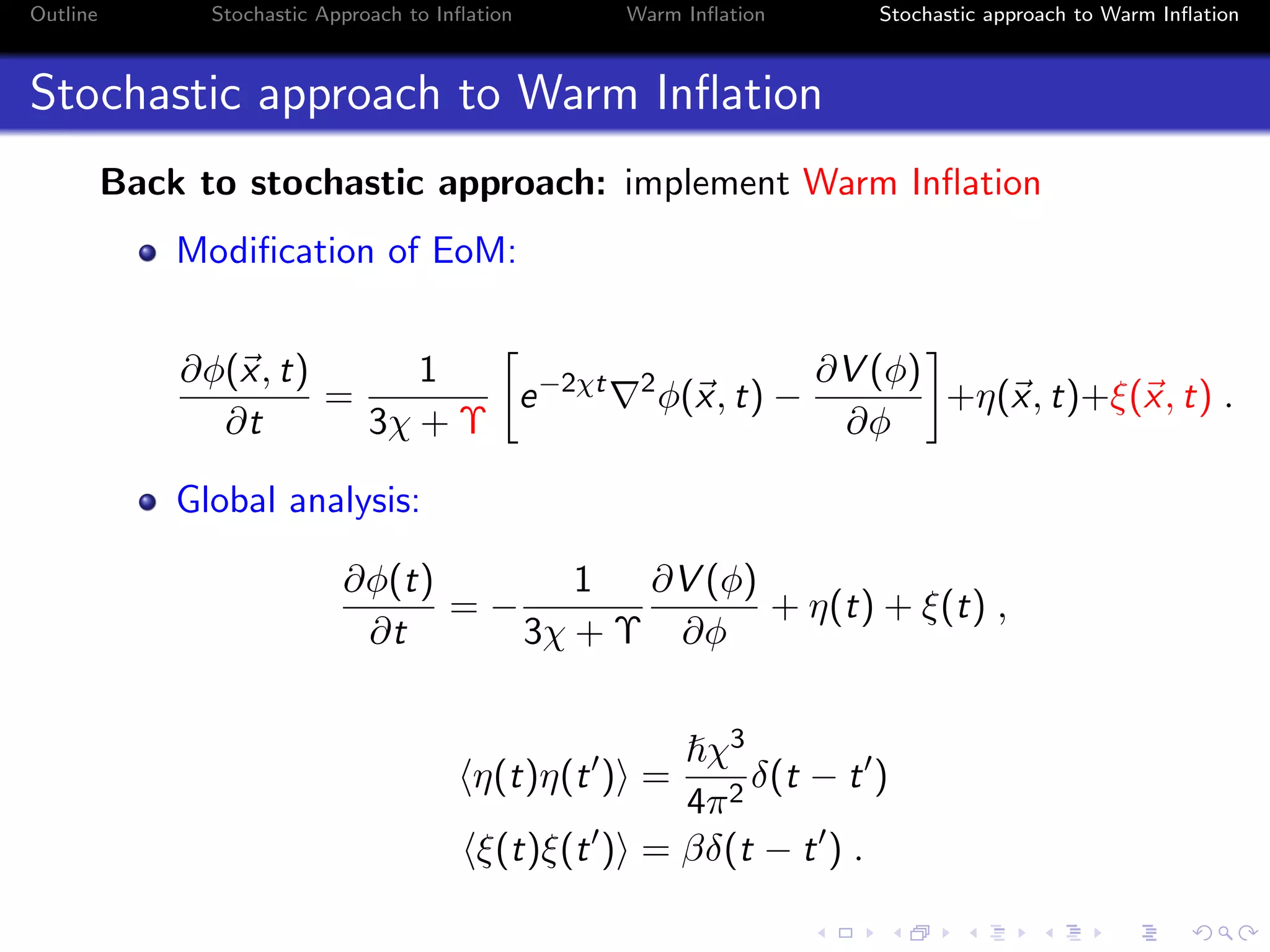
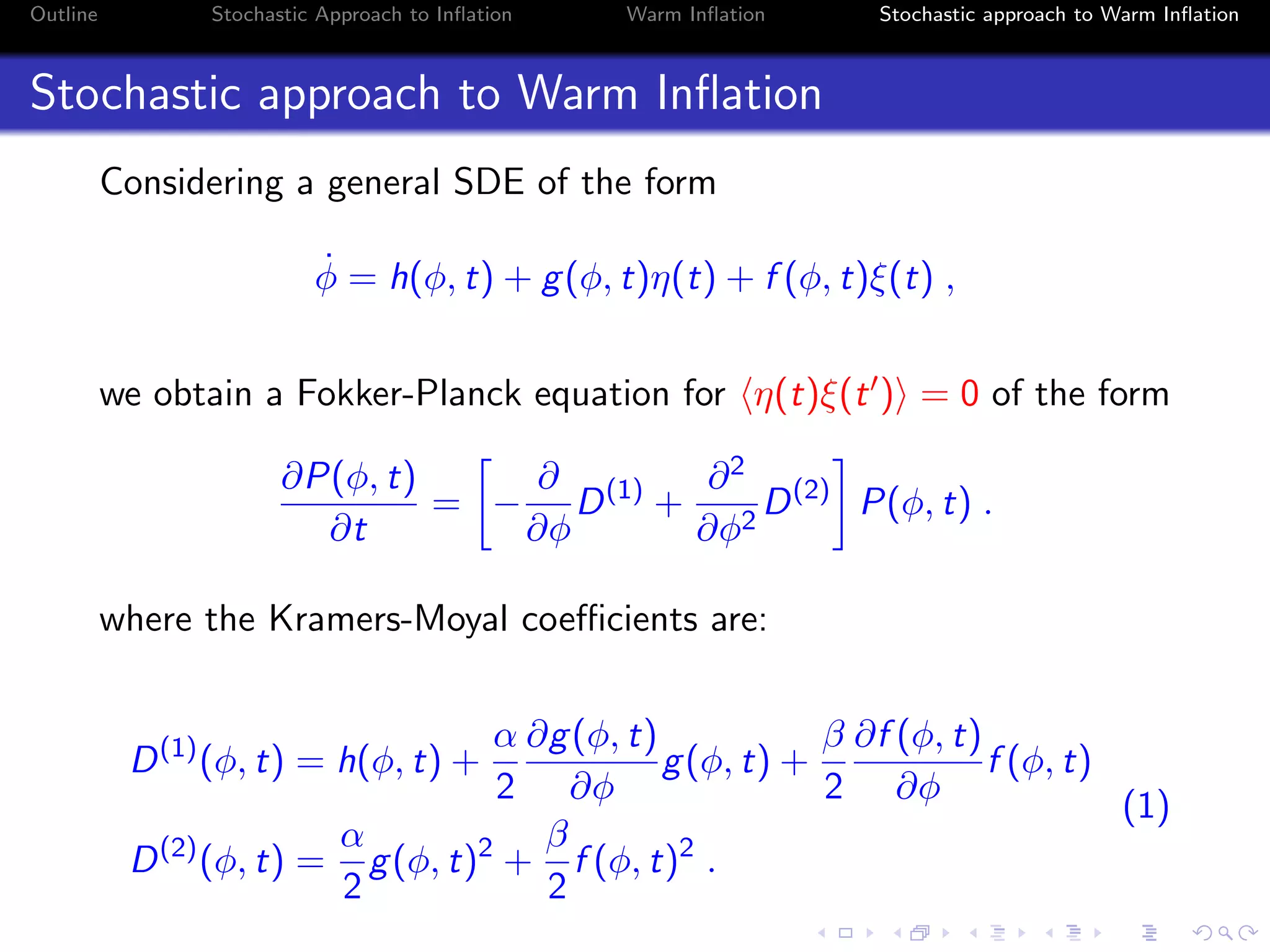
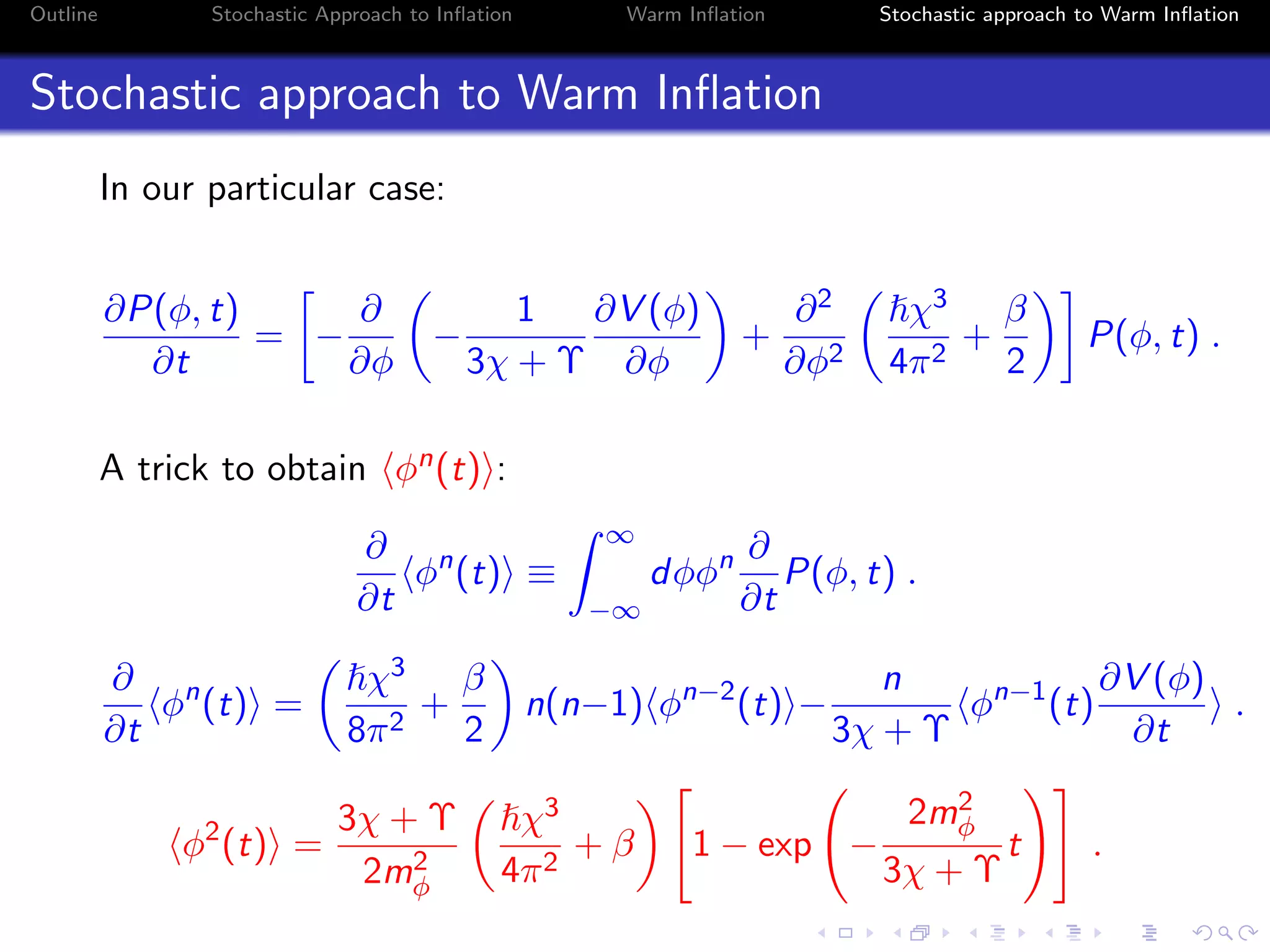
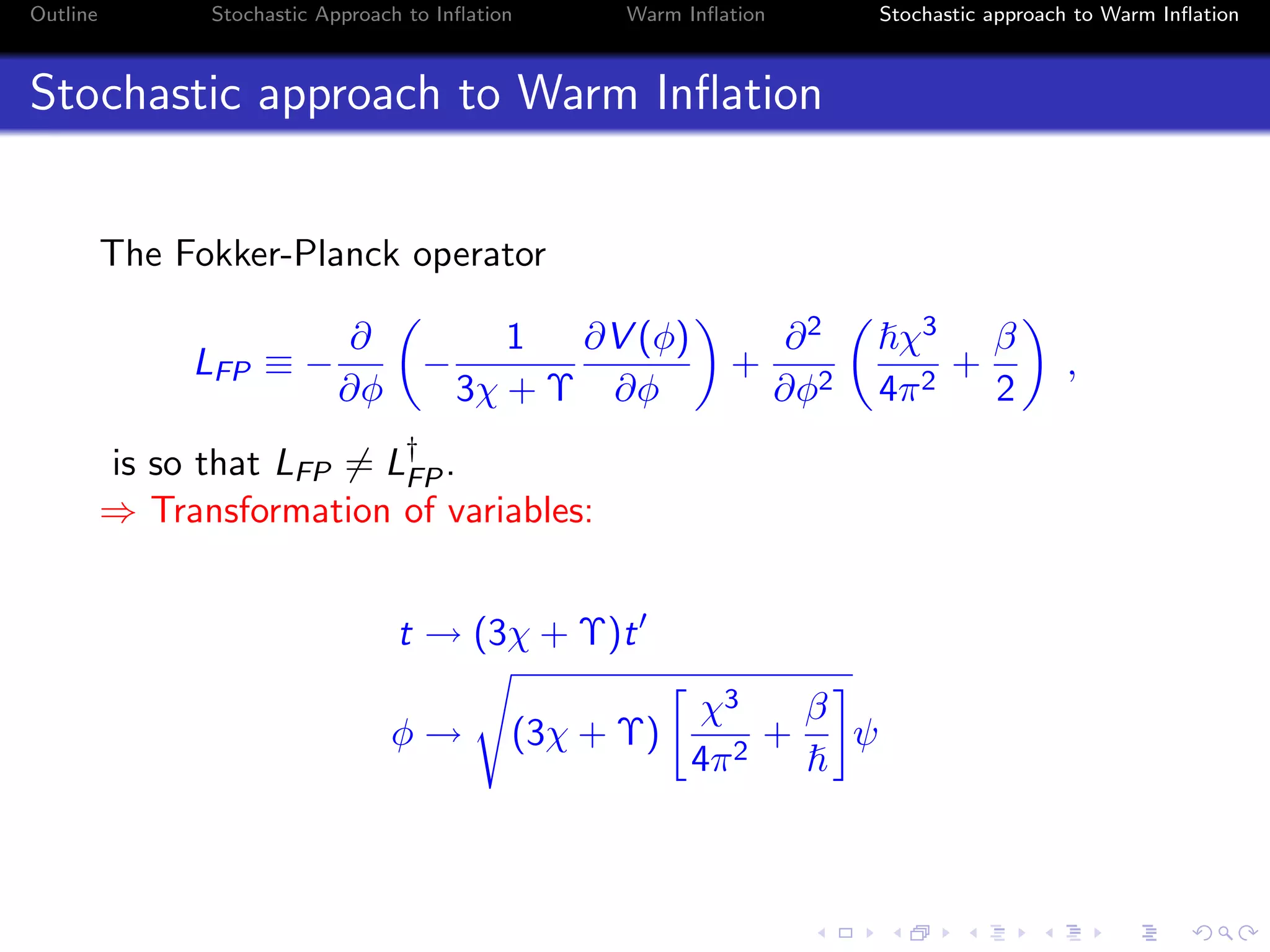
1) The document outlines a stochastic approach to modeling warm inflation, where inflation occurs in the presence of radiation.
