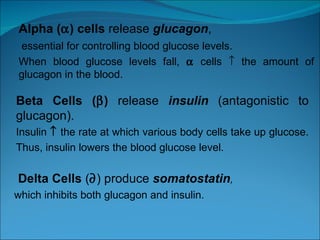
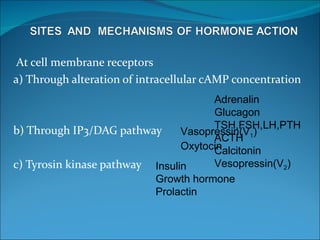
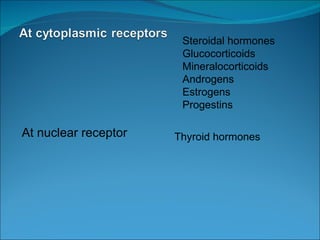
The endocrine system consists of glands that release hormones to regulate bodily functions. The major glands include the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, pancreas, adrenal glands, and gonads. Each gland produces specific hormones that target other glands or body systems to perform functions like calcium regulation, metabolism, growth, and reproduction. Hormones travel through the bloodstream and act through receptor pathways or nuclear receptors in cells.