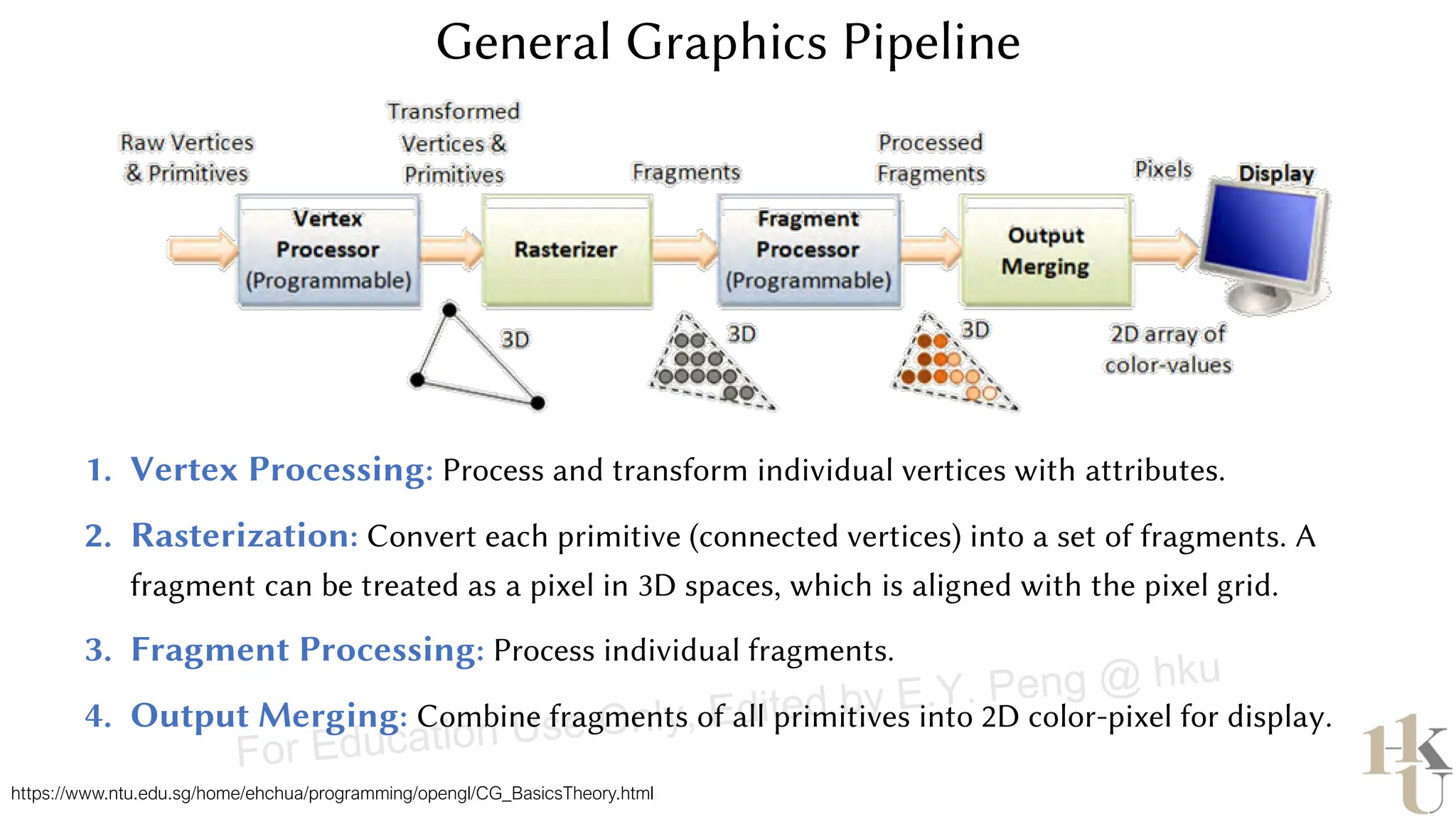
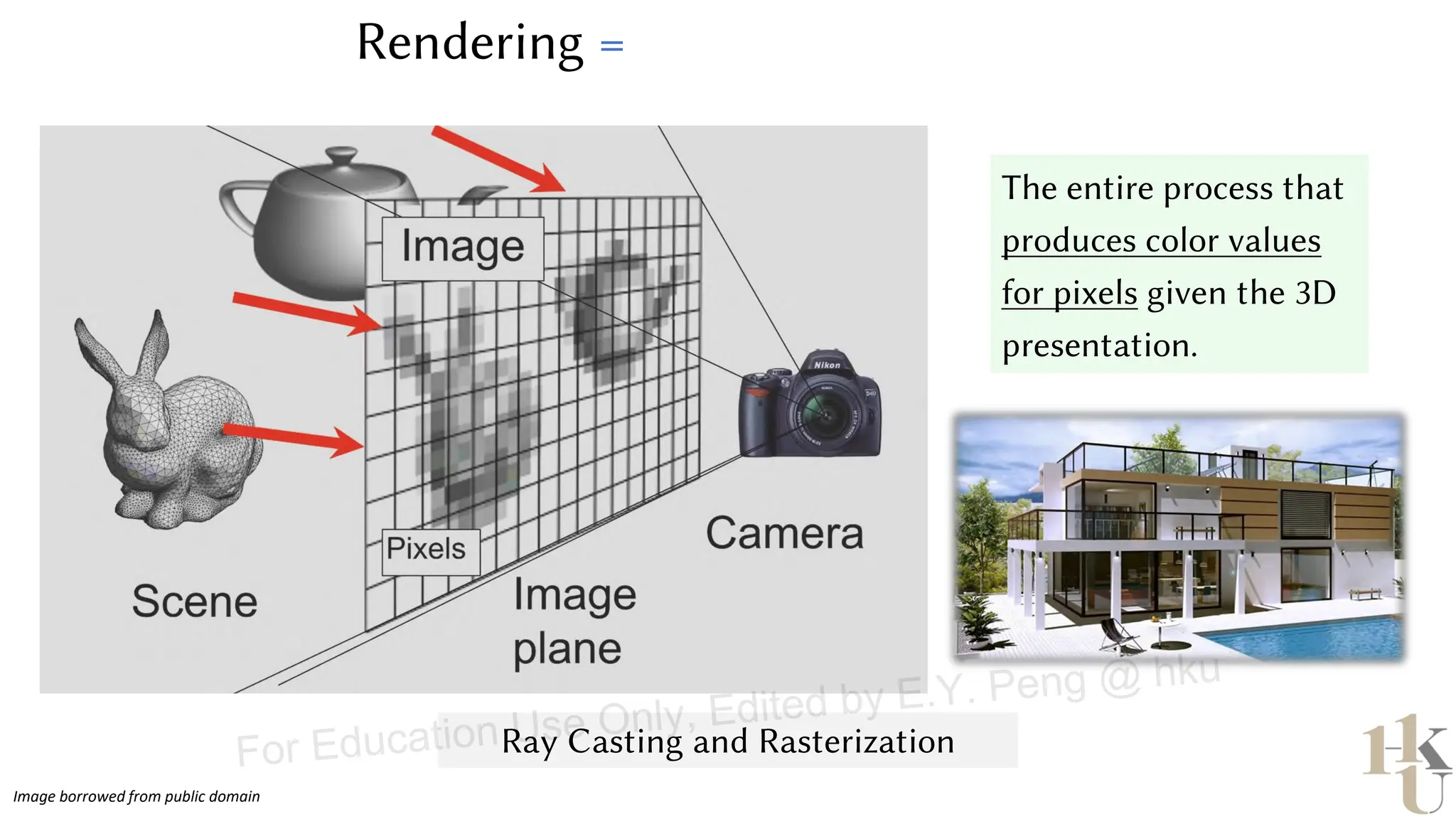
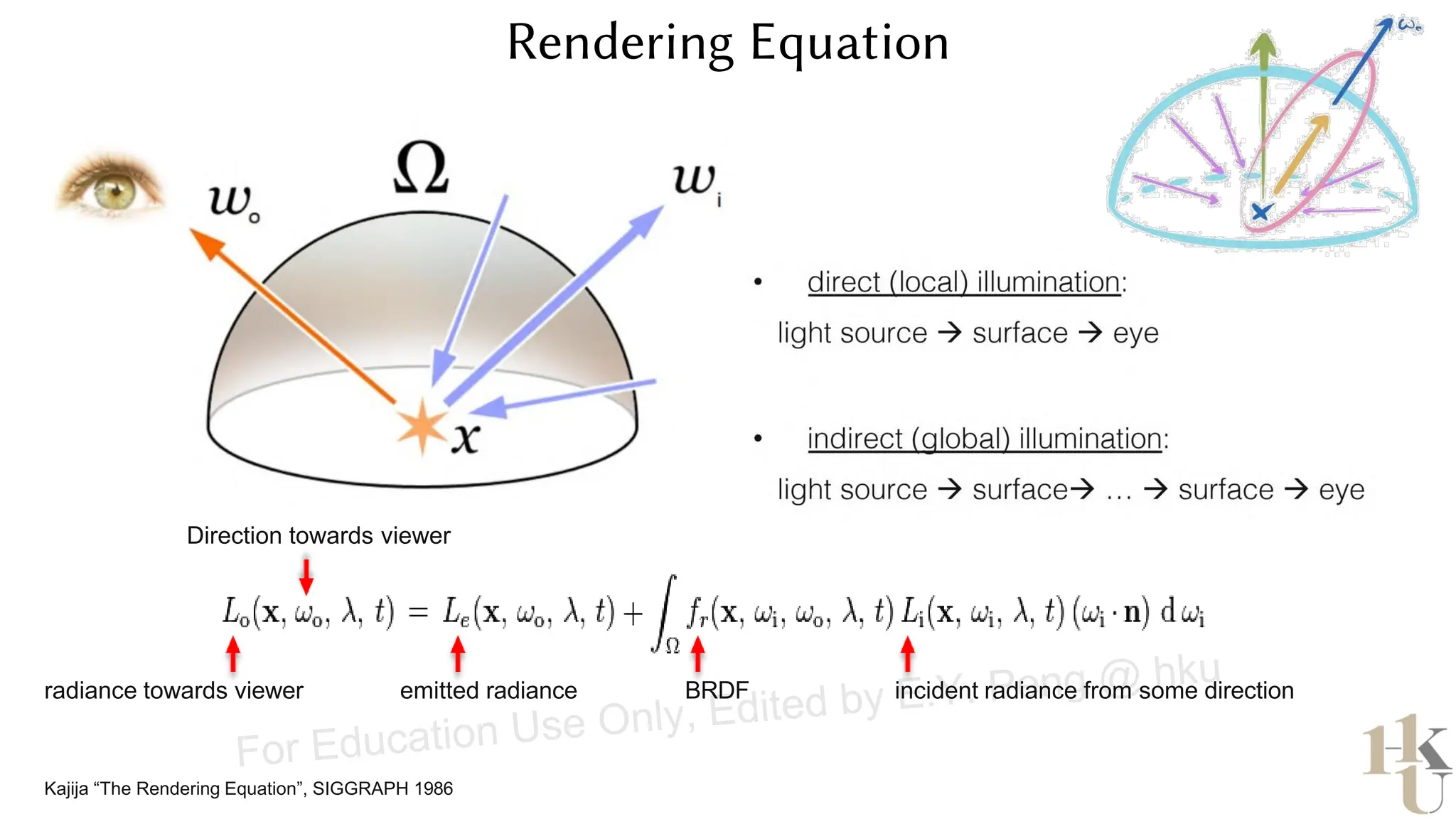
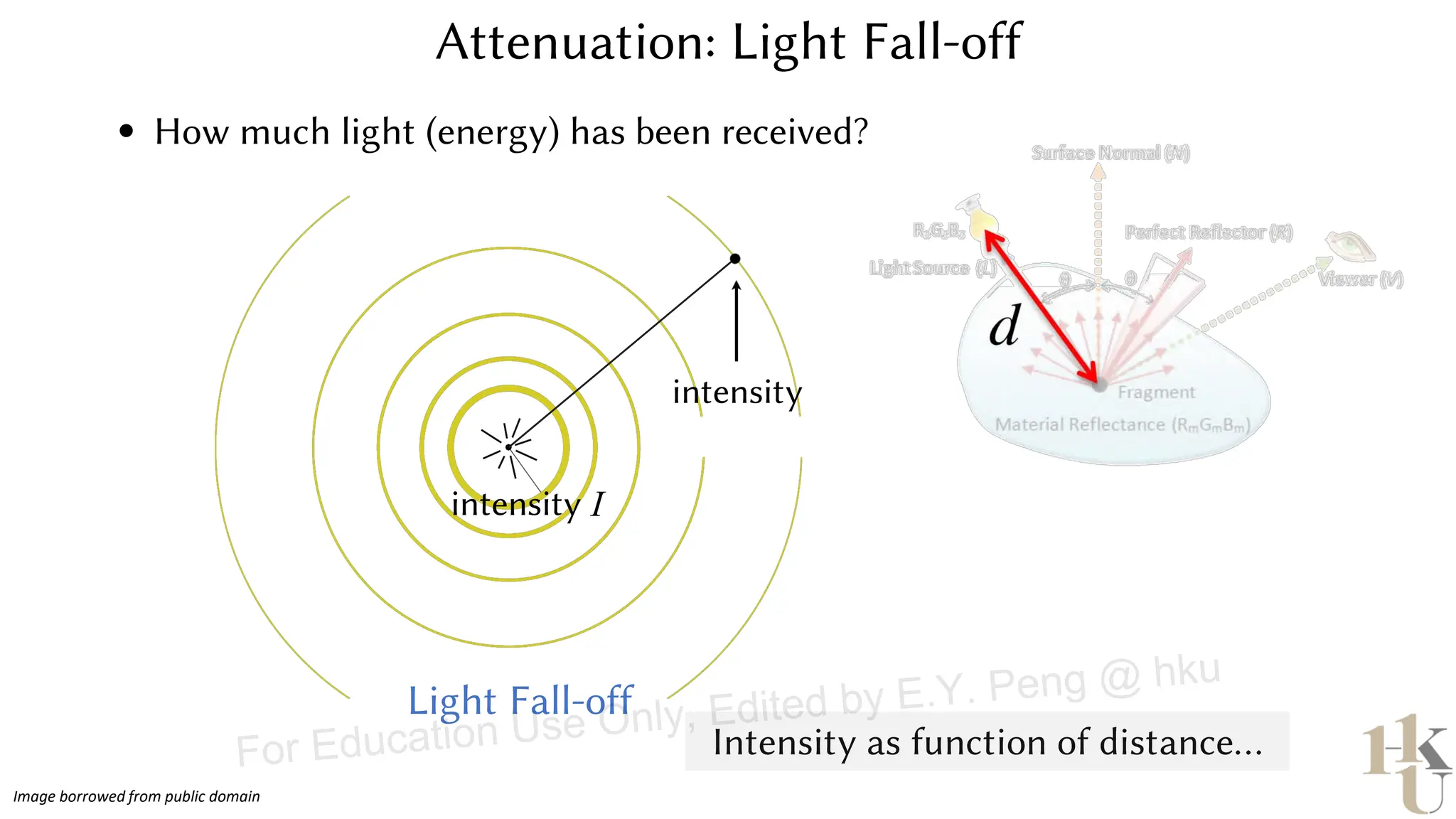