2) It discusses using a Langevin equation to describe the dynamics of the inflaton field interacting with other fields, resulting in the production of radiation during inflation.
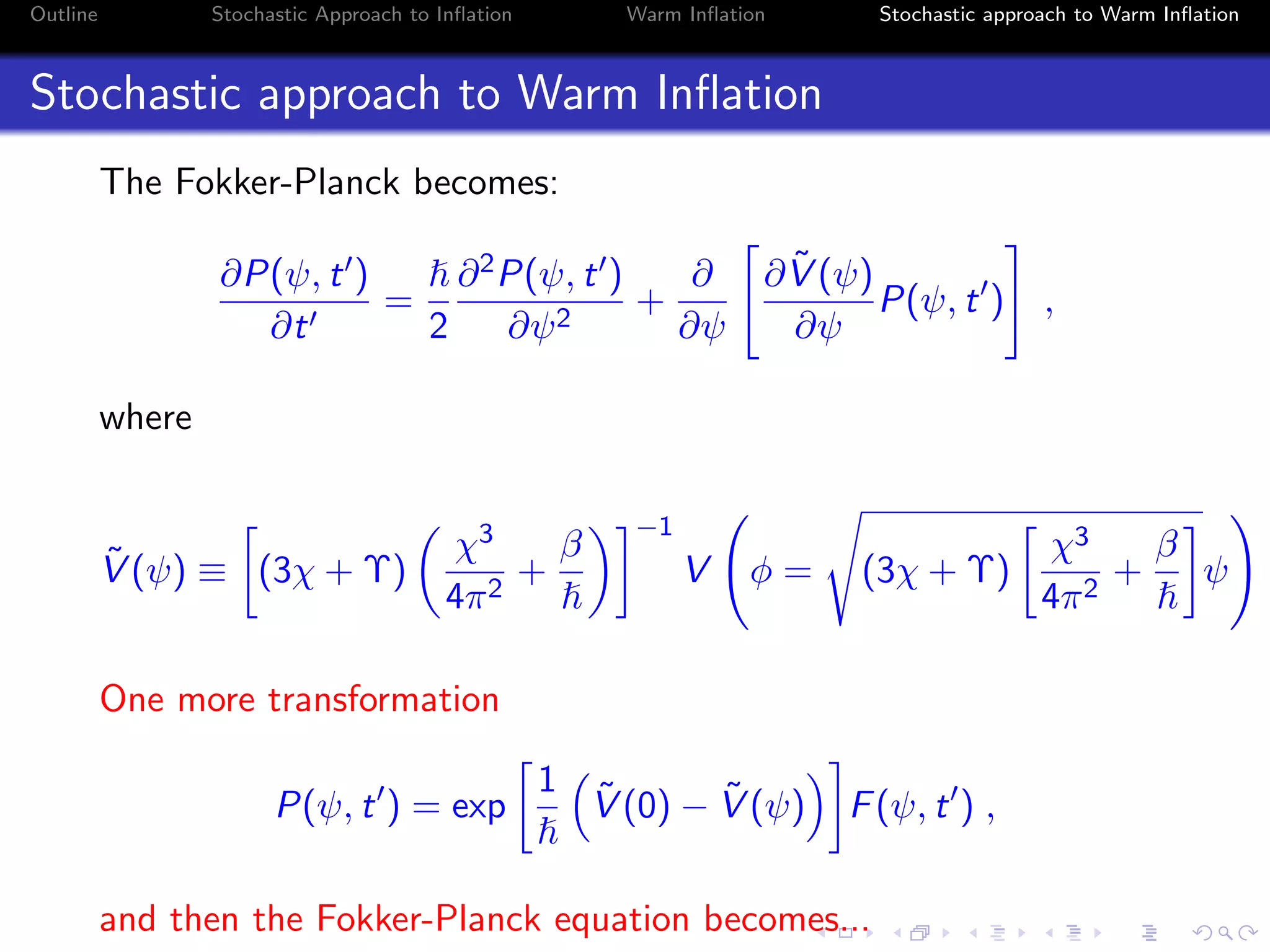
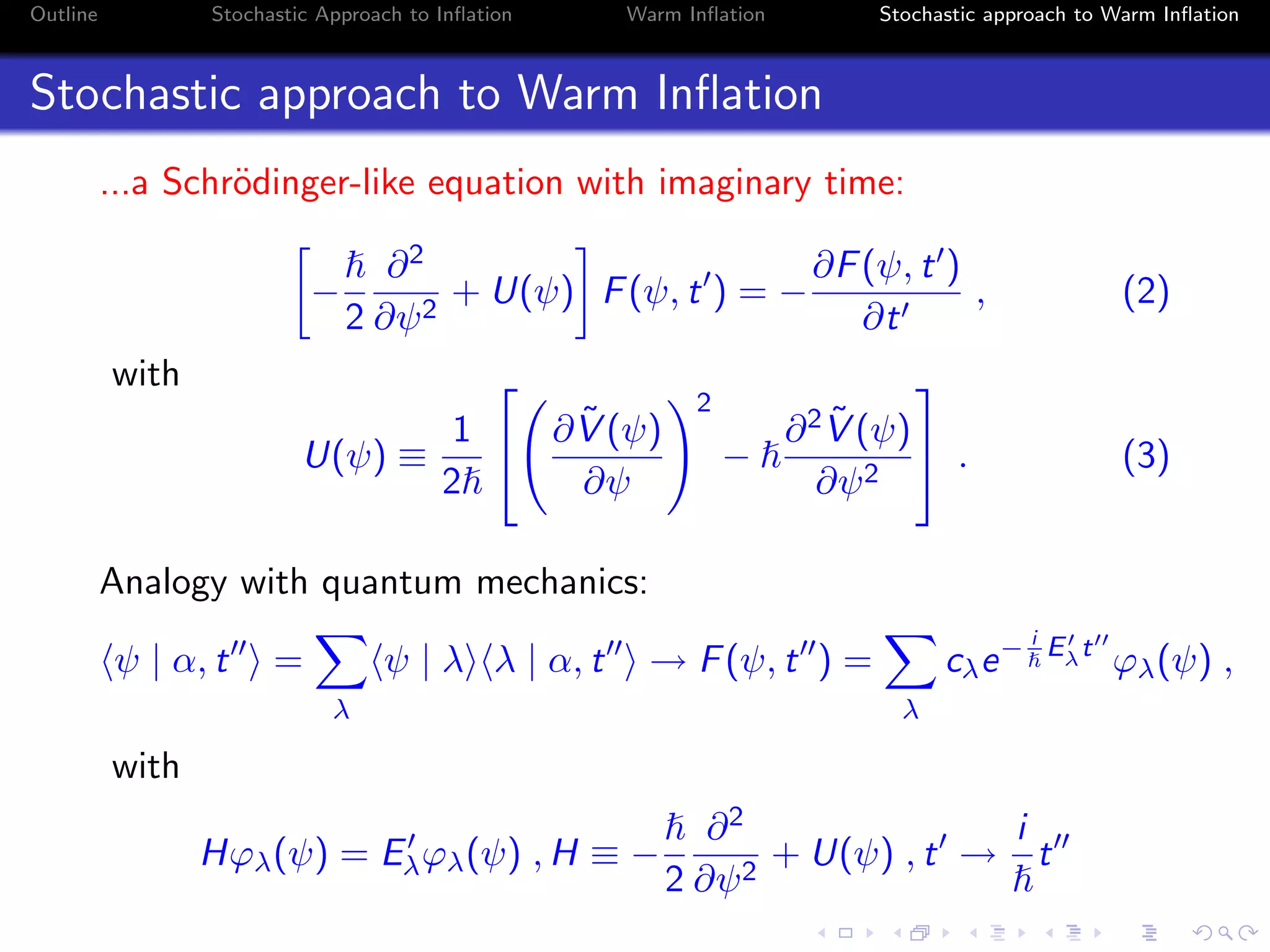
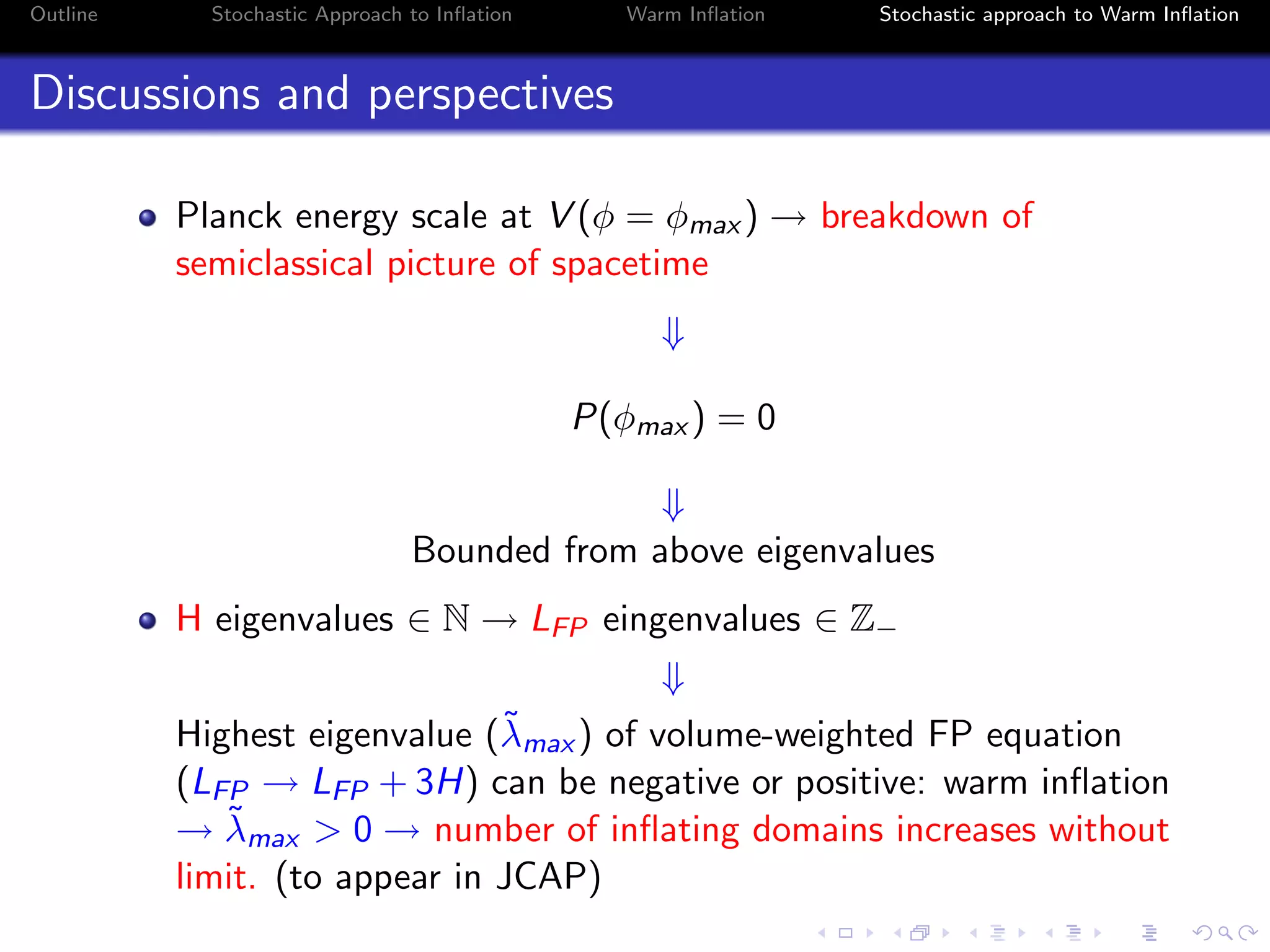
