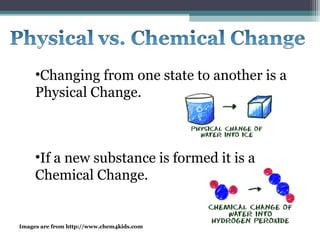
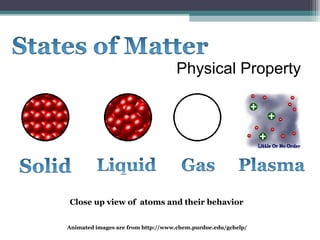
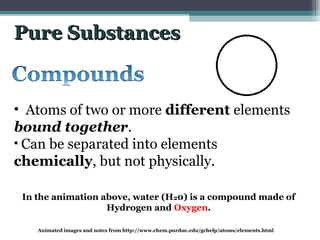
The document provides instructions to set up Cornell notes on specific pages of a textbook. It then summarizes key concepts about elements, compounds, and mixtures from a middle school science website. Specifically, it defines pure substances as materials made of only one type of atom that cannot be broken down further. Compounds are defined as pure substances made of two or more elements bound chemically. Physical and chemical changes are also briefly discussed. Animated images are included from additional websites to illustrate atomic structure and behavior.