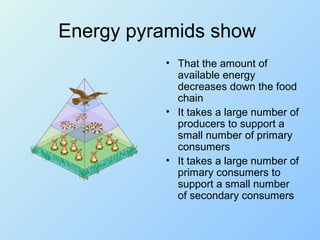
This document discusses energy flow through ecosystems. It begins by explaining photosynthesis and how plants use energy from the sun to produce glucose from carbon dioxide and water. Producers, like plants, use this energy primarily for themselves through cellular respiration. Consumers cannot produce their own energy and obtain it by eating producers or other consumers. This transfer of energy between trophic levels can be represented by food chains or energy pyramids, which show that the amount of available energy decreases at each level. Food webs illustrate the complex interconnected feeding relationships between organisms in an ecosystem.