3) The approach uses a Fokker-Planck equation to model the probability distribution of the inflaton field, transforming it into a Schrodinger-like equation with an effective potential that incorporates the effects of radiation on the inflationary dynamics.


![Outline Stochastic Approach to Inflation Warm Inflation Stochastic approach to Warm Inflation
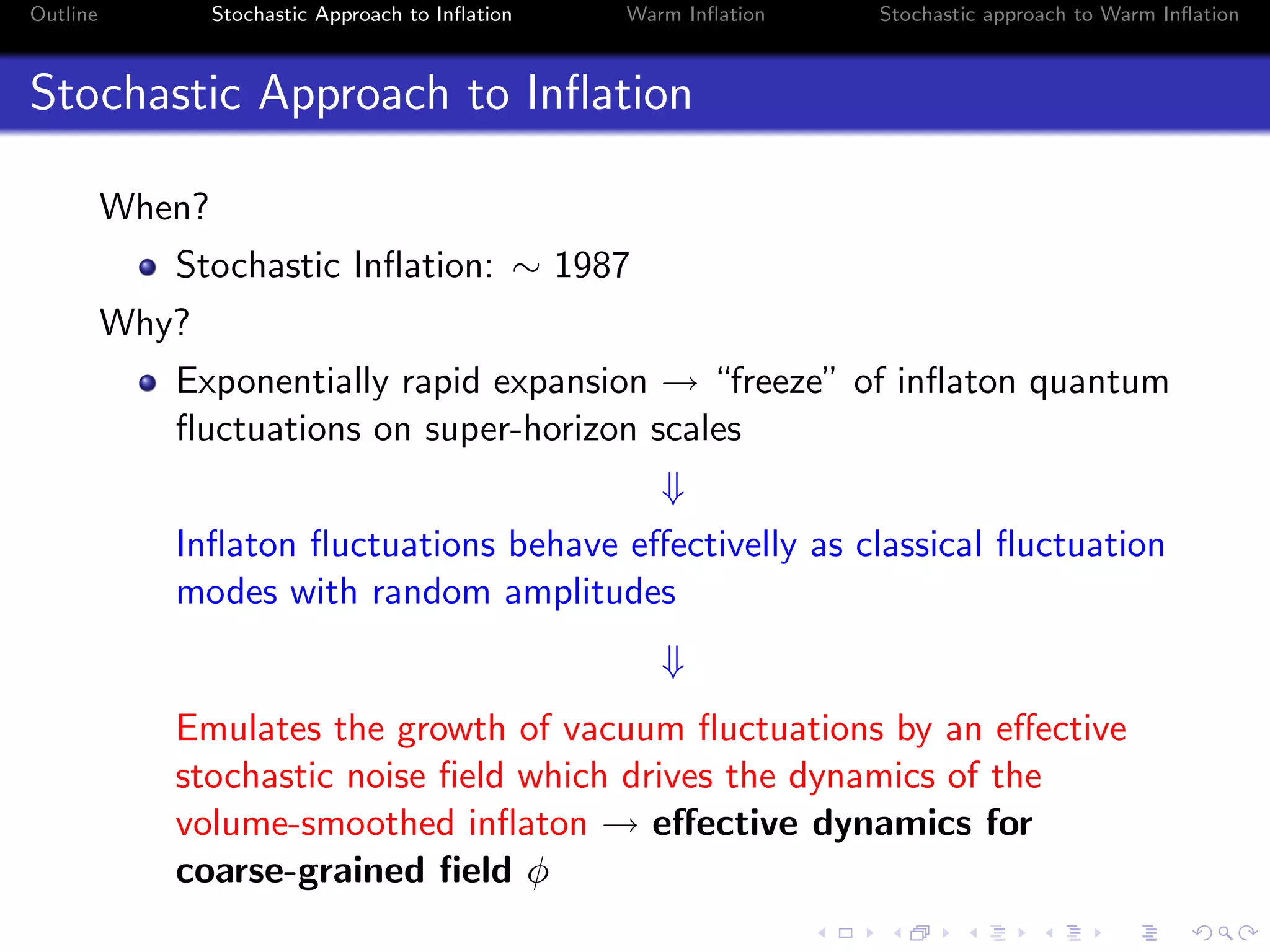
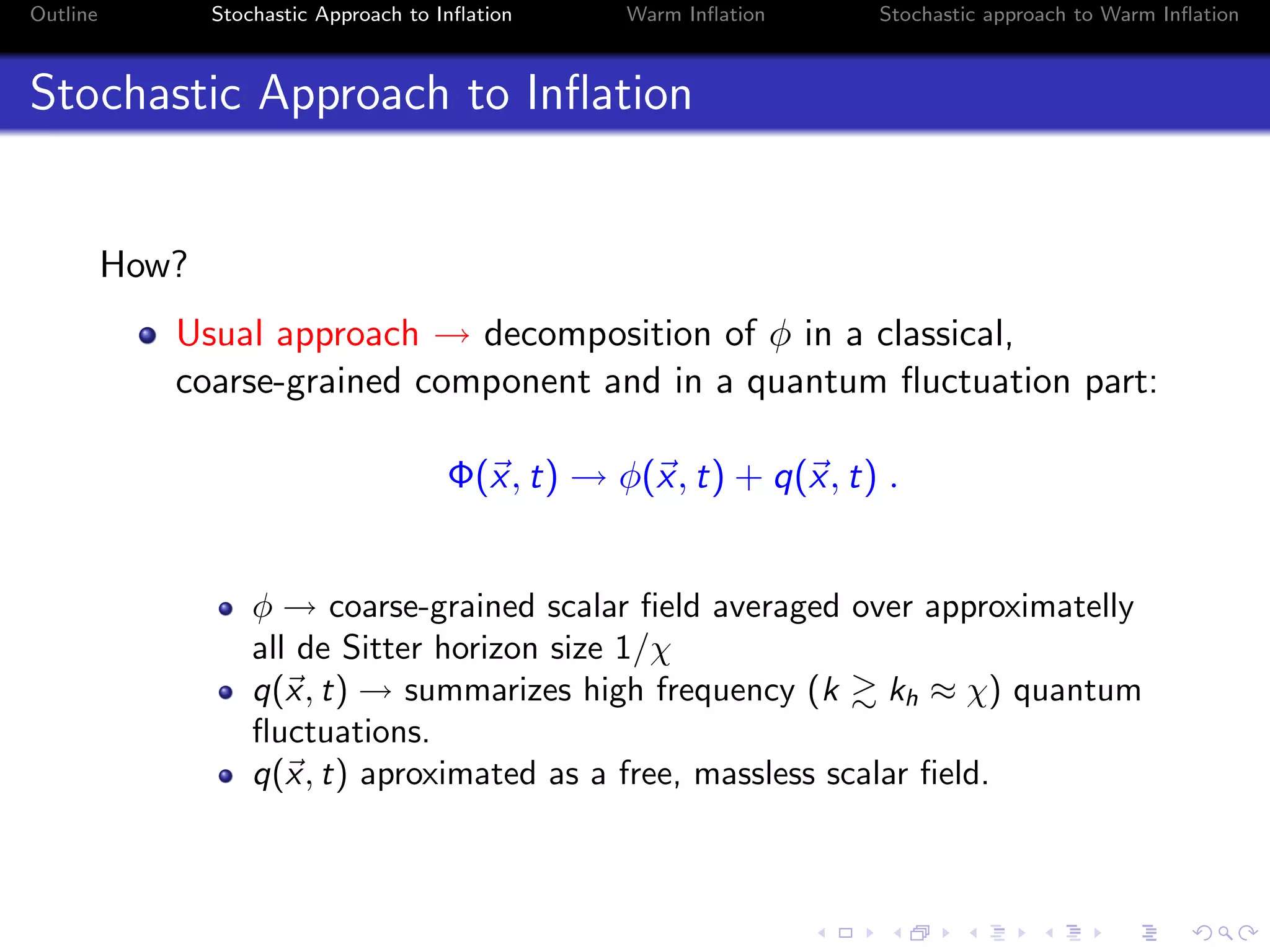
Stochastic Approach to Inflation
de Sitter metric:
ds2
= dxµ
dxν
gµν = −dt2
+ e2χt
dx2
,
Lagrangian density:
L =
1
2
√
−g [gµν
∂µΦ∂νφ − 2V (Φ)]
Equation of motion(EoM):
−3χ
∂
∂t
−
∂2
∂t2
+ e−2χt 2
Φ(x, t) −
∂V (Φ)
∂Φ
= 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enfpclas2010-130501132000-phpapp01/75/ENFPC-2010-5-2048.jpg)
![Outline Stochastic Approach to Inflation Warm Inflation Stochastic approach to Warm Inflation
Stochastic Approach to Inflation
Making the field decomposition (slow-roll: ¨φ(x, t) ≈ 0):
3χ
∂
∂t
− e−2χt 2
[φ(x, t) + q(x, t)] +
∂V (φ)
∂φ
= 0
3χ
∂
∂t
− e−2χt 2
φ(x, t) +
∂V (φ)
∂φ
= 3χη(x, t) ,
Noise term:
η(x, t) ≡ −
∂
∂t
+
e−2χt
3χ
2
q(x, t)
Fourier mode expansion in de Sitter background:
q(x, t) ≡ d3
kWχ(k) σk
(t)e−ik·x
ˆak
+ σ∗
k
(t)eik·x
ˆa†
k
.
