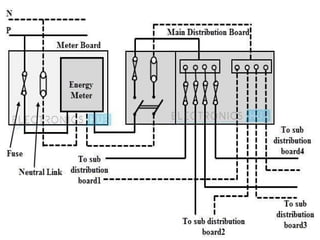
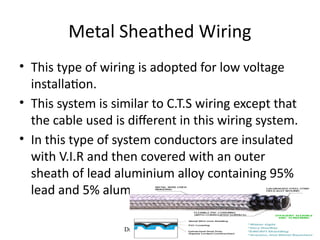
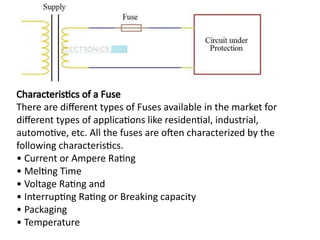
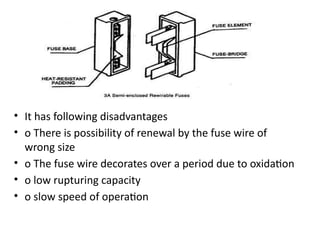
The document covers various aspects of electrical wiring estimation and costing, focusing on the types, advantages, and disadvantages of different wiring systems such as cleat wiring, wooden casing and capping, C.T.S or T.R.S wiring, metal sheathed wiring, and conduit wiring. It outlines general rules for wiring design, including considerations for safety, appearance, cost, and maintenance, as well as types of cables used in internal wiring. The document serves as a guide for the effective distribution of electrical energy in residential and commercial buildings while adhering to safety and aesthetic standards.