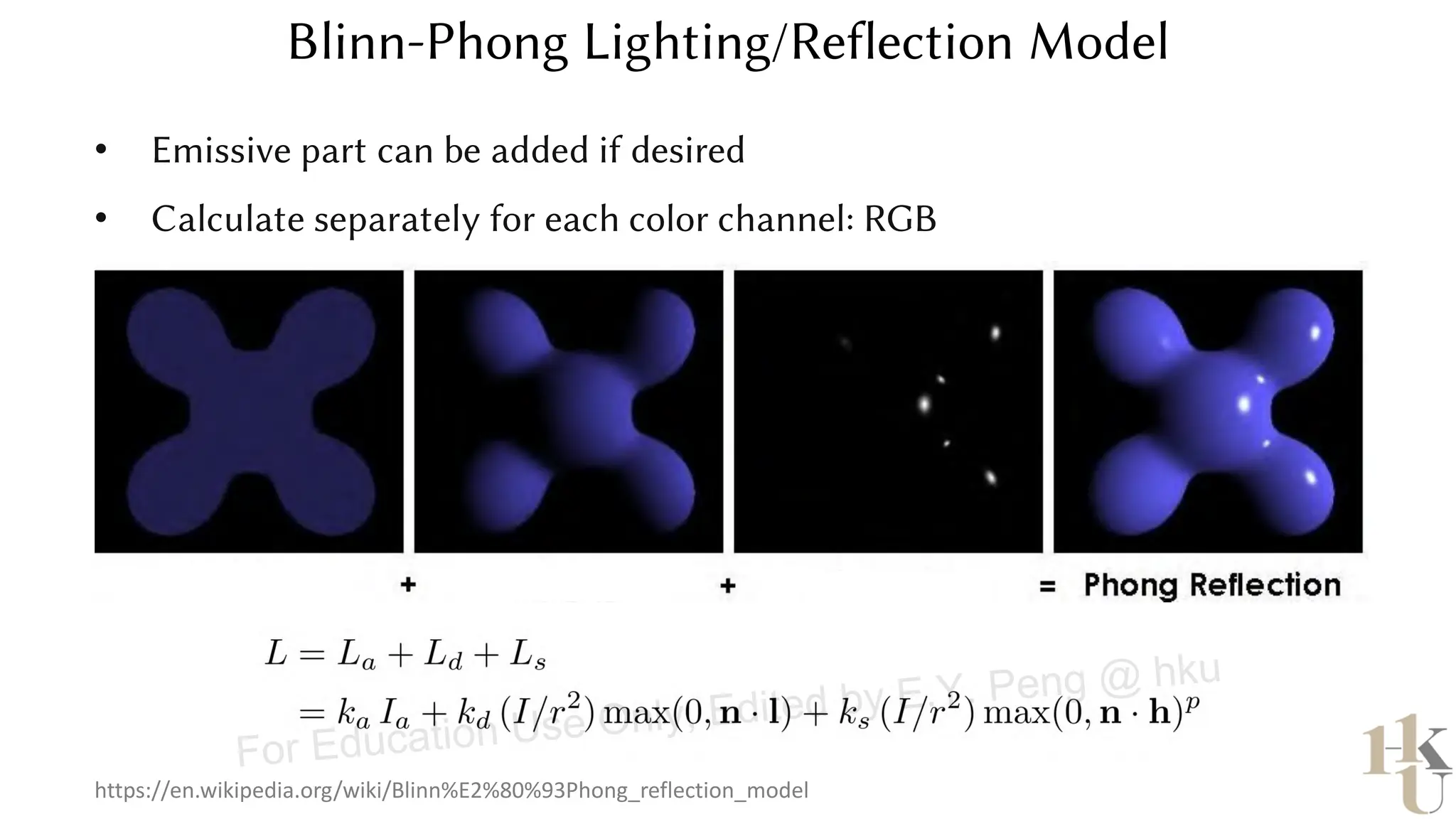
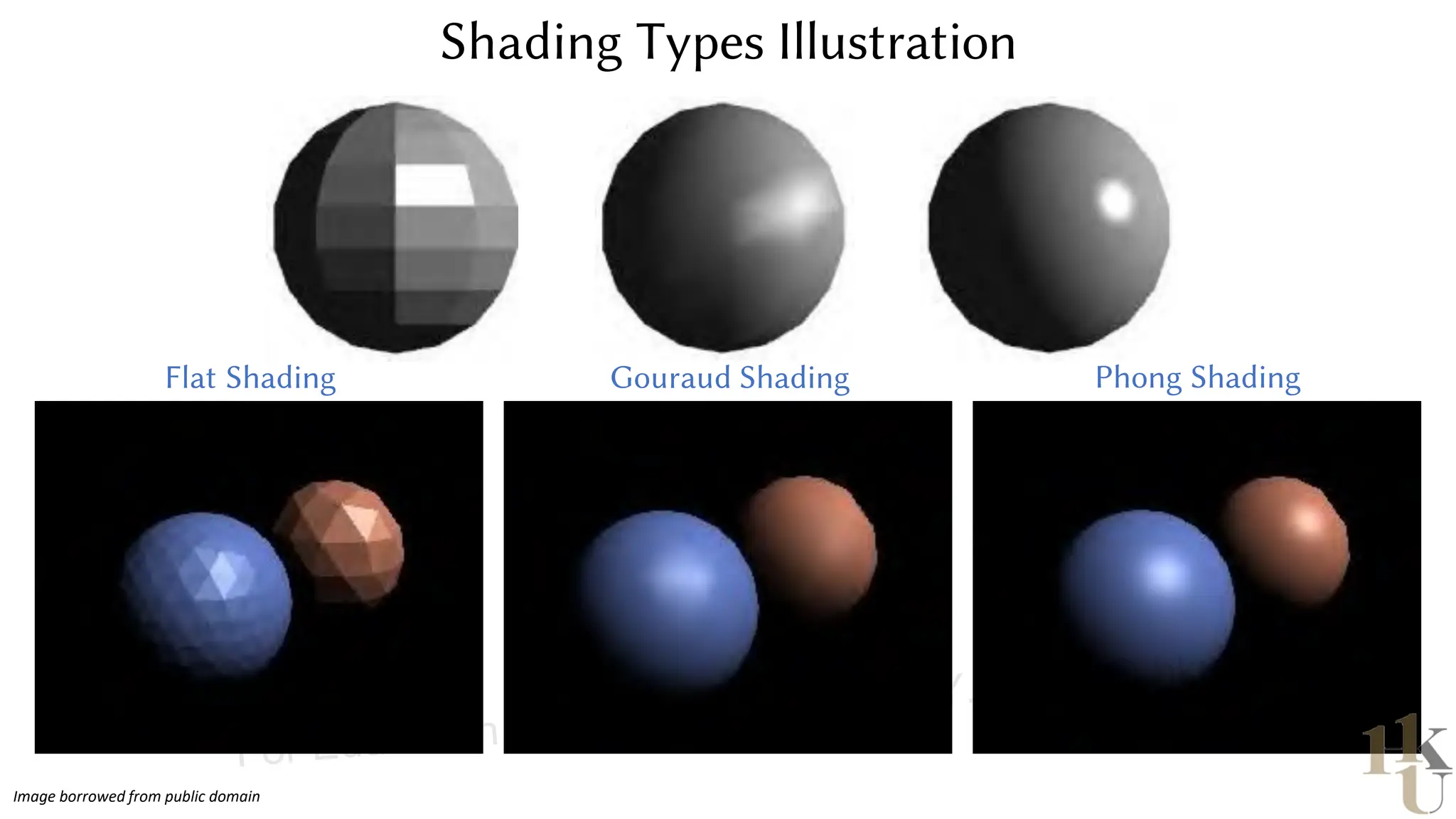
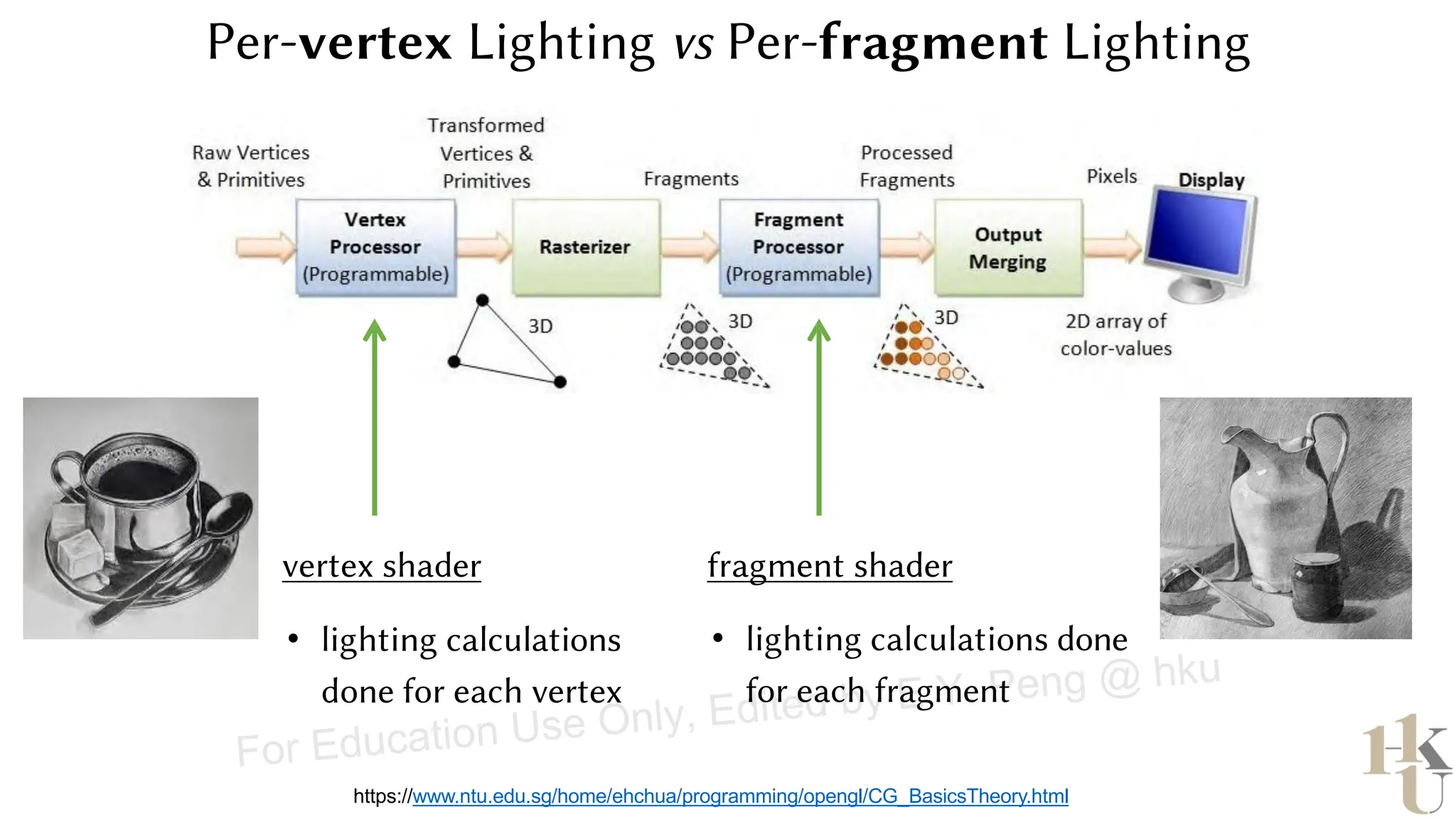
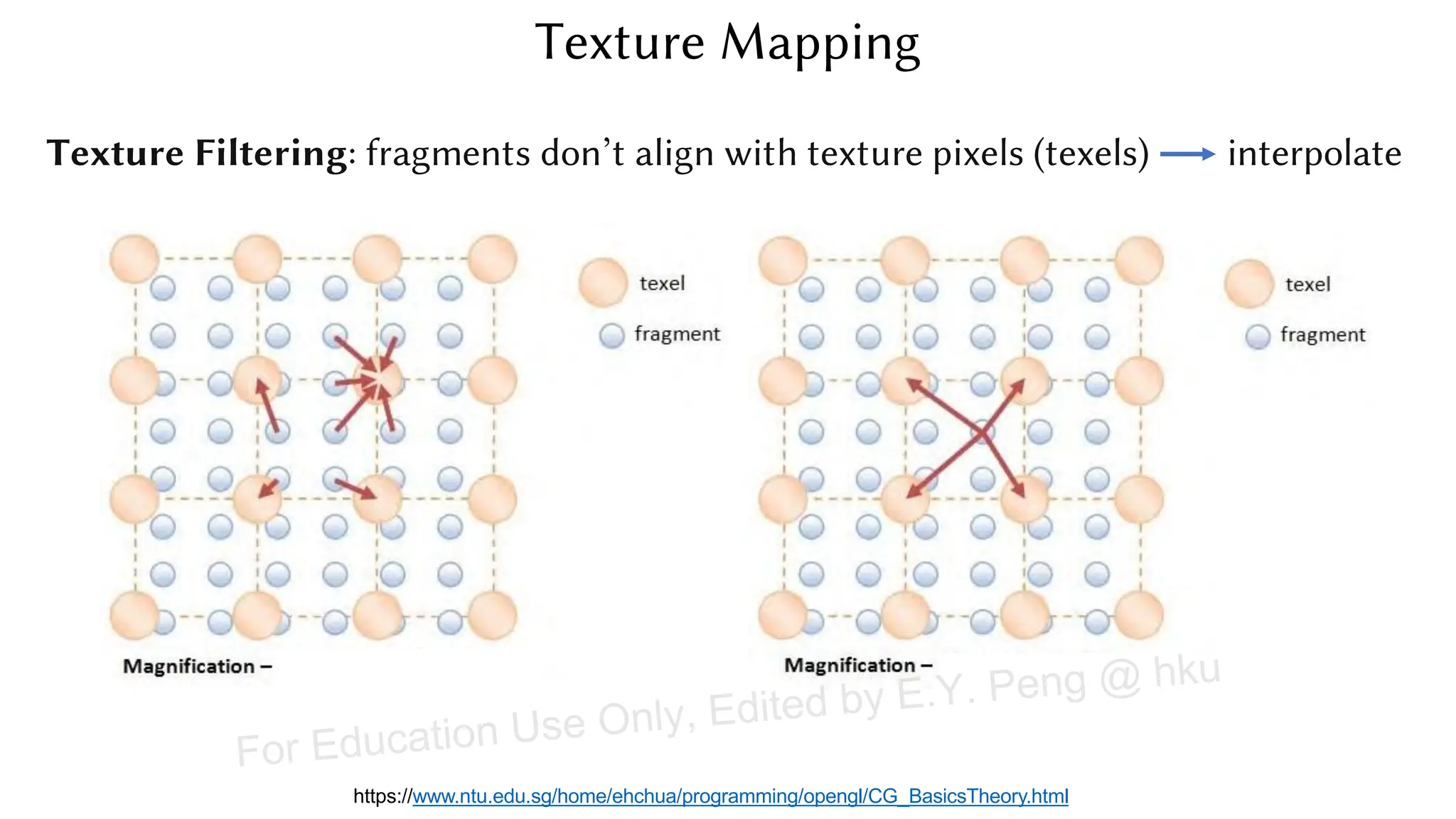
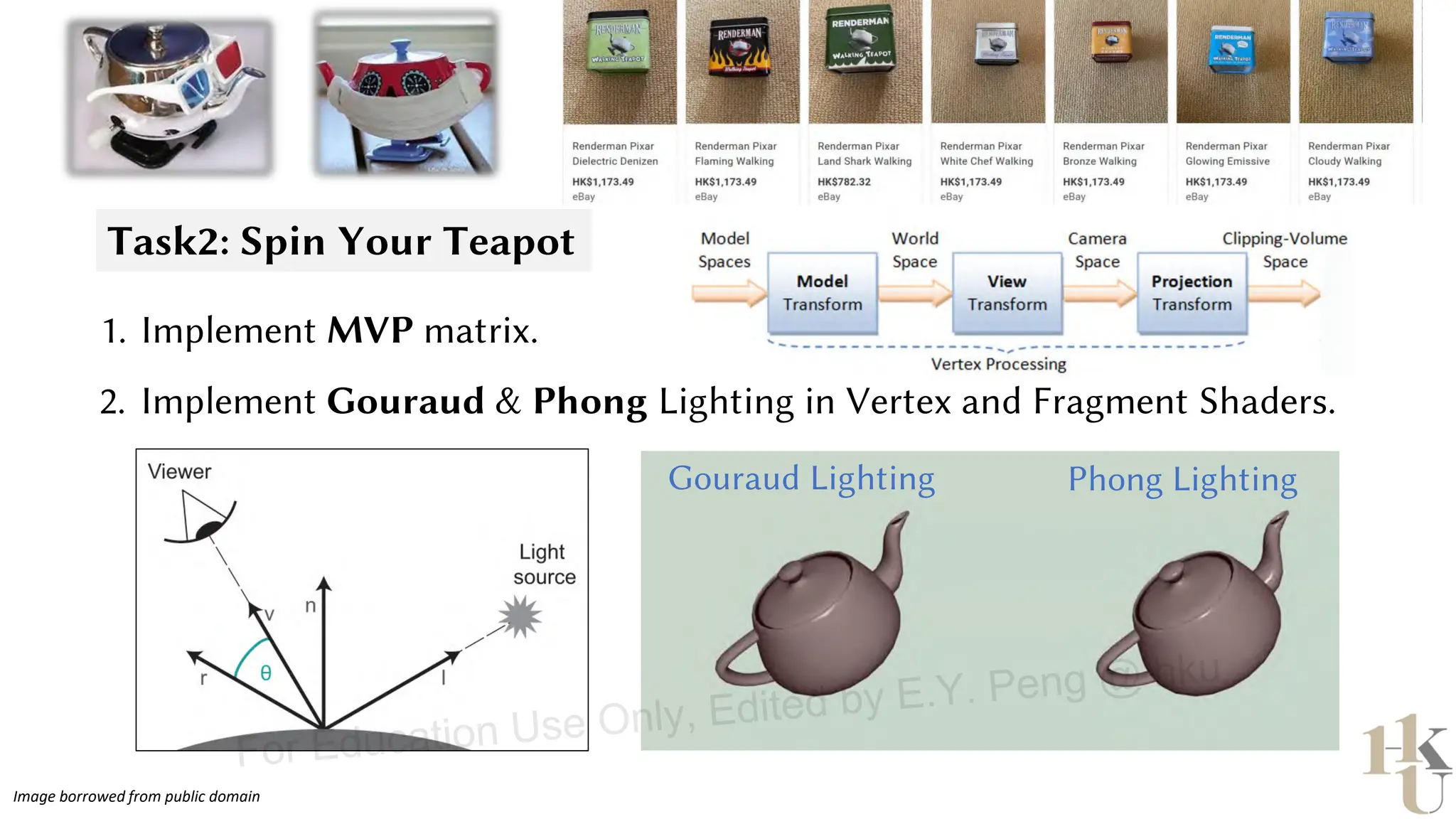