Wχ(k) → filter or window function. Sharp momentum cutoff
implementation: Wχ(k) ≡ θ(k − χeχt).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enfpclas2010-130501132000-phpapp01/75/ENFPC-2010-6-2048.jpg)
![Outline Stochastic Approach to Inflation Warm Inflation Stochastic approach to Warm Inflation
Stochastic Approach to Inflation
σk
(t) ≡
1
2k(2π)3
χτ − i
χ
k
e−ikτ
.
Commutator:
[η(x, τ), η(y, τ)] = 0
⇓
Classical behaviour of quantum noise!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enfpclas2010-130501132000-phpapp01/75/ENFPC-2010-7-2048.jpg)
![Outline Stochastic Approach to Inflation Warm Inflation Stochastic approach to Warm Inflation
Stochastic Approach to Inflation
σk
(t) ≡
1
2k(2π)3
χτ − i
χ
k
e−ikτ
.
Commutator:
[η(x, τ), η(y, τ)] = 0
⇓
Classical behaviour of quantum noise!
Propagator:
0 | η(x, t)η(y, t ) | 0 =
χ3
4π2
δ(t − t )
sin τ | x − y |
τ | x − y |
.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enfpclas2010-130501132000-phpapp01/75/ENFPC-2010-8-2048.jpg)
