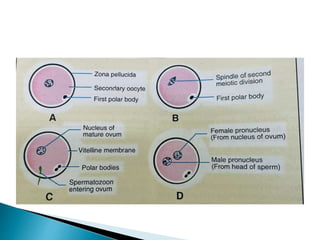
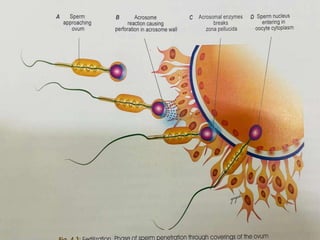
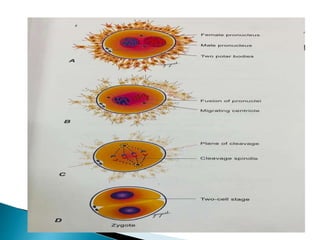
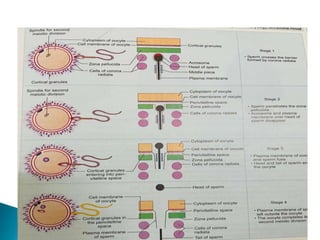
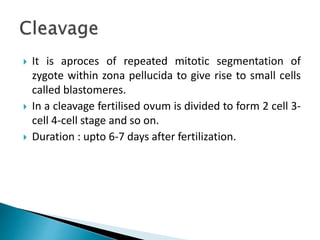
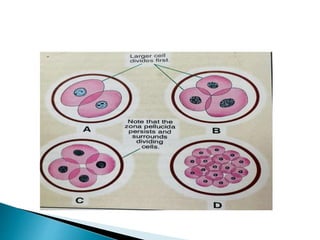
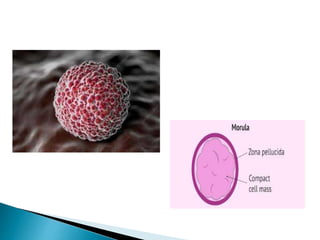
The document explains the process of fertilization, detailing the fusion of an ovum and spermatozoon to form a zygote, which occurs in the ampulla of the fallopian tube. It outlines the stages of fertilization, the transportation of sperm and ovum, and the biochemical processes involved, including the acrosome reaction and formation of a diploid zygote. Additionally, it describes the early development stages, including cleavage and the formation of a morula.