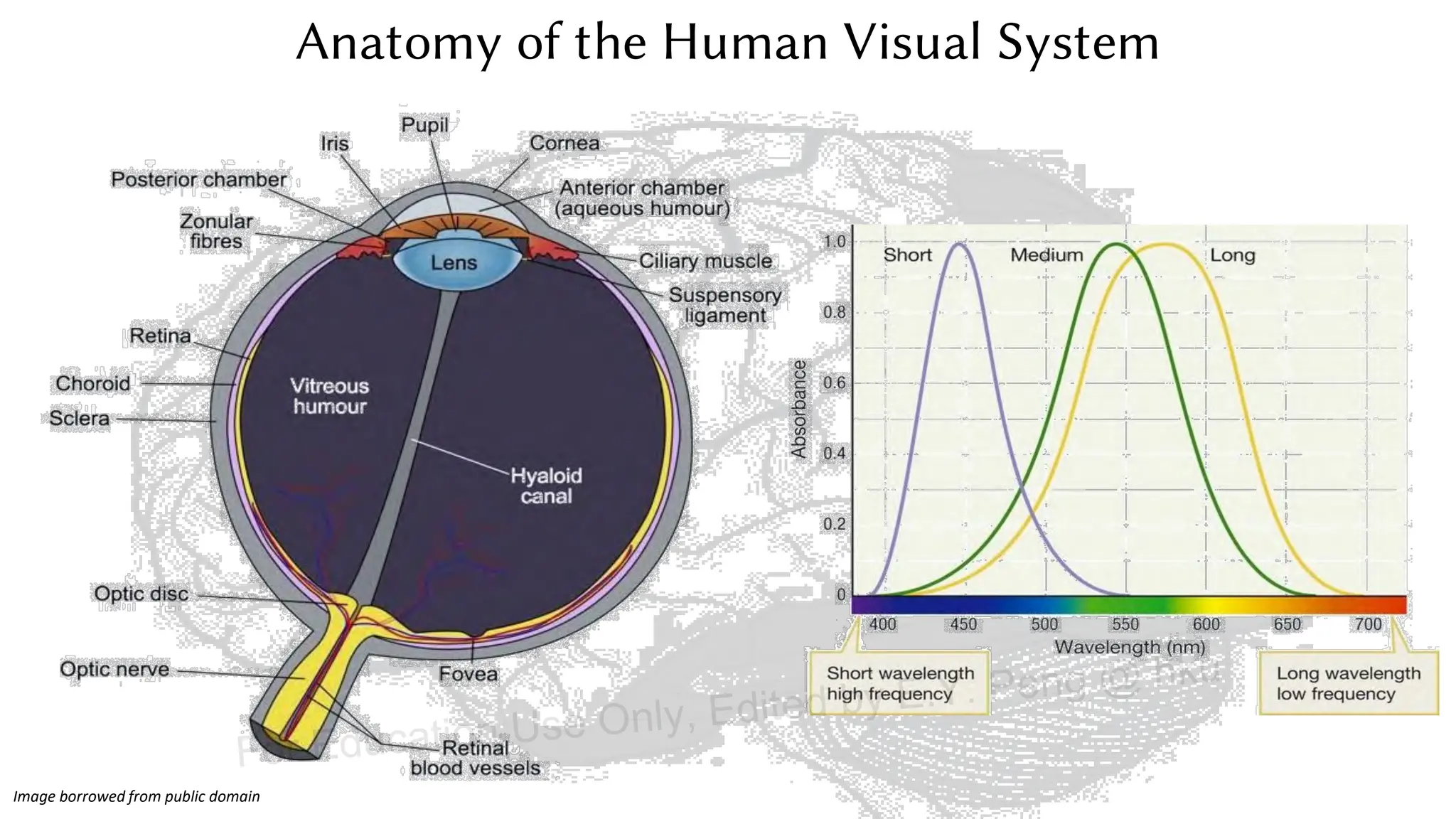
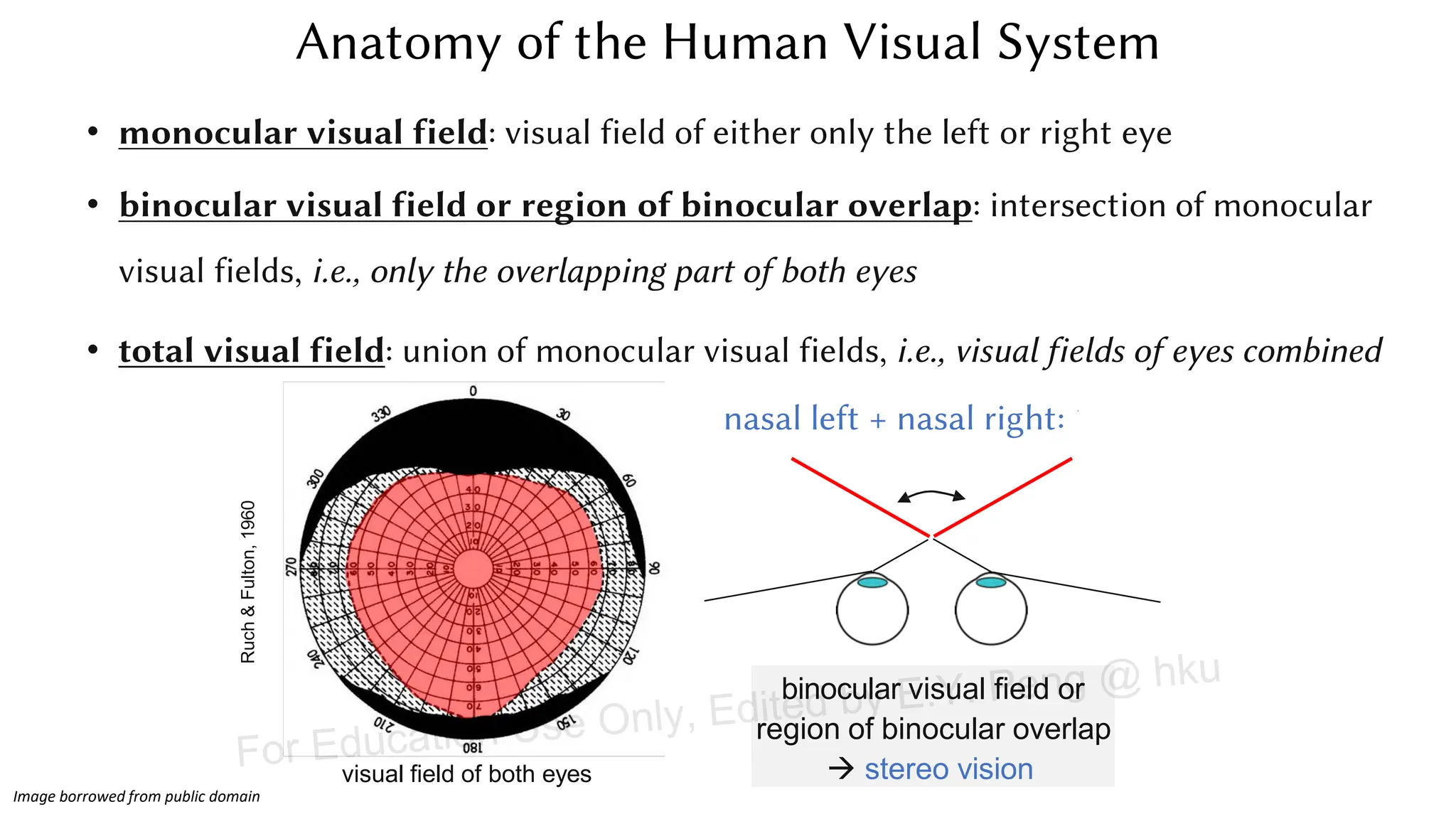
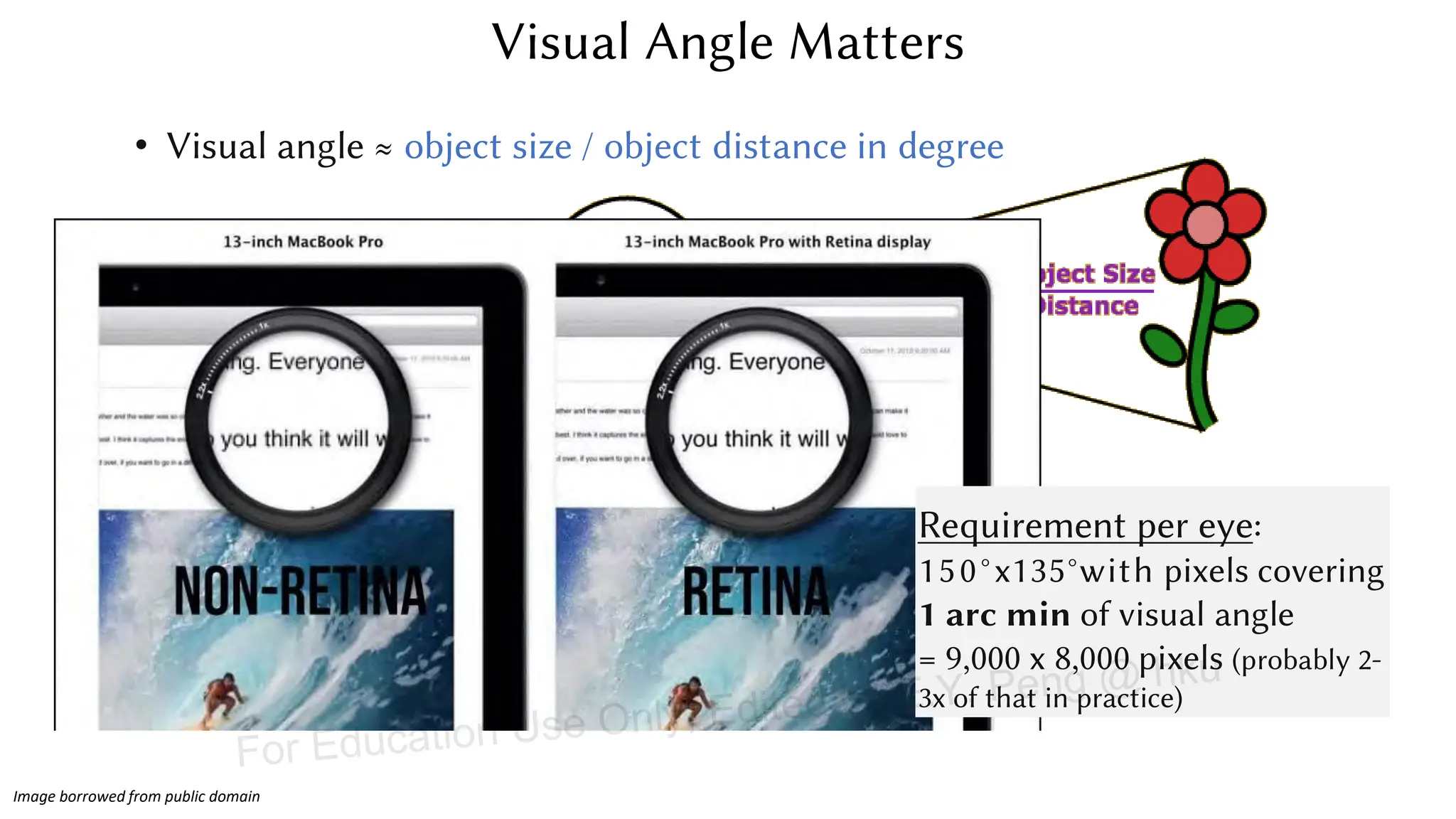
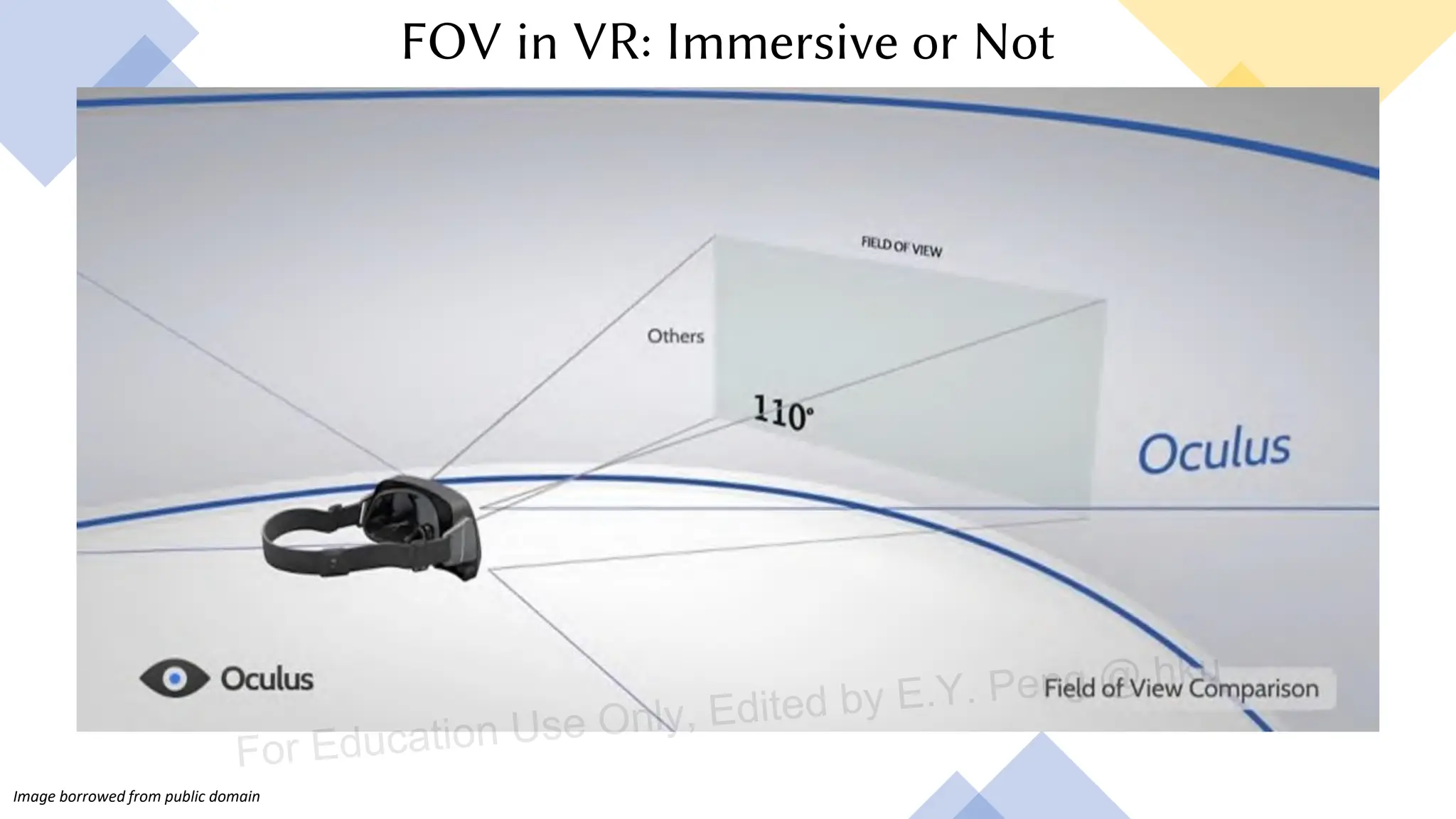
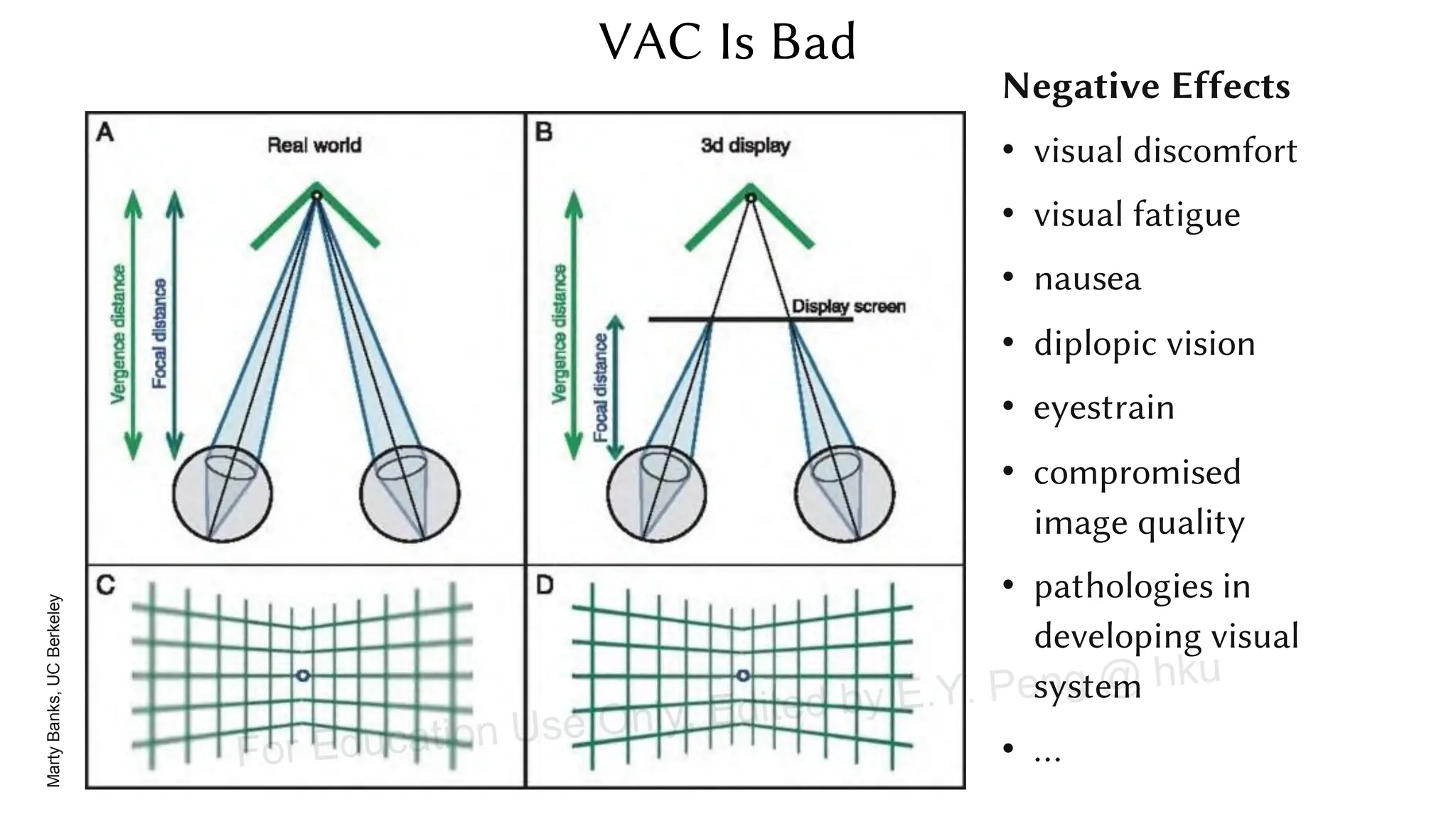
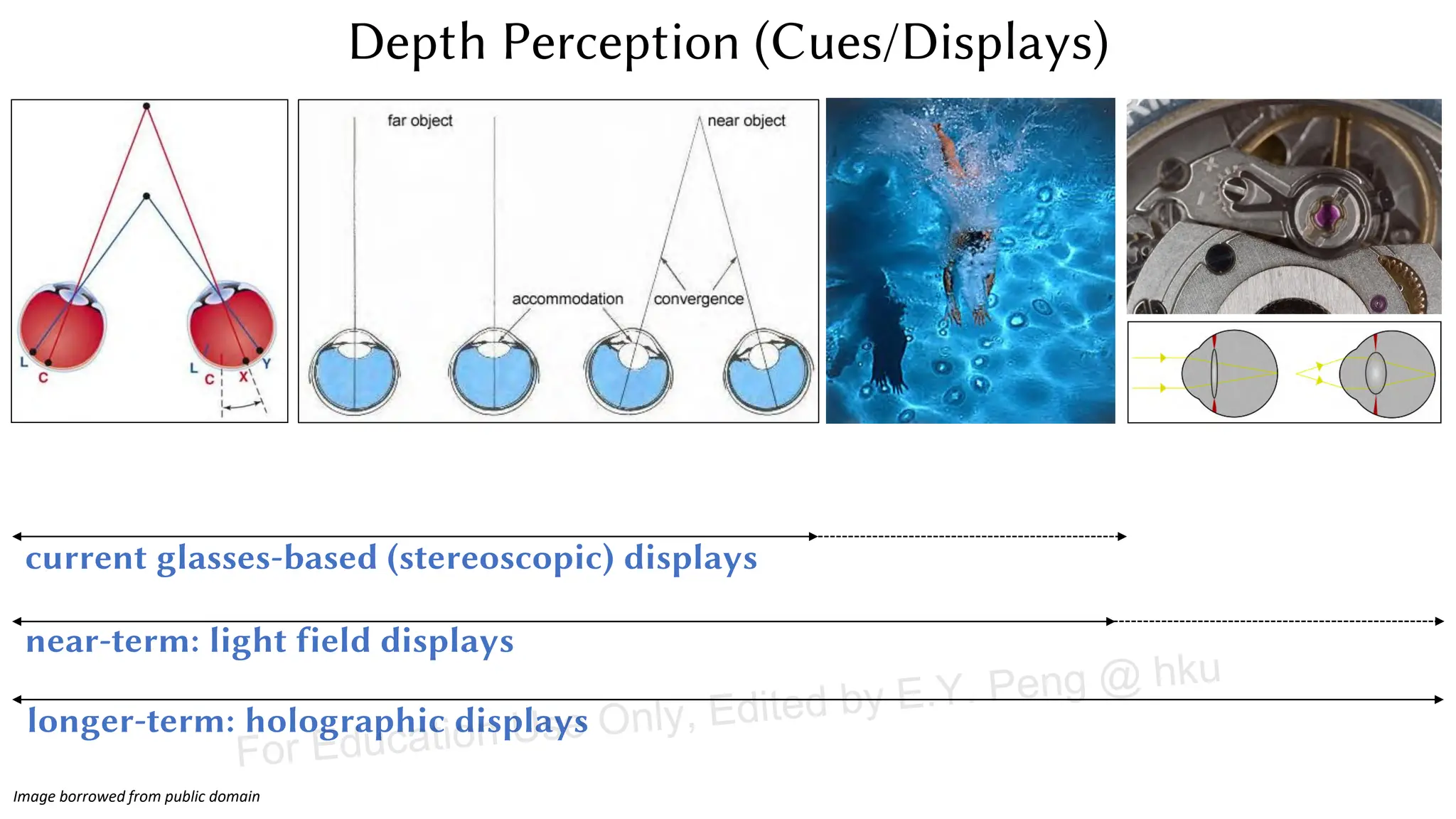
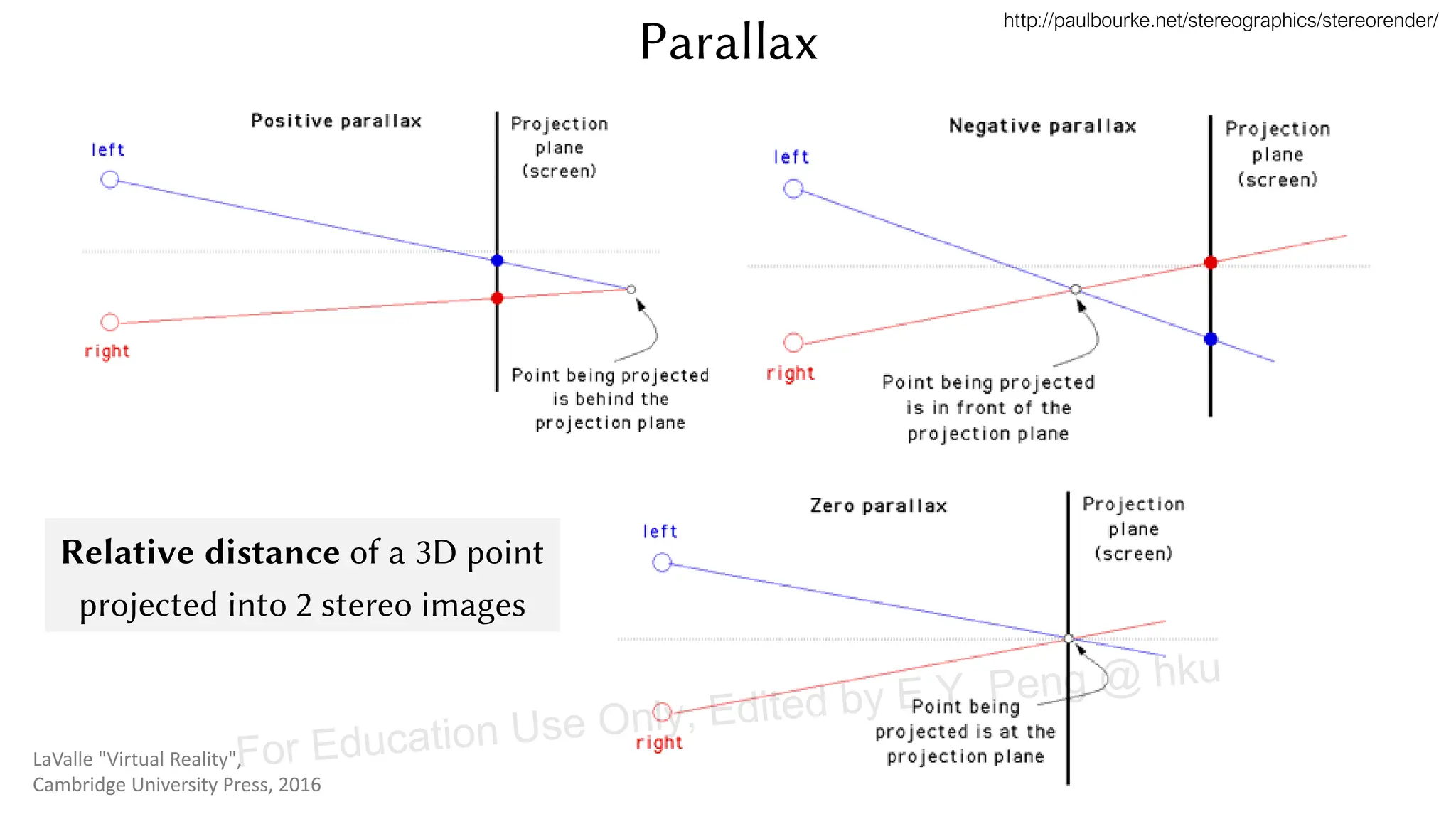
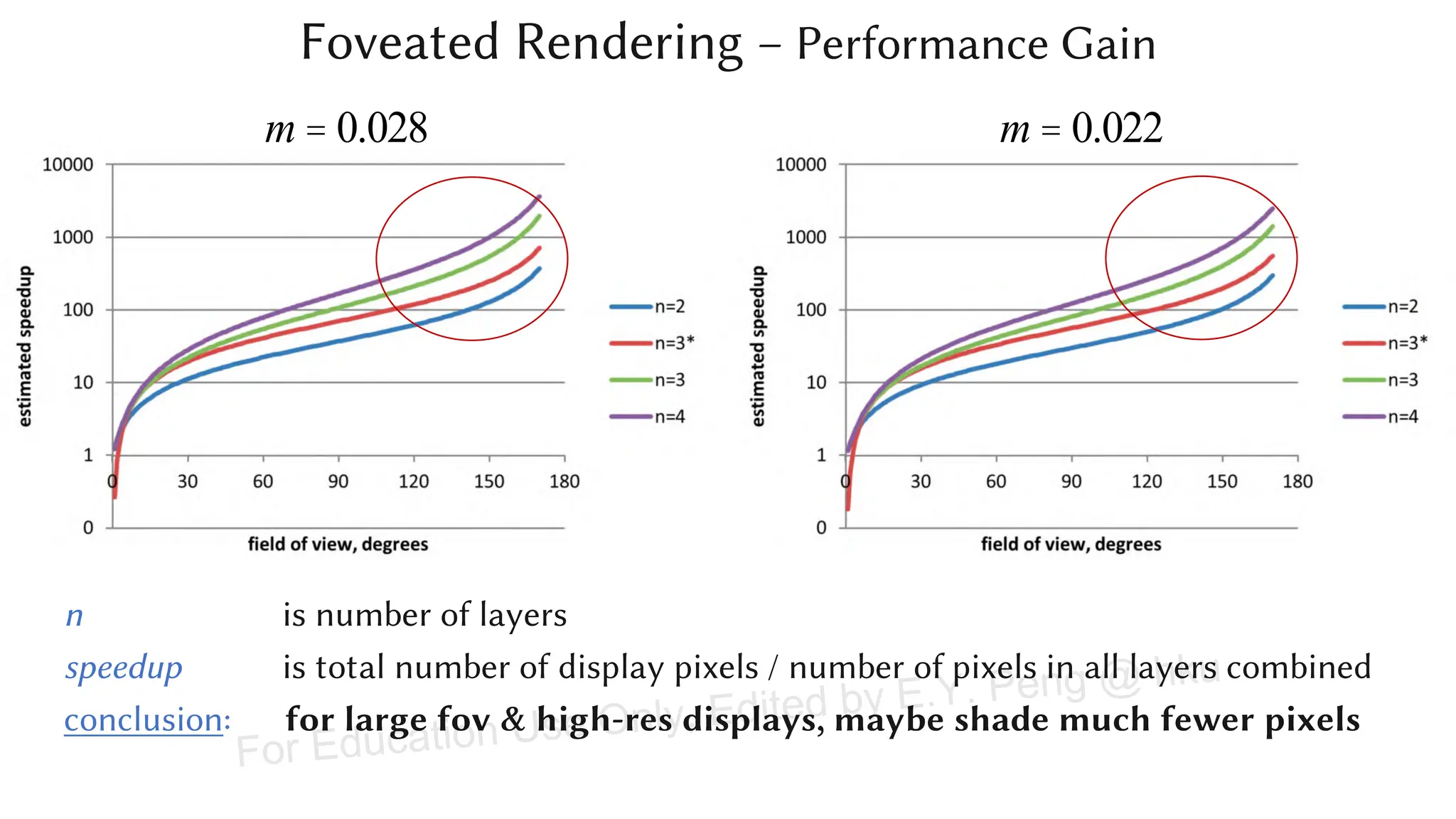
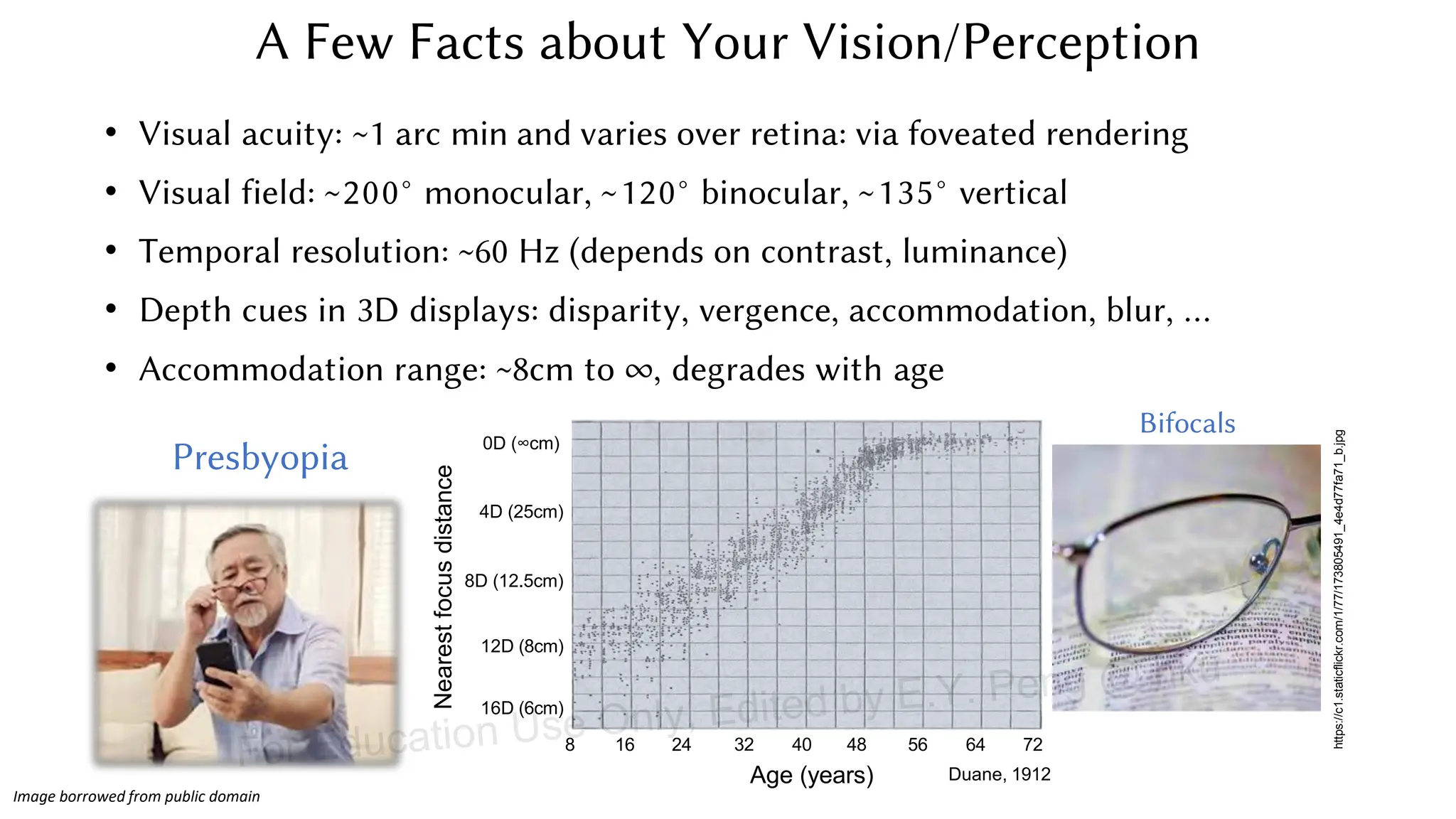
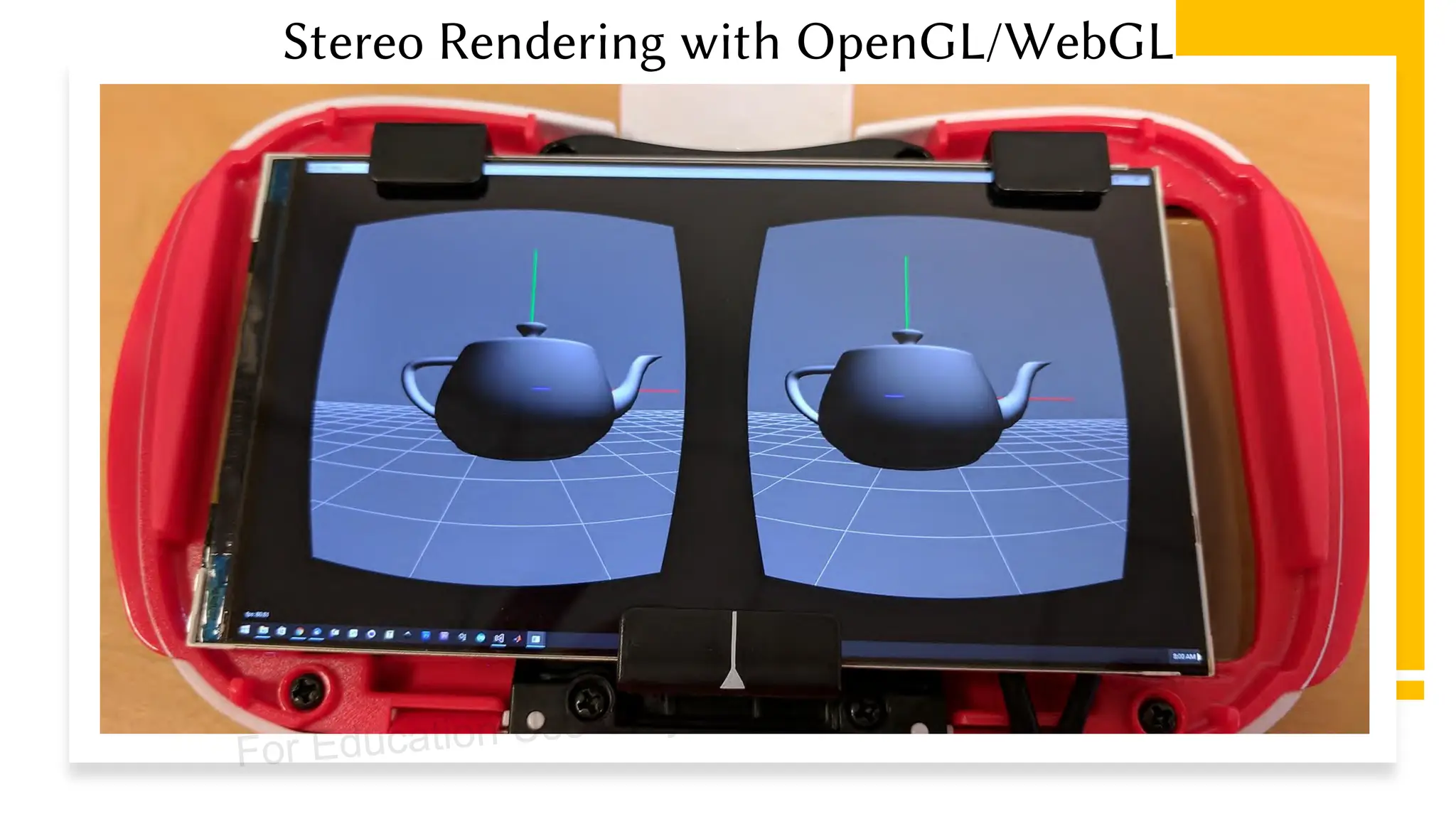
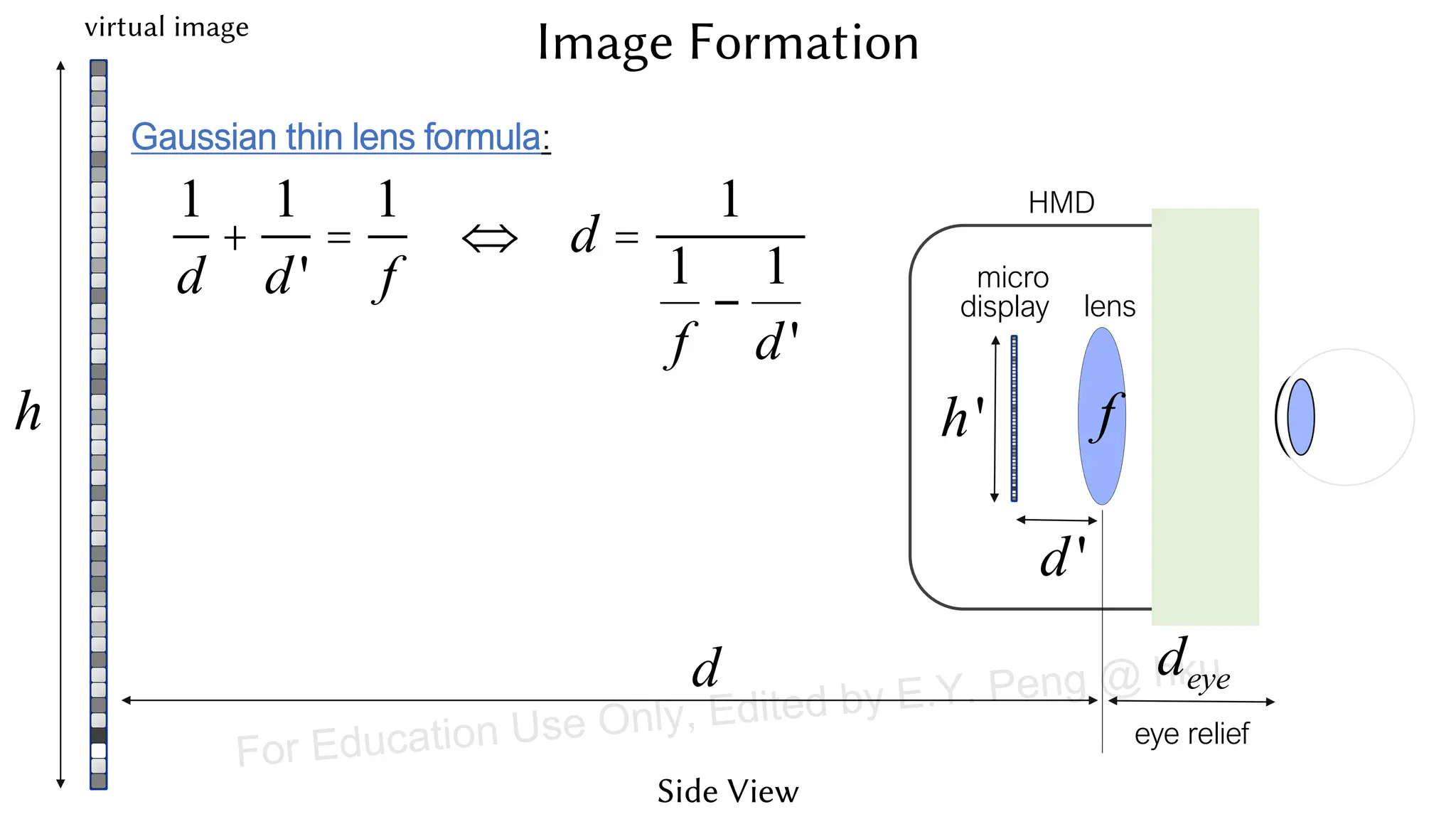
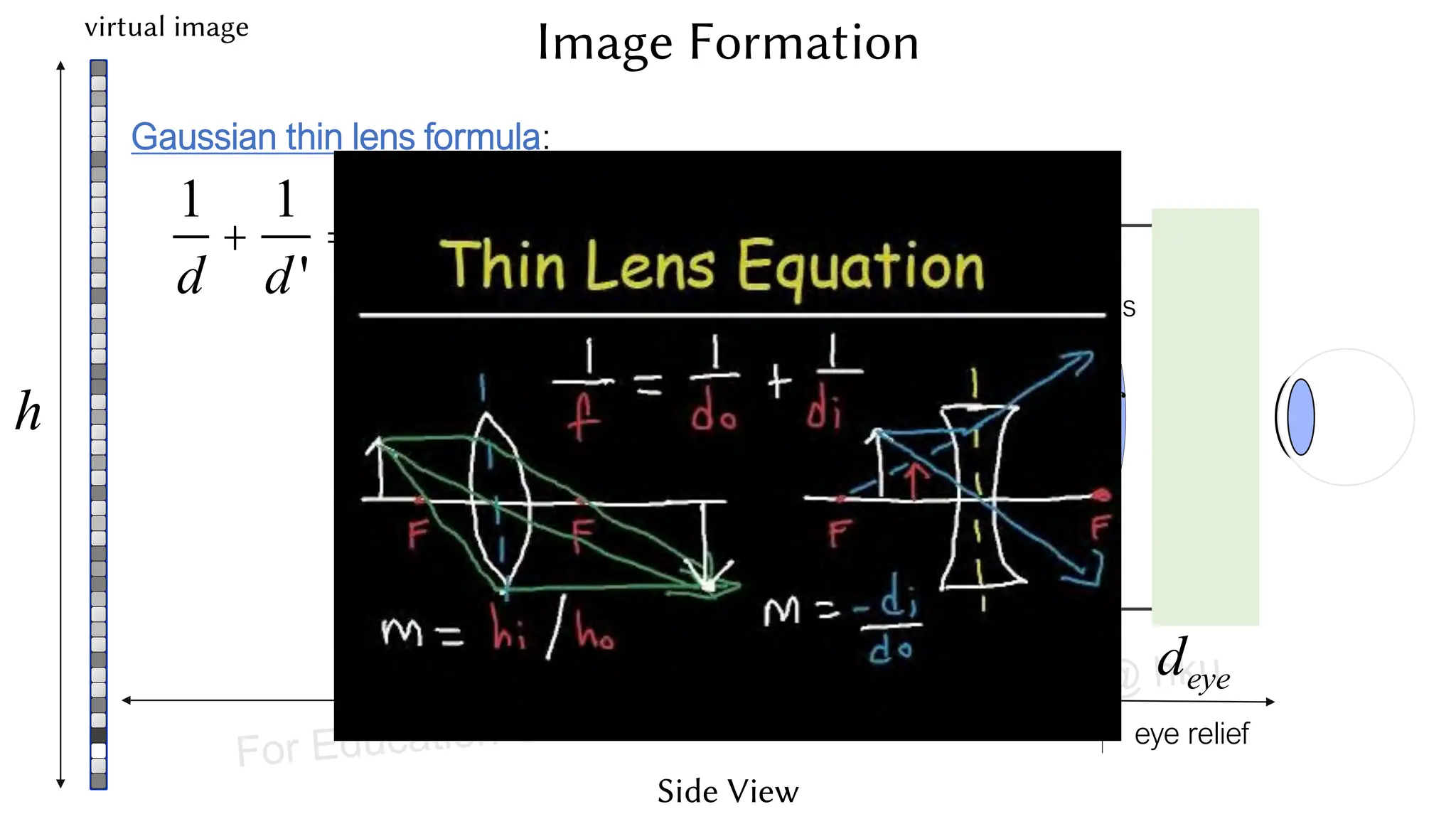
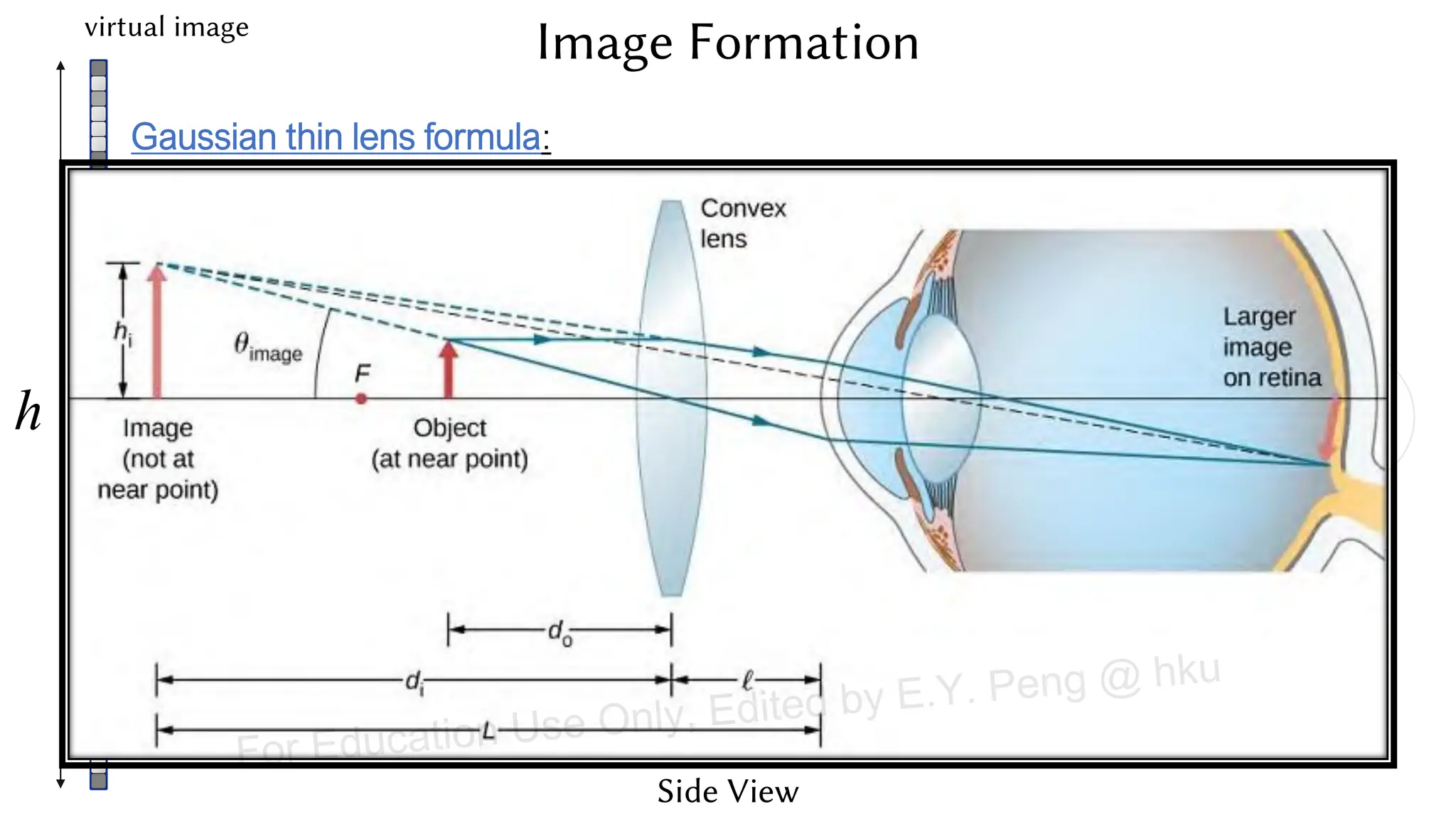
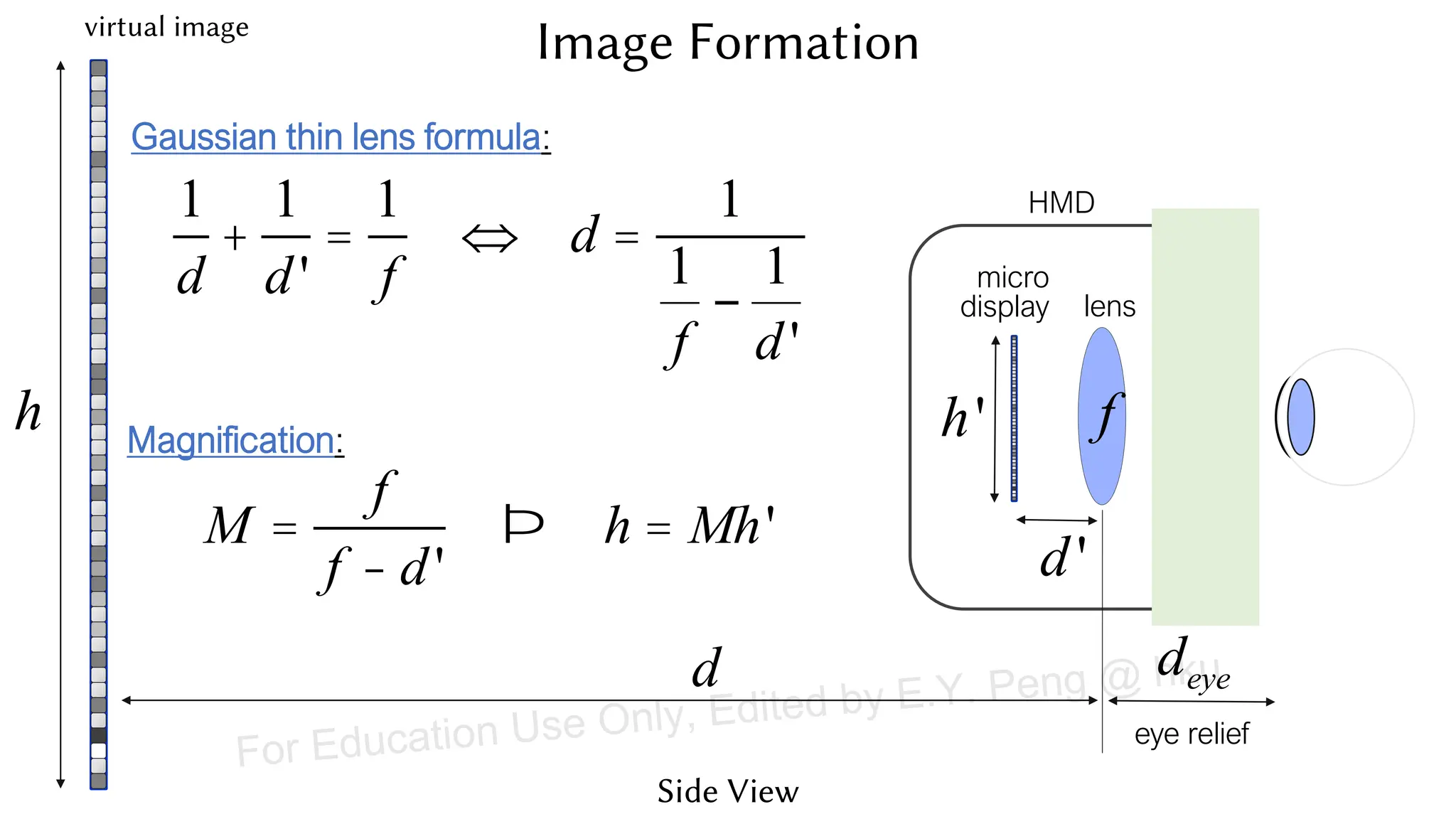
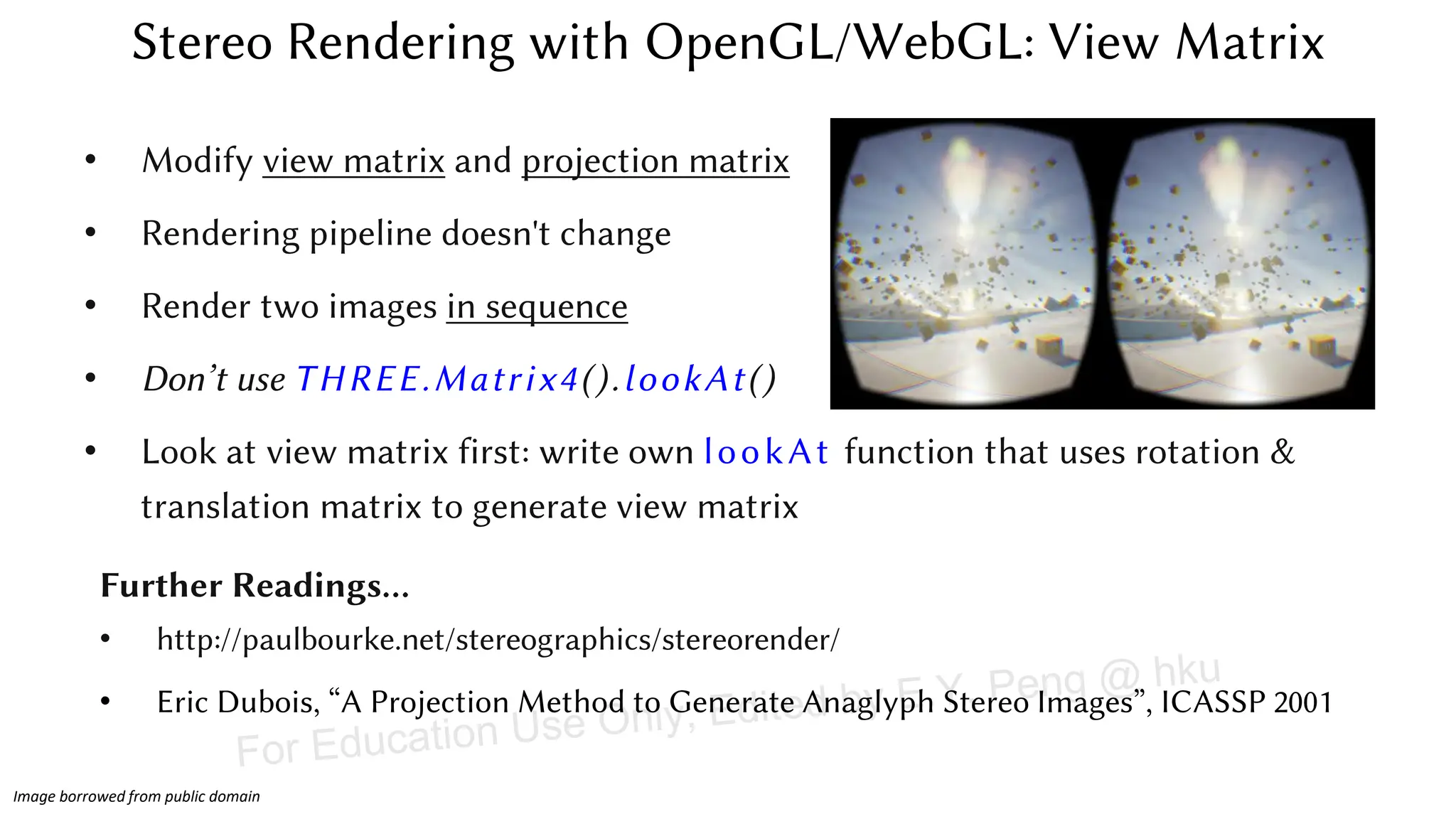
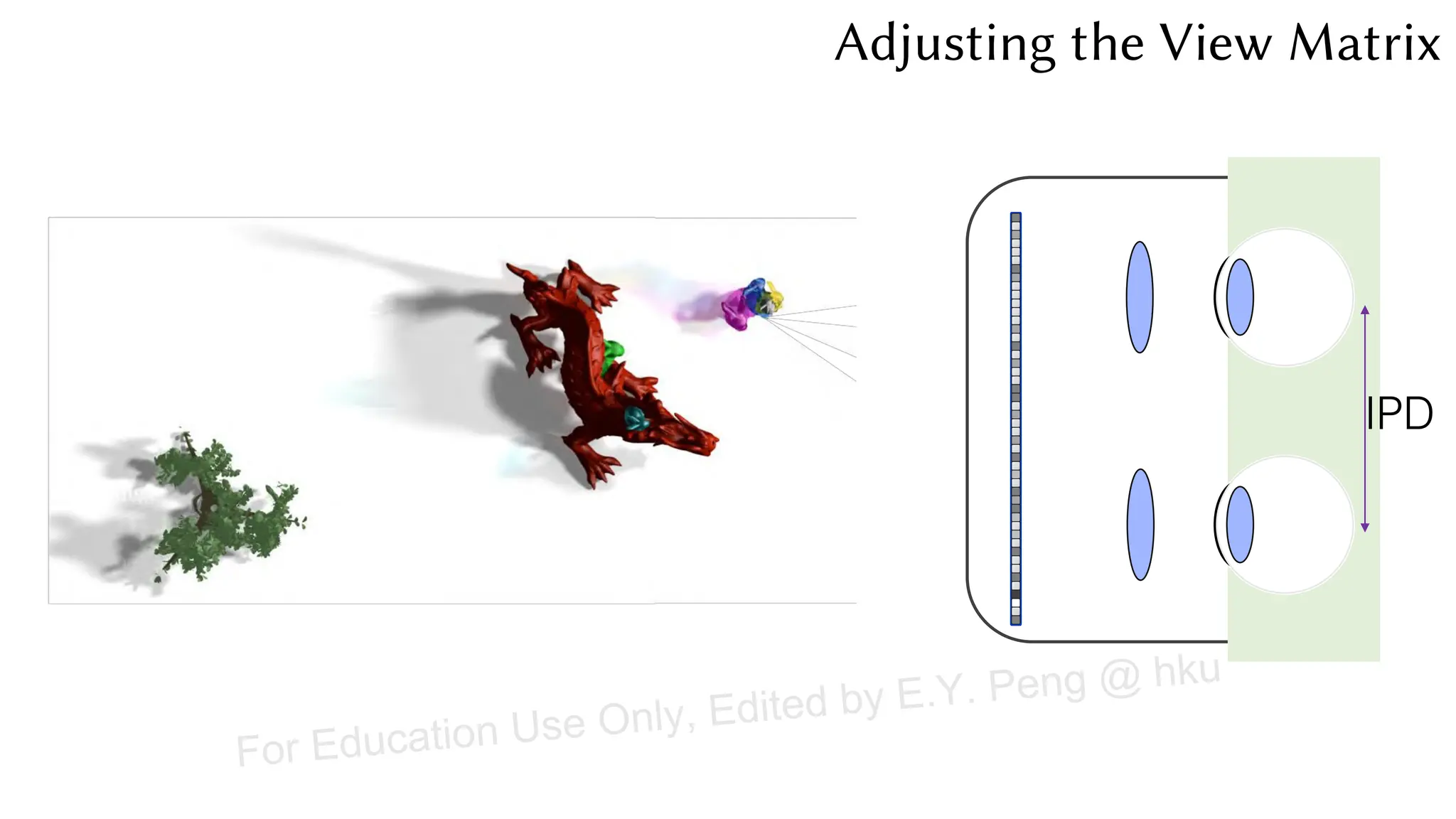
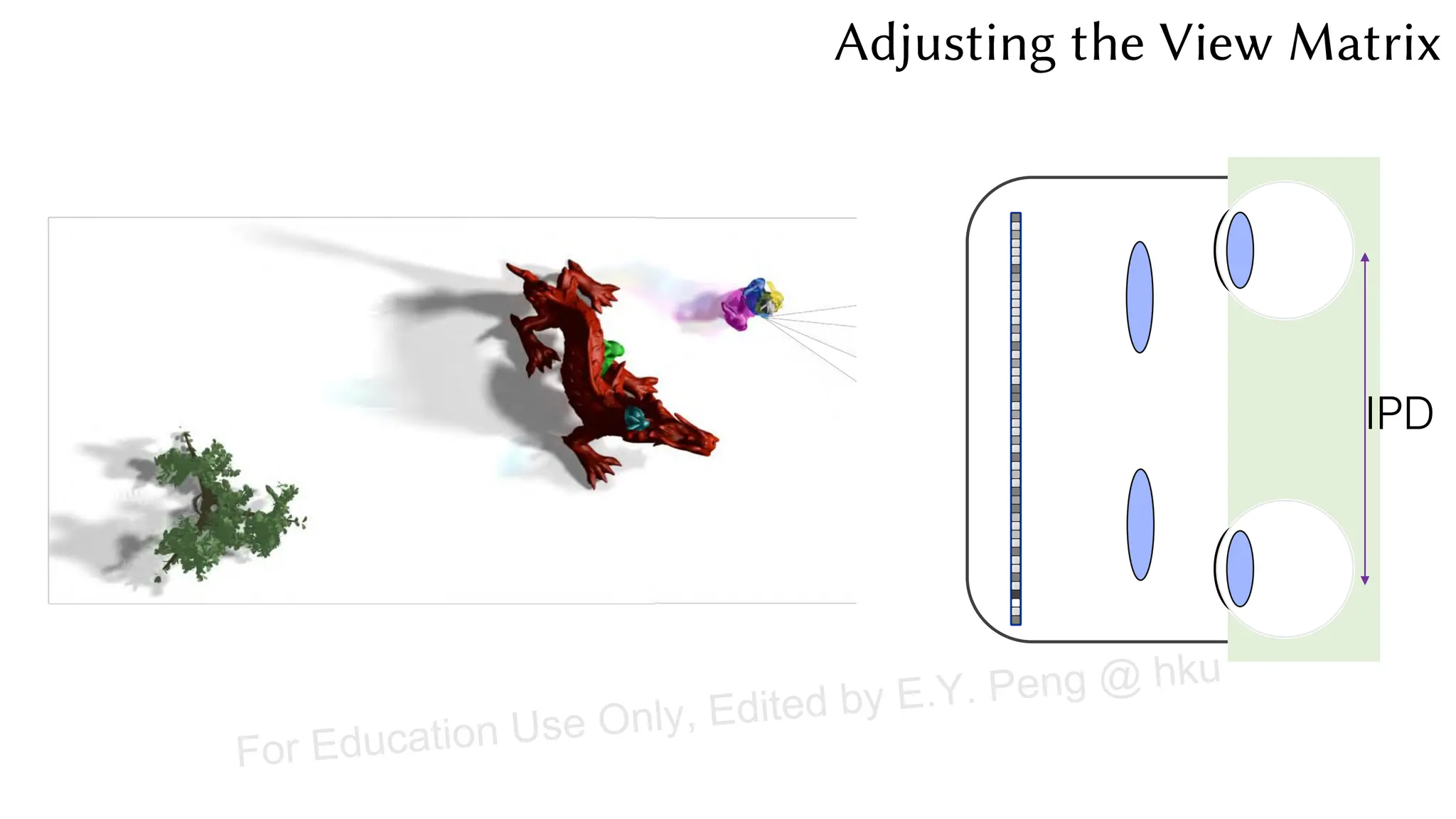
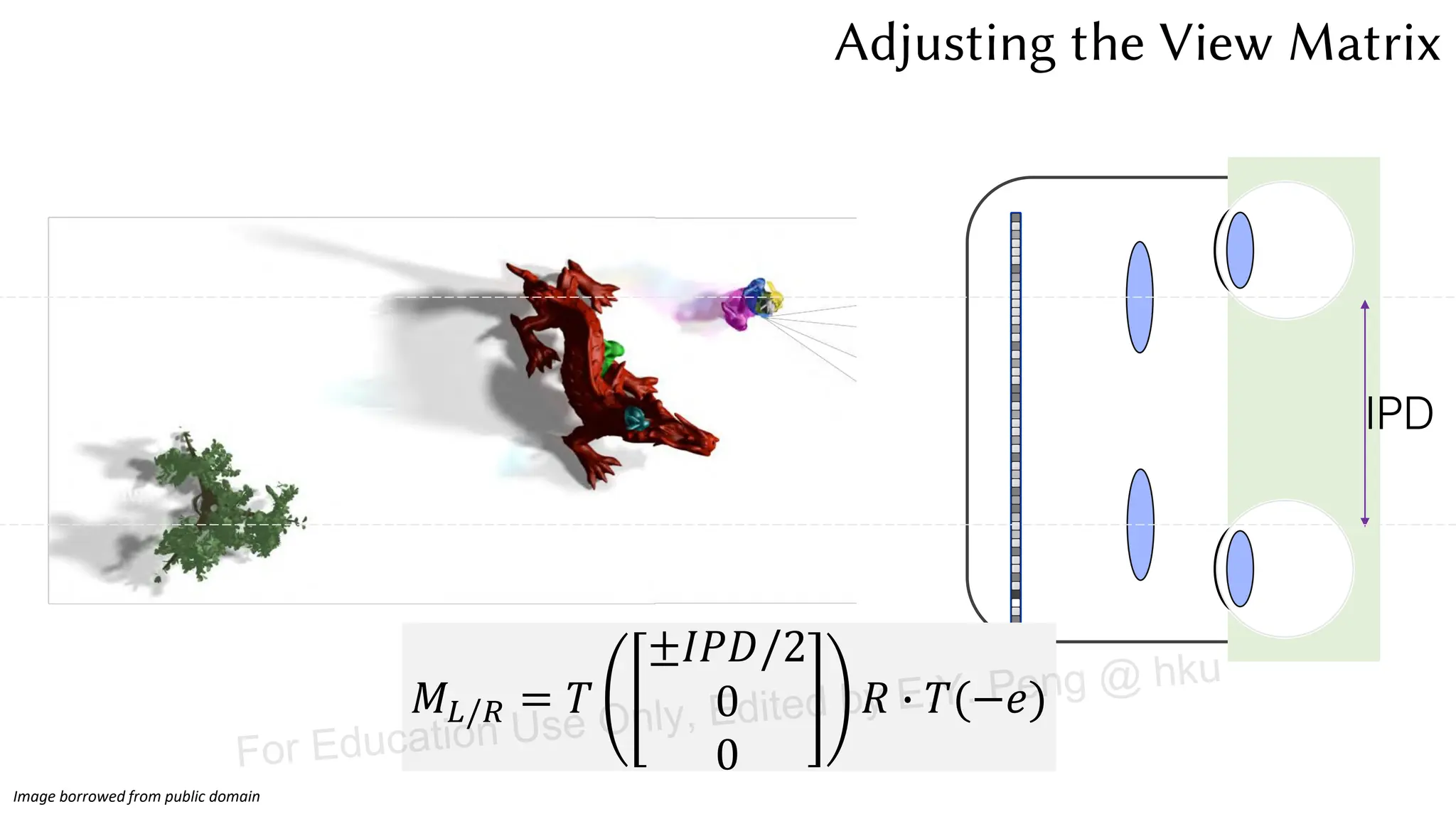
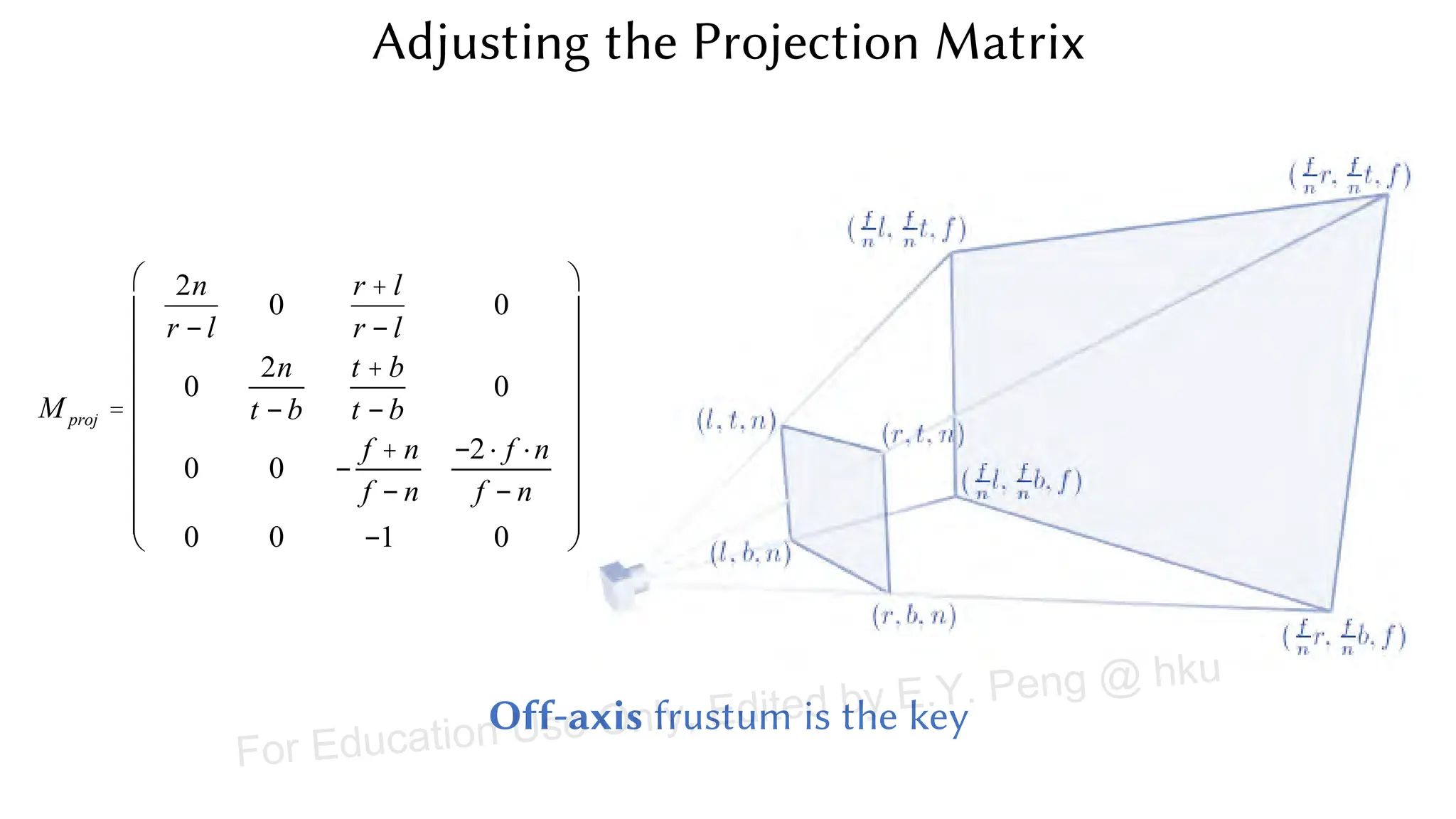
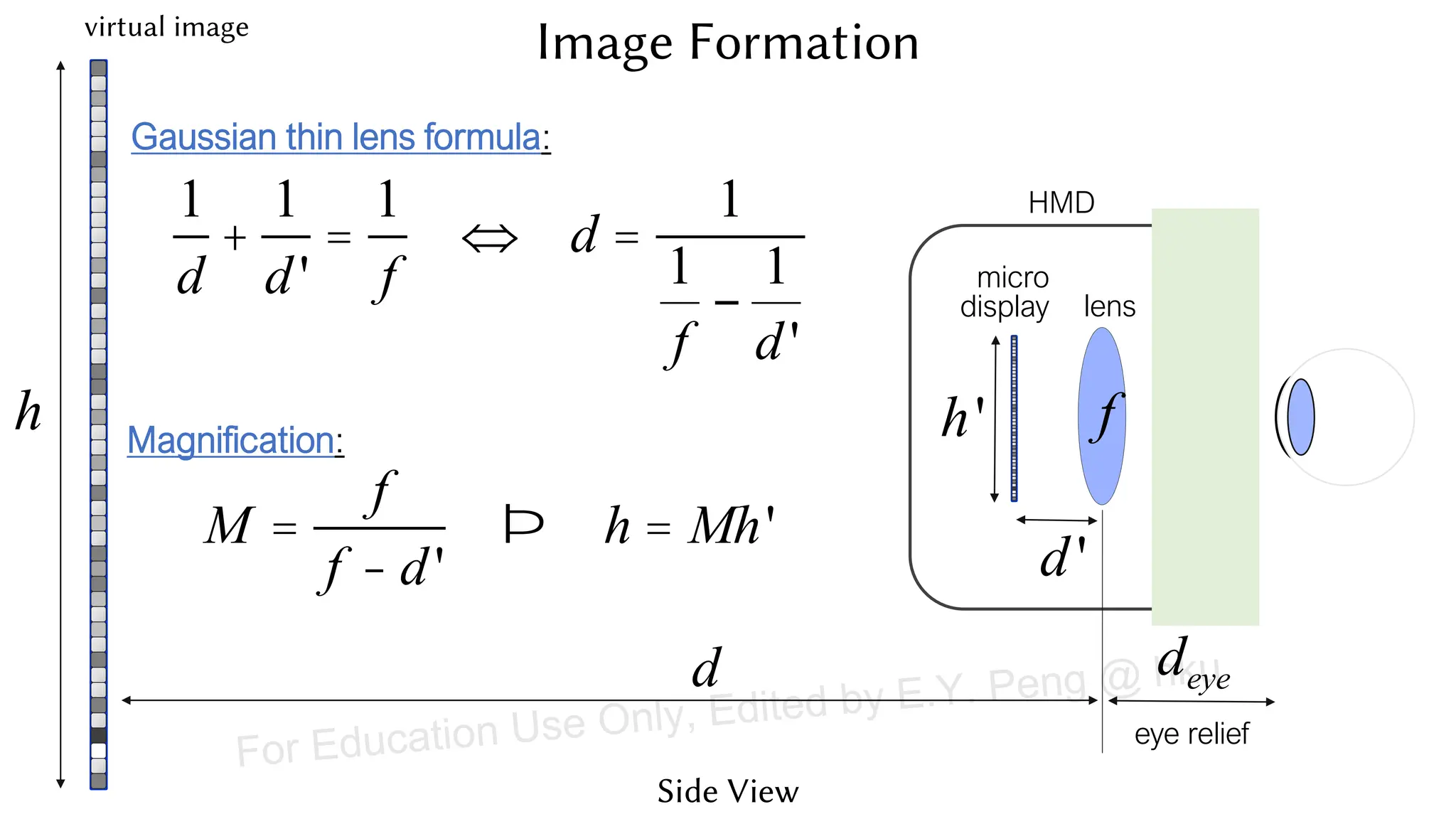
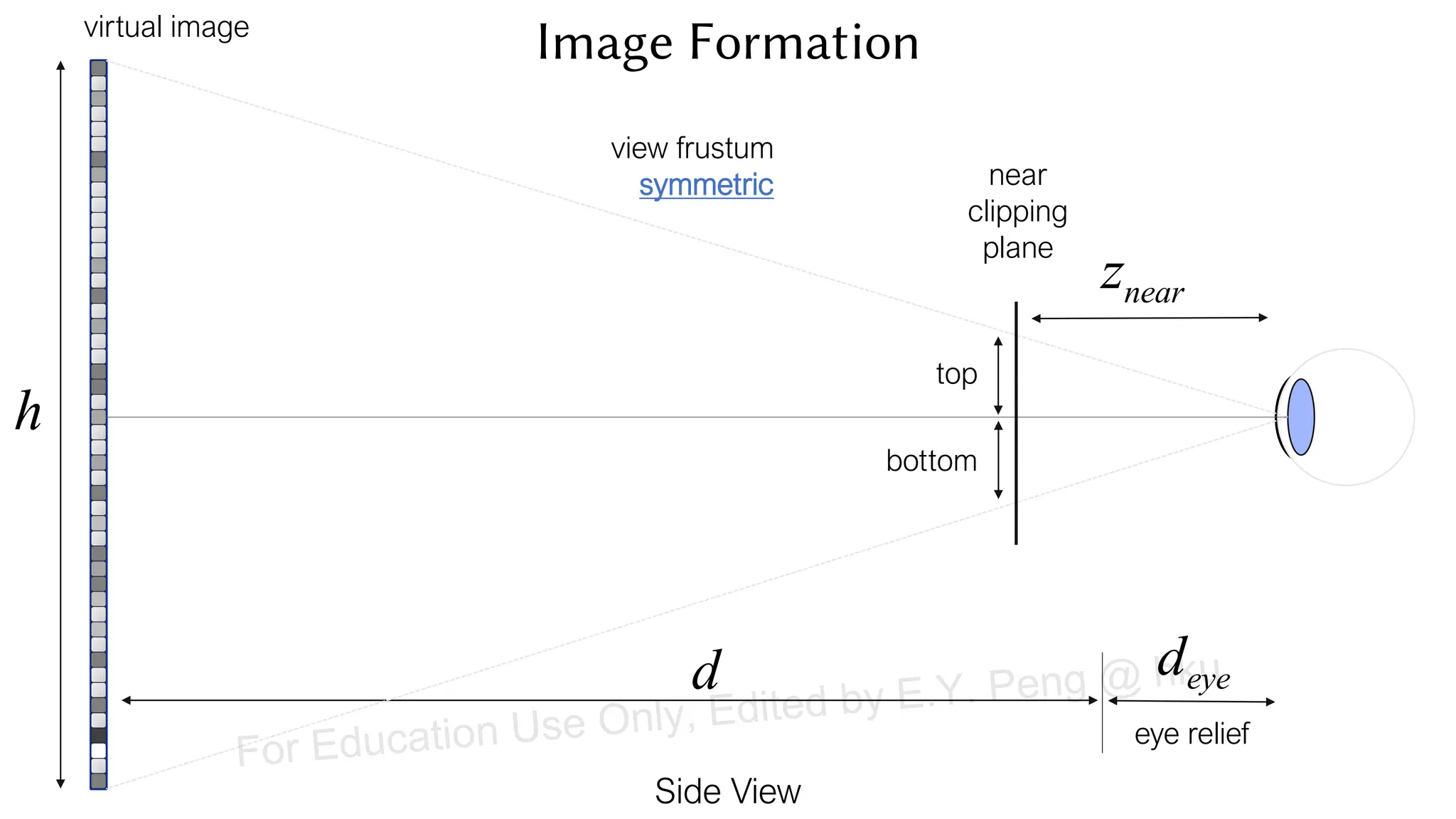
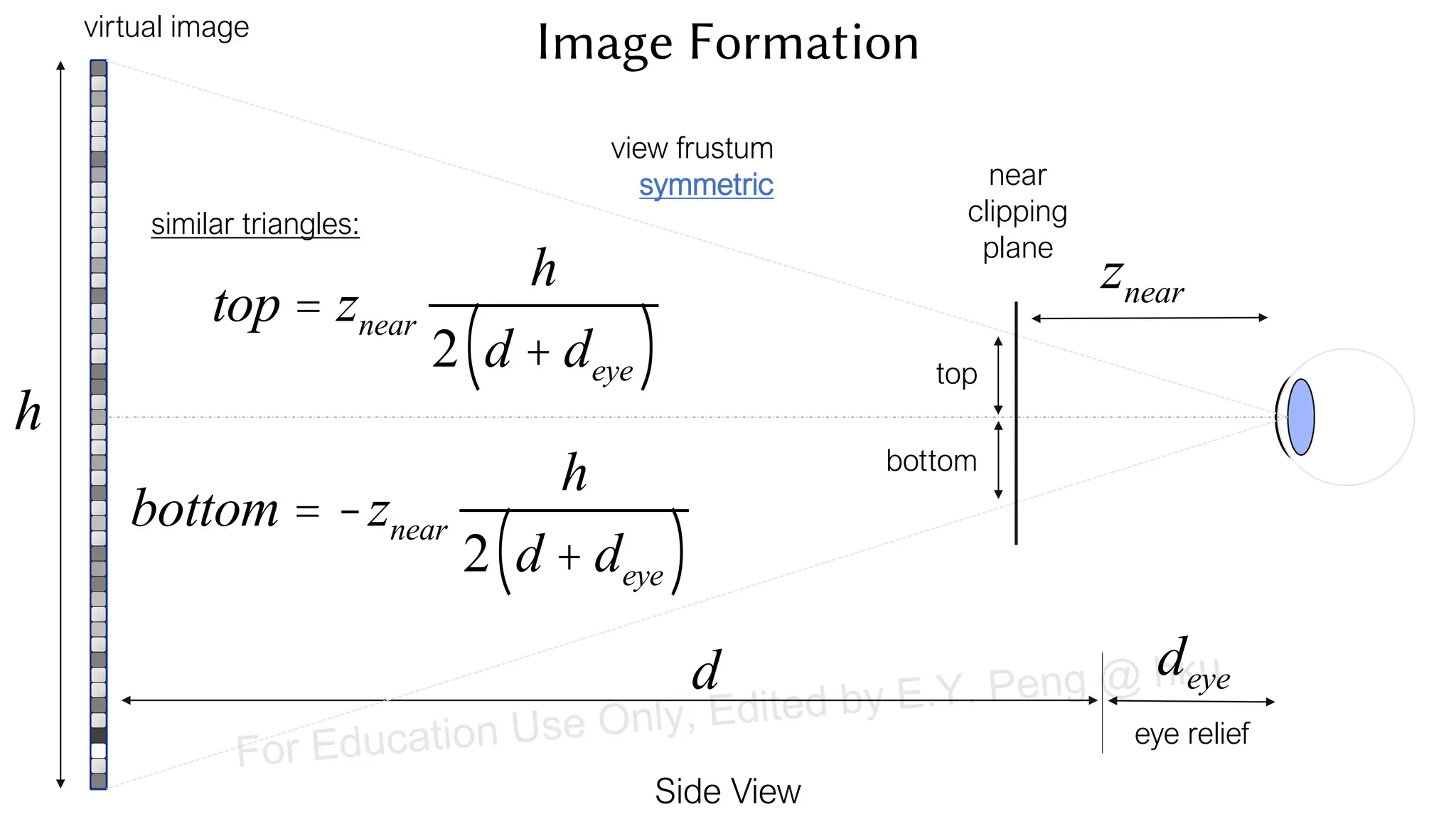
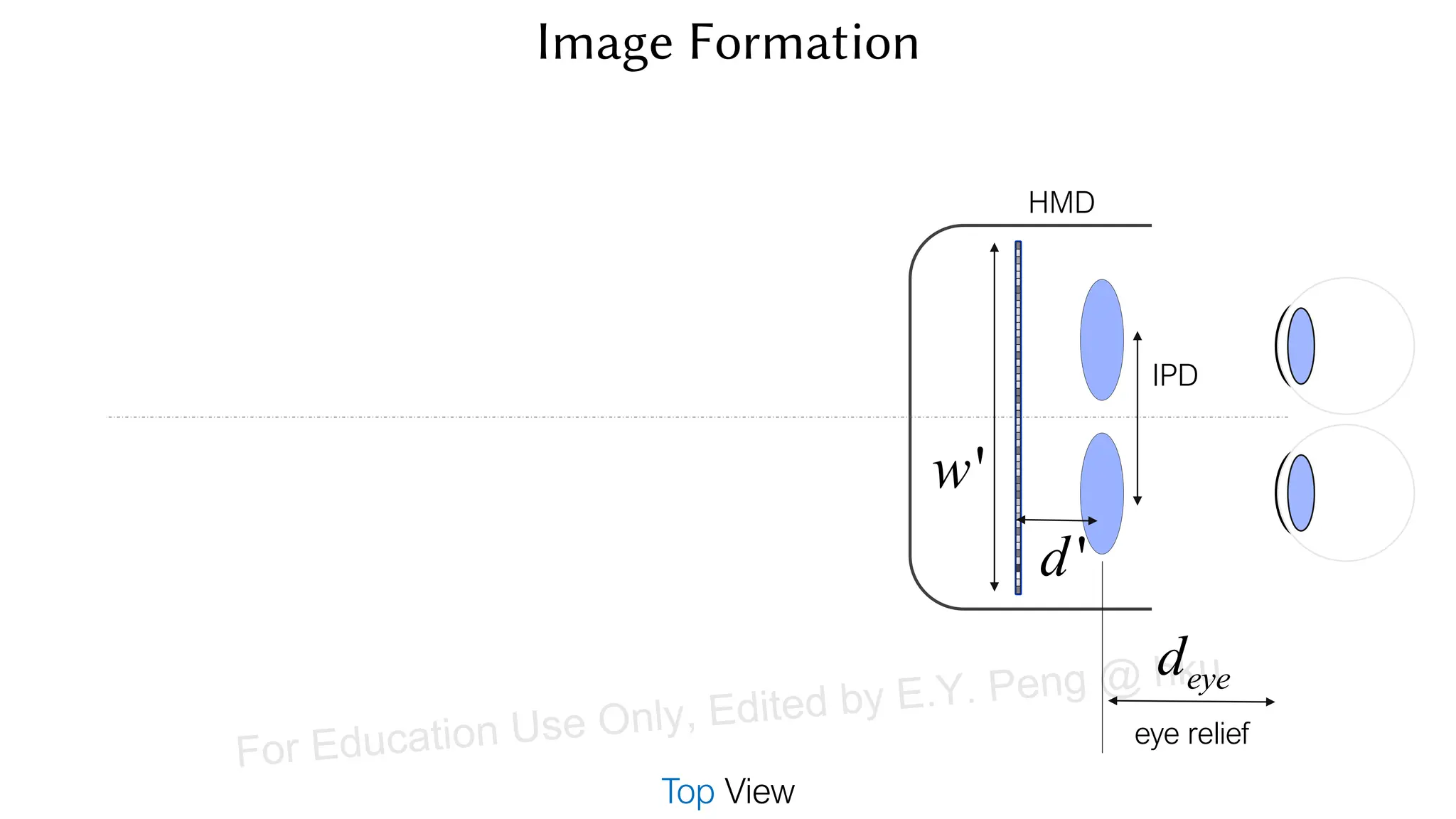
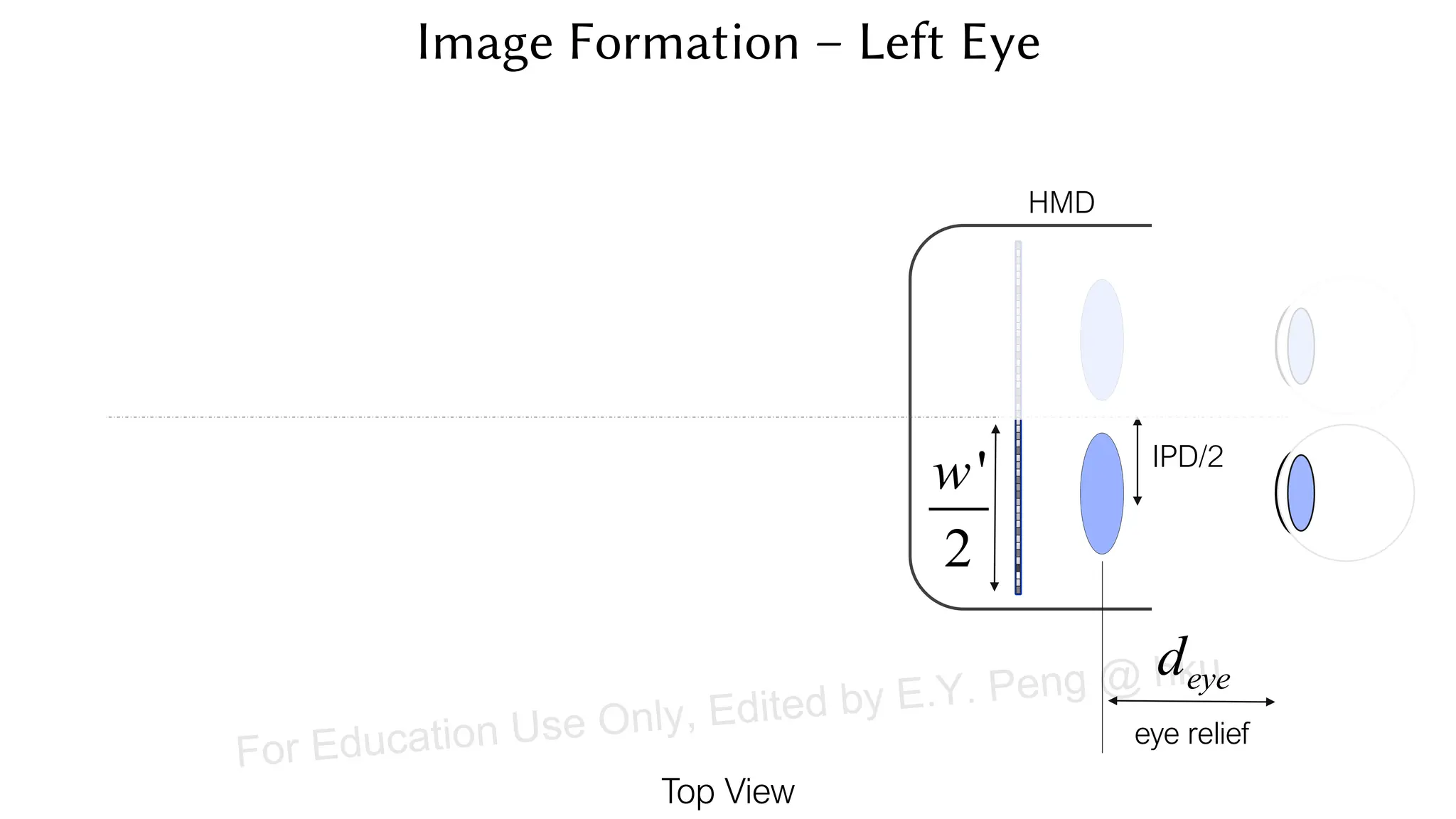
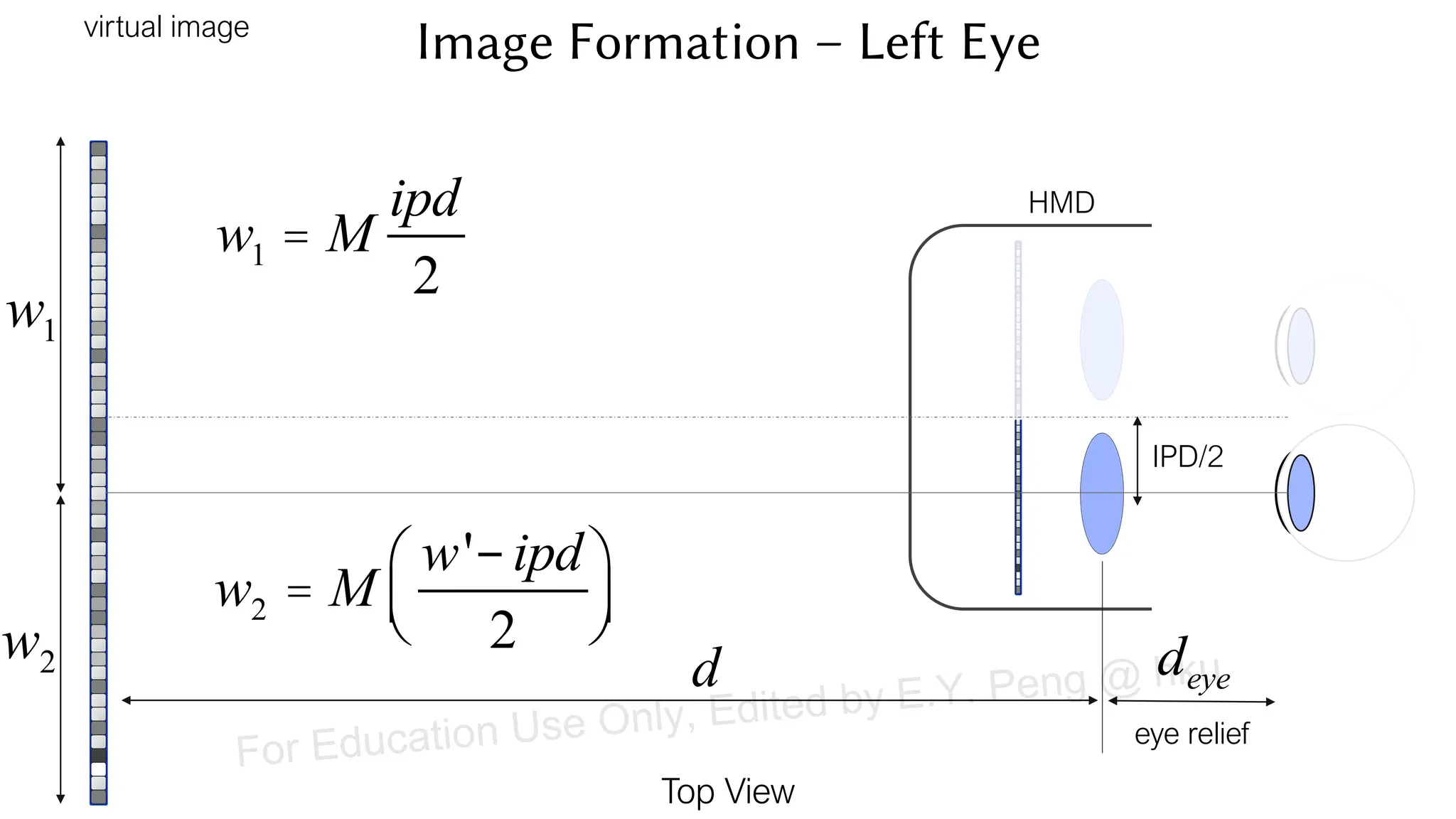
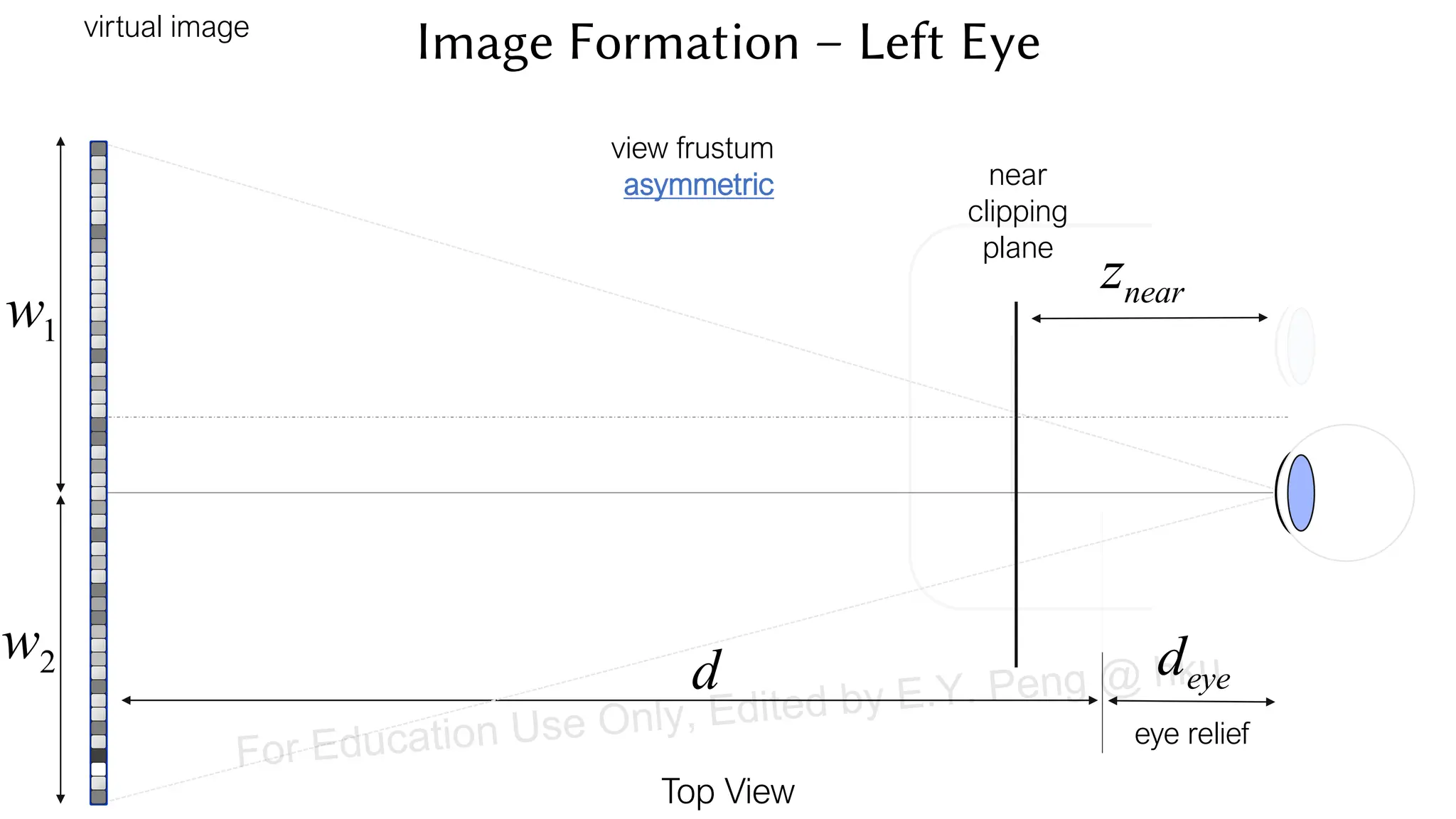
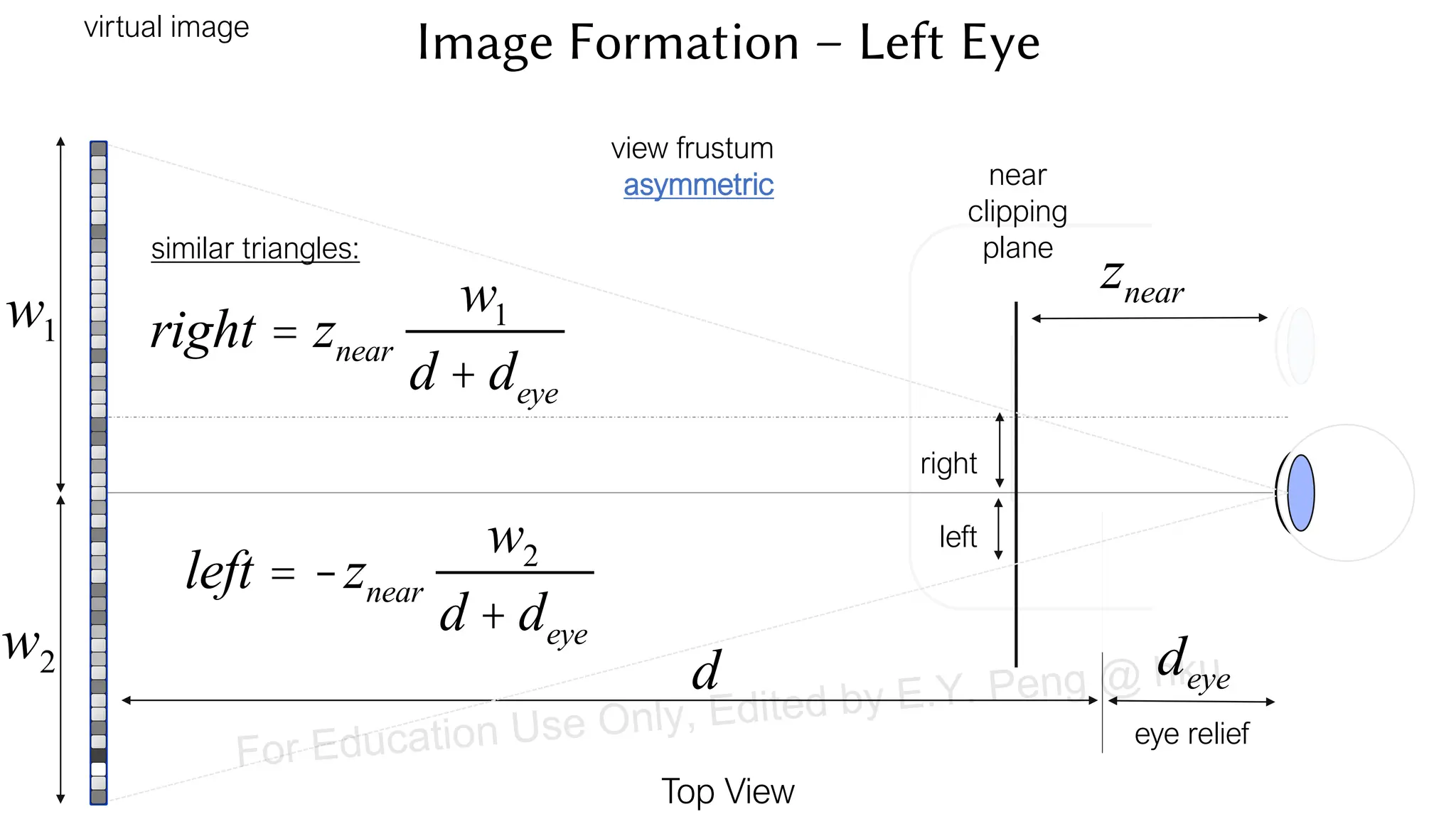
