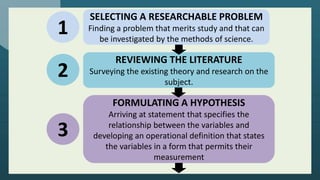
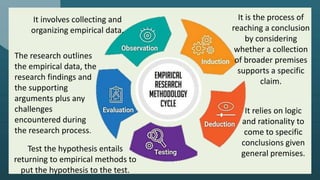
The document outlines the steps in conducting empirical research which includes selecting a research problem, reviewing existing literature, formulating a hypothesis, choosing a research design, collecting data, analyzing results, and stating conclusions. Empirical research involves testing hypotheses through experimentation, observation or experience. It has advantages such as being used for authentication and understanding dynamic changes, but also disadvantages like being time consuming and expensive.