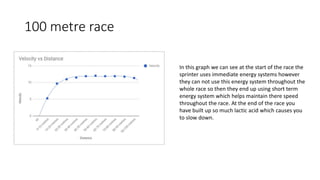
This document discusses different energy systems in the body. It explains that there are three main energy systems: ATP-PC, anaerobic, and aerobic. The ATP-PC system provides immediate energy through breakdown of ATP and phosphocreatine. The anaerobic system produces energy without oxygen through glycolysis. It can fuel high-intensity exercise for 1-2 minutes. The aerobic system produces the most ATP through multiple stages but more slowly, fueling lower-intensity exercise for longer. Examples are given of sports that rely on each system, like sprints using ATP-PC and long distance using aerobic.