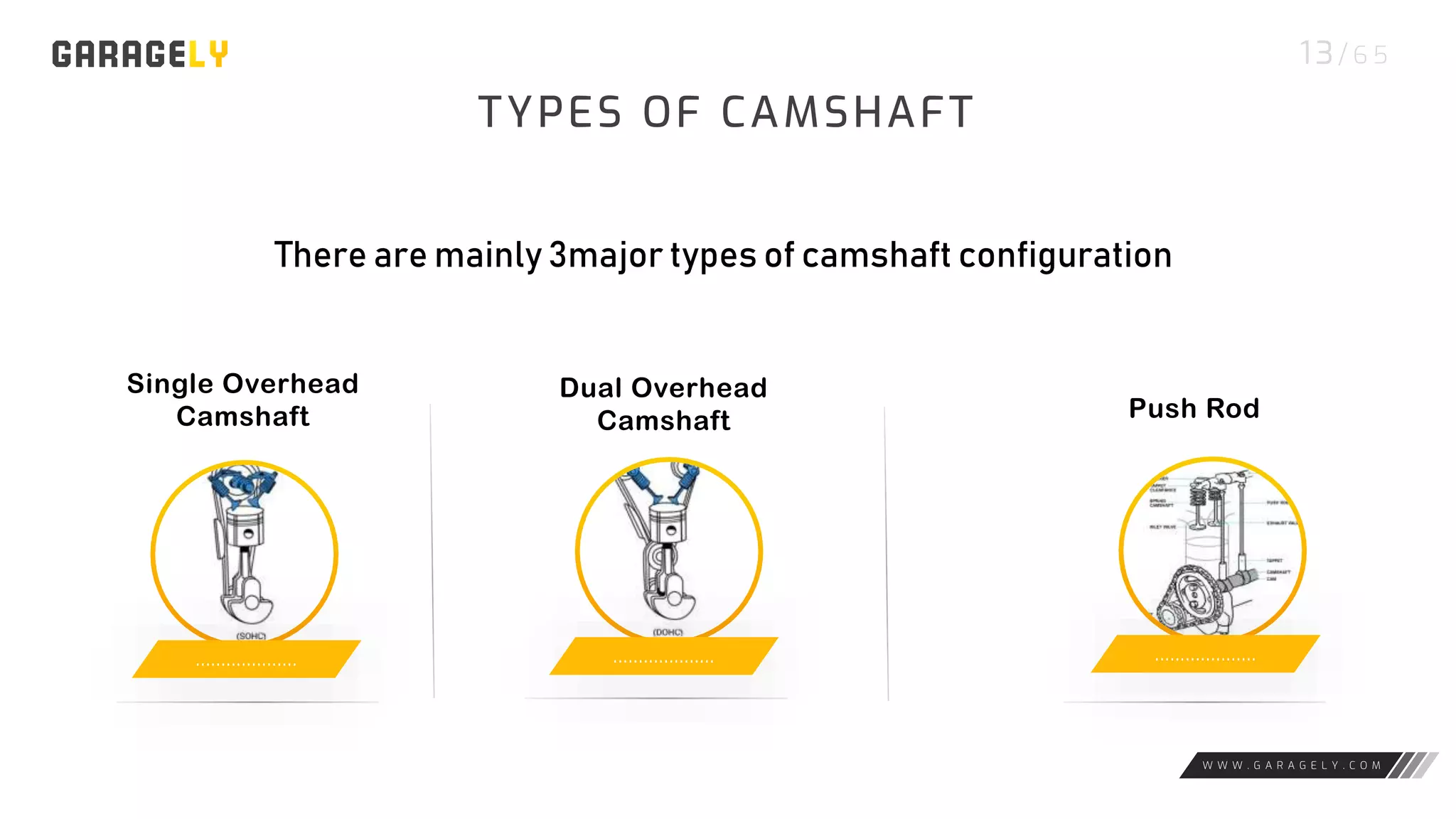
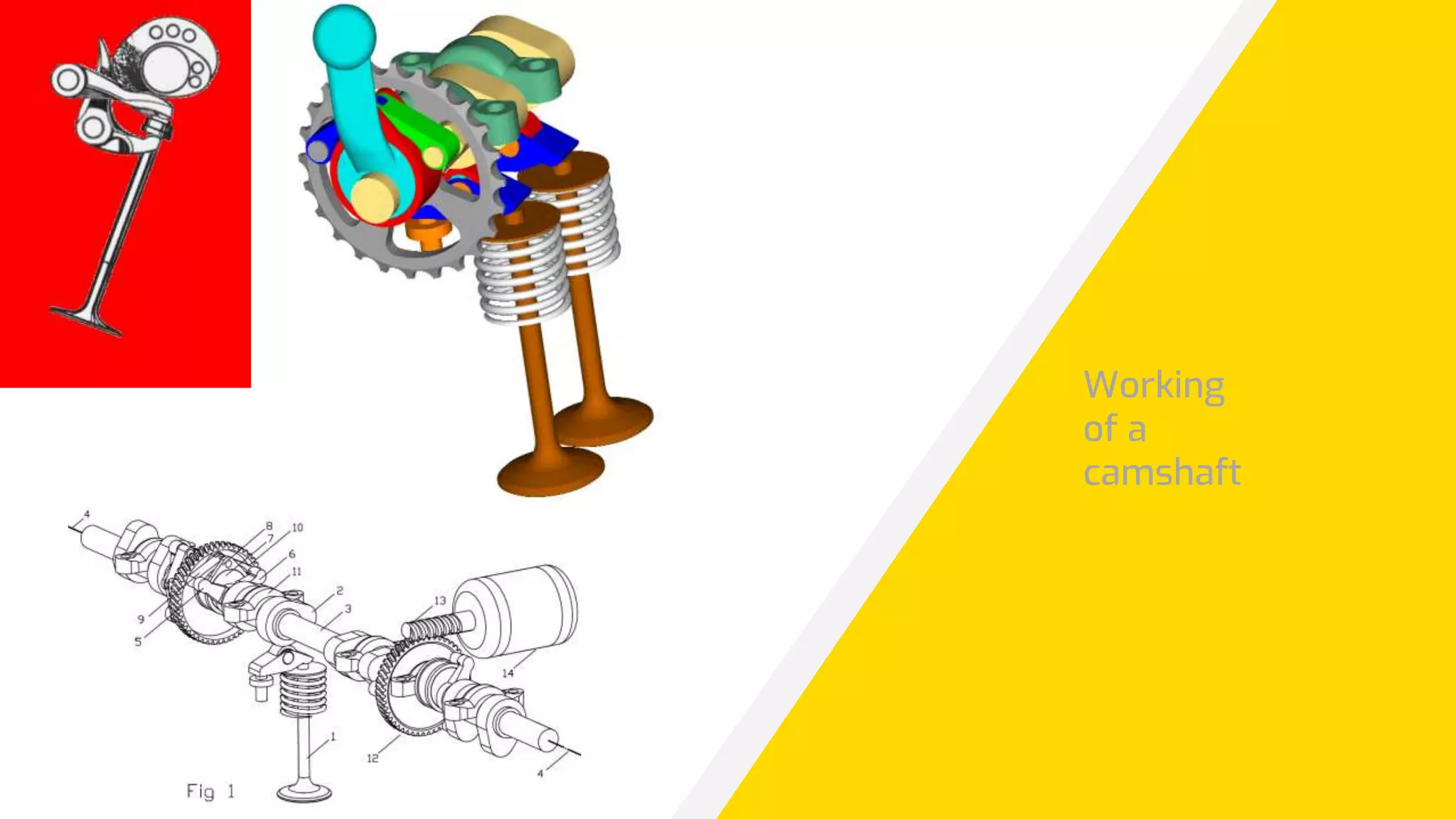
The document discusses different types of engines, including external combustion engines and internal combustion engines. It provides details on petrol engines and diesel engines, describing their basic workings, components like camshafts, and the differences between petrol and diesel engines. Both engine types provide advantages like increased productivity but also disadvantages such as negative environmental impacts from emissions.