![Outline Stochastic Approach to Inflation Warm Inflation Stochastic approach to Warm Inflation
Microscopic motivation to Warm Inflation
Example:
S[φ, χ, σ] = d4
x
1
2
(∂µφ)2
−
1
2
m2
φφ2
−
λ
4!
φ4
+
1
2
(∂µχ)2
−
1
2
m2
χχ2
+
1
2
(∂µσ)2
−
1
2
m2
σσ2
−
g2
2
φ2
χ2
− f χσ2
.
φ → classical field in which dynamics we are interested in
χ → intermediate field that couples to σ and φ
σ → Thermally equilibrated field at temperature T](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enfpclas2010-130501132000-phpapp01/75/ENFPC-2010-10-2048.jpg)

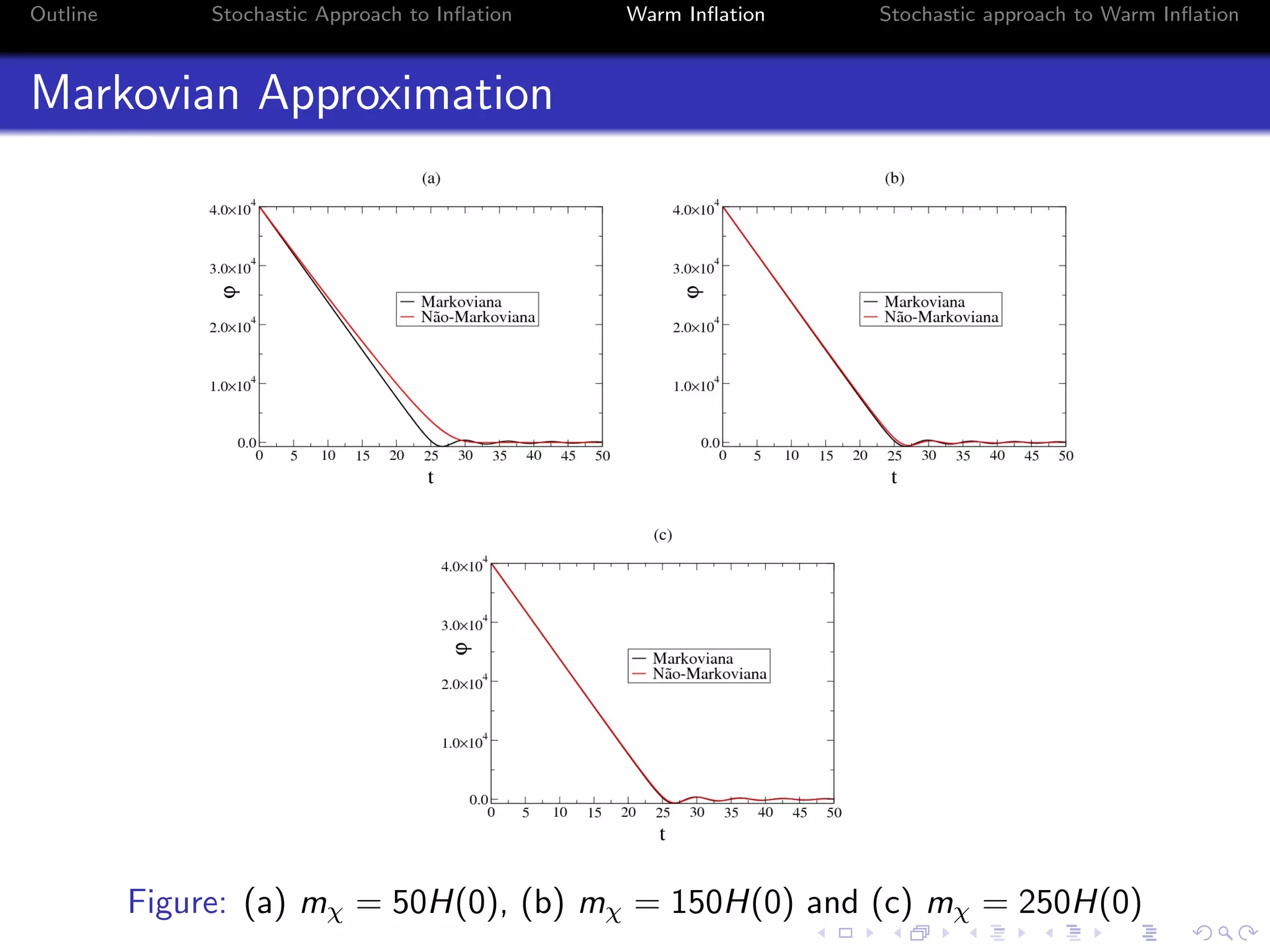

![Outline Stochastic Approach to Inflation Warm Inflation Stochastic approach to Warm Inflation
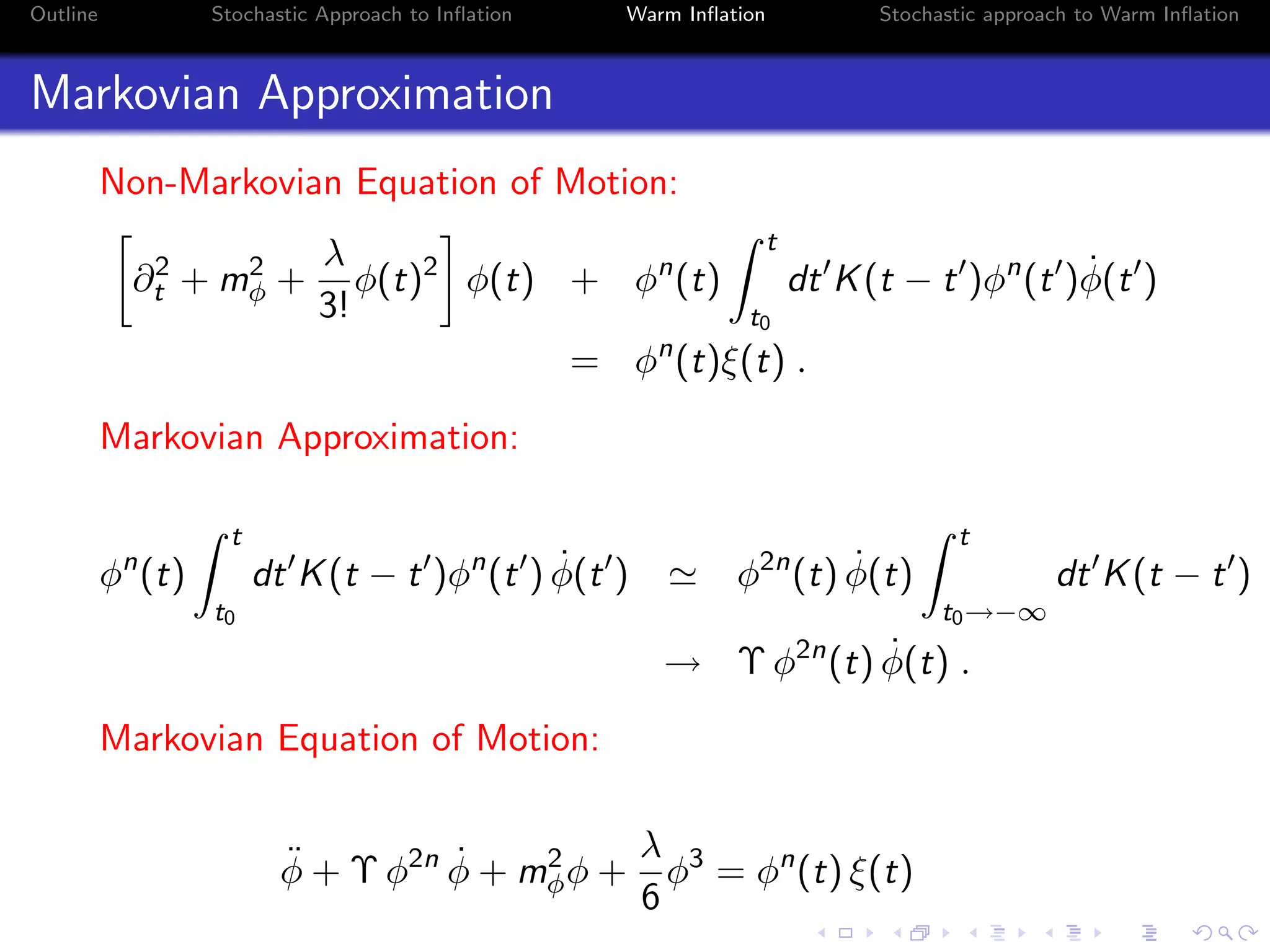
Markovian Approximation
Considering the additive case:
¨φ + [3H + Υ] ˙φ + V (φ) = ξ ,
¨a = −
8π
3m2
pl
ρr + ˙φ2
− V (φ) a ,
˙ρφ = −3
˙a
a
˙φ2
− Υ ˙φ2
+ ν ˙φ , ˙ρr = −4
˙a
a
ρr + Υ ˙φ2
− ξ ˙φ .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enfpclas2010-130501132000-phpapp01/75/ENFPC-2010-15-2048.jpg)