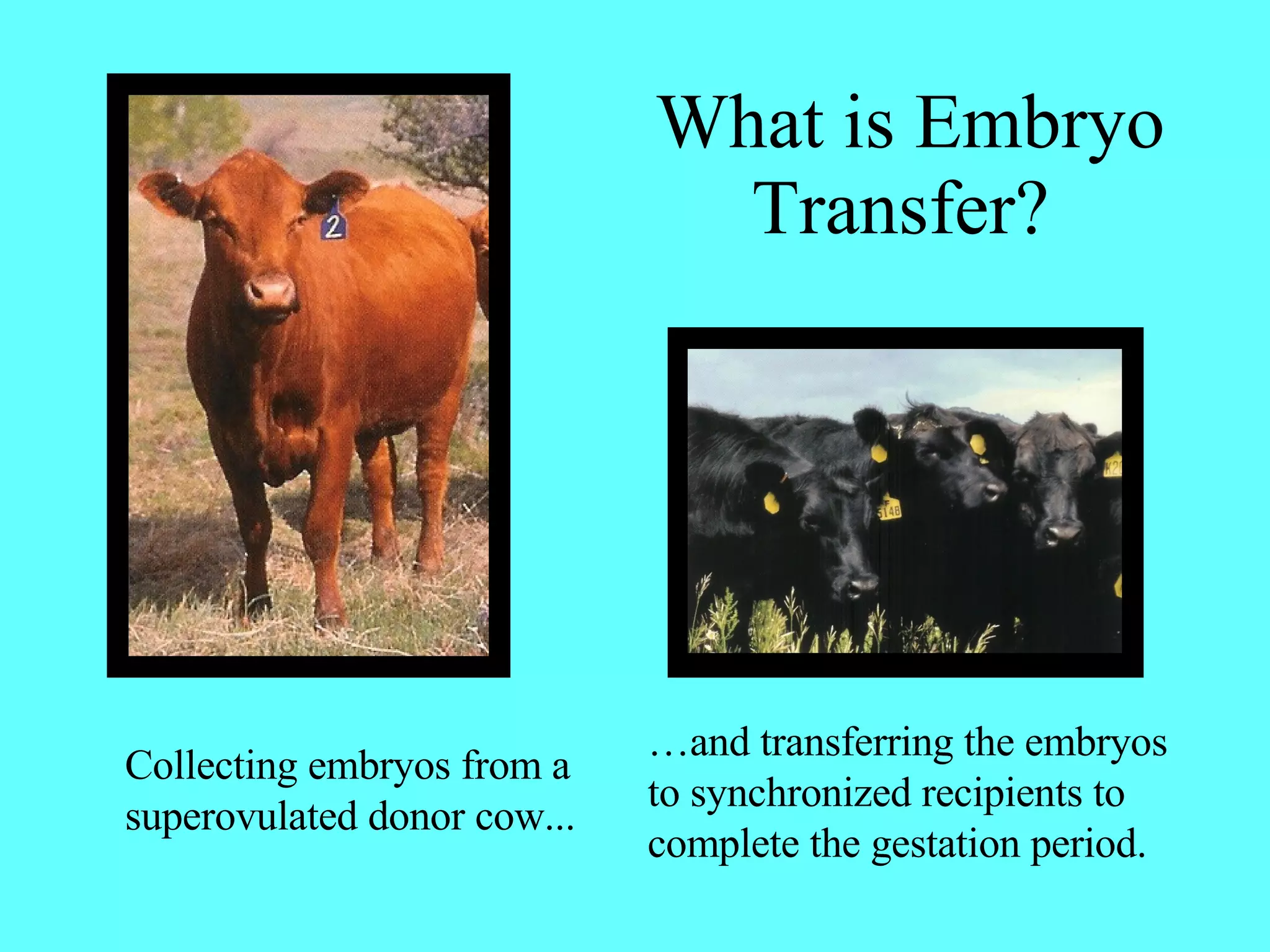
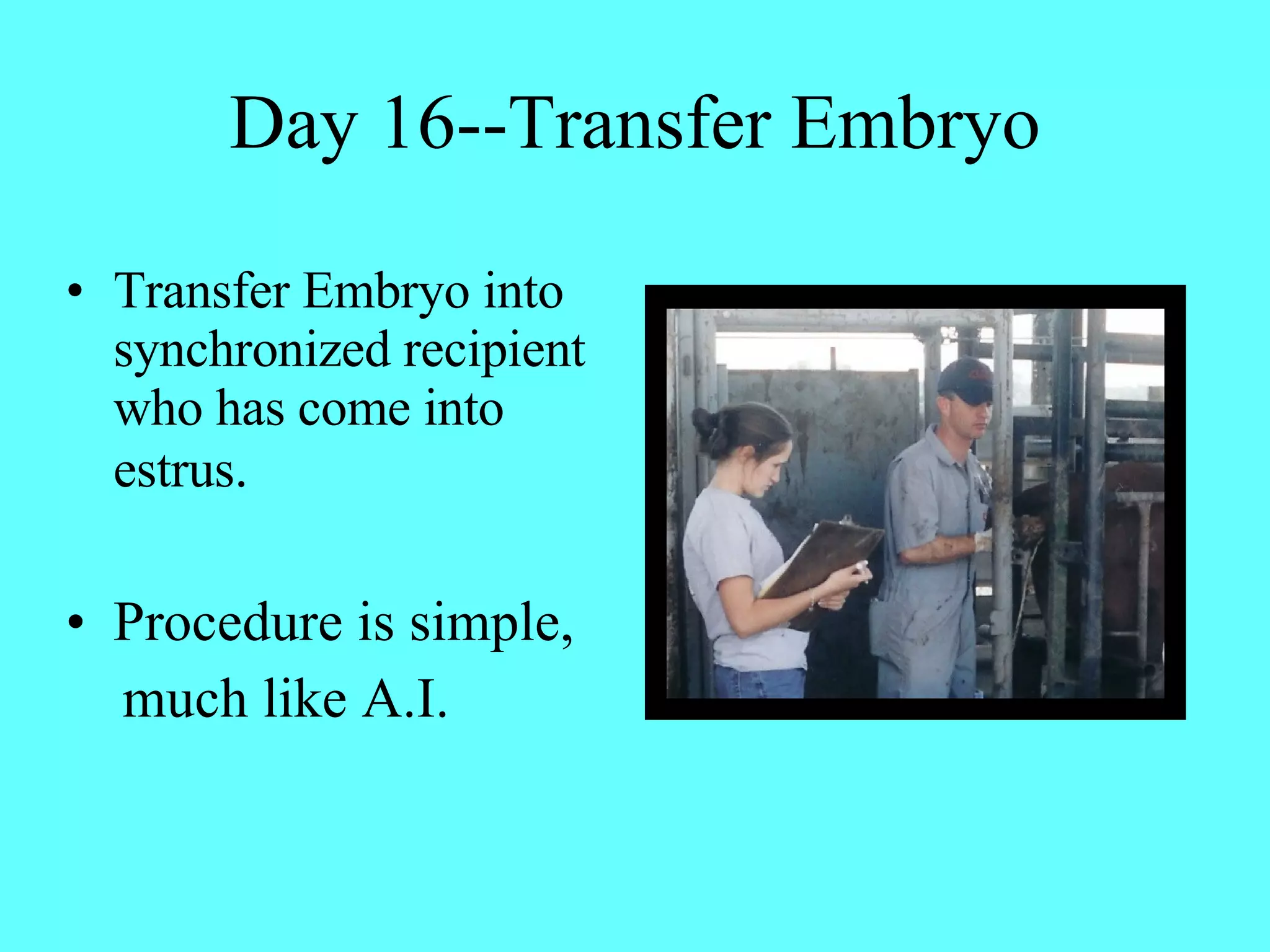
Embryo transfer involves collecting embryos from a donor cow and transferring them to recipient cows. The donor cow is given follicle stimulating hormones to cause it to superovulate and produce multiple embryos. The embryos are then collected from the donor cow approximately 7 days after artificial insemination. The embryos are evaluated and the highest quality embryos are transferred into recipient cows that have been synchronized to the same stage of estrus as the donor cow through the use of hormones. Embryo transfer allows for the propagation of genetics from superior cows and makes it possible to export or store embryos indefinitely.