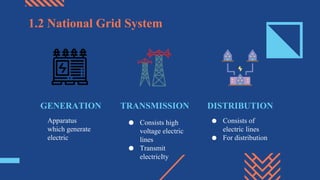
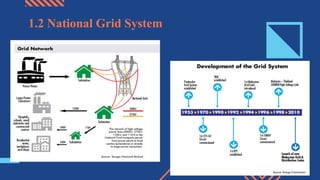
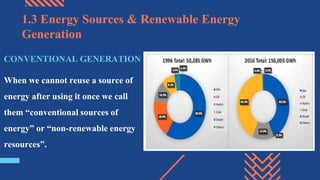
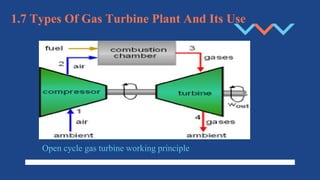
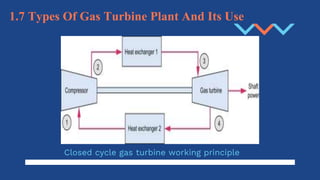
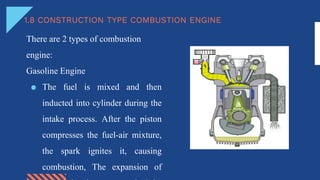
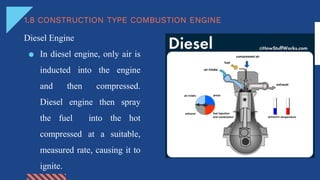
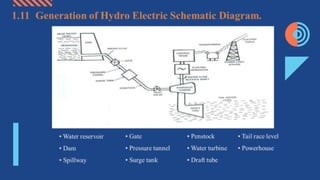
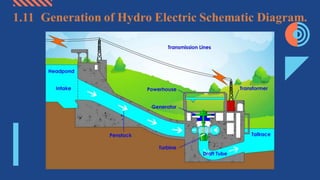
The document discusses different aspects of electrical power generation systems in Malaysia. It begins with a brief history of electricity in Malaysia starting from 1894. It then discusses the national grid system which consists of generation, transmission, and distribution components. It also covers various energy sources used for conventional generation such as oil, coal, natural gas, and nuclear. Renewable energy sources like solar, hydro, and biomass are also mentioned. Different electrical power generation systems like steam turbines, gas turbines, and combustion engines are described. The principles and types of various power plants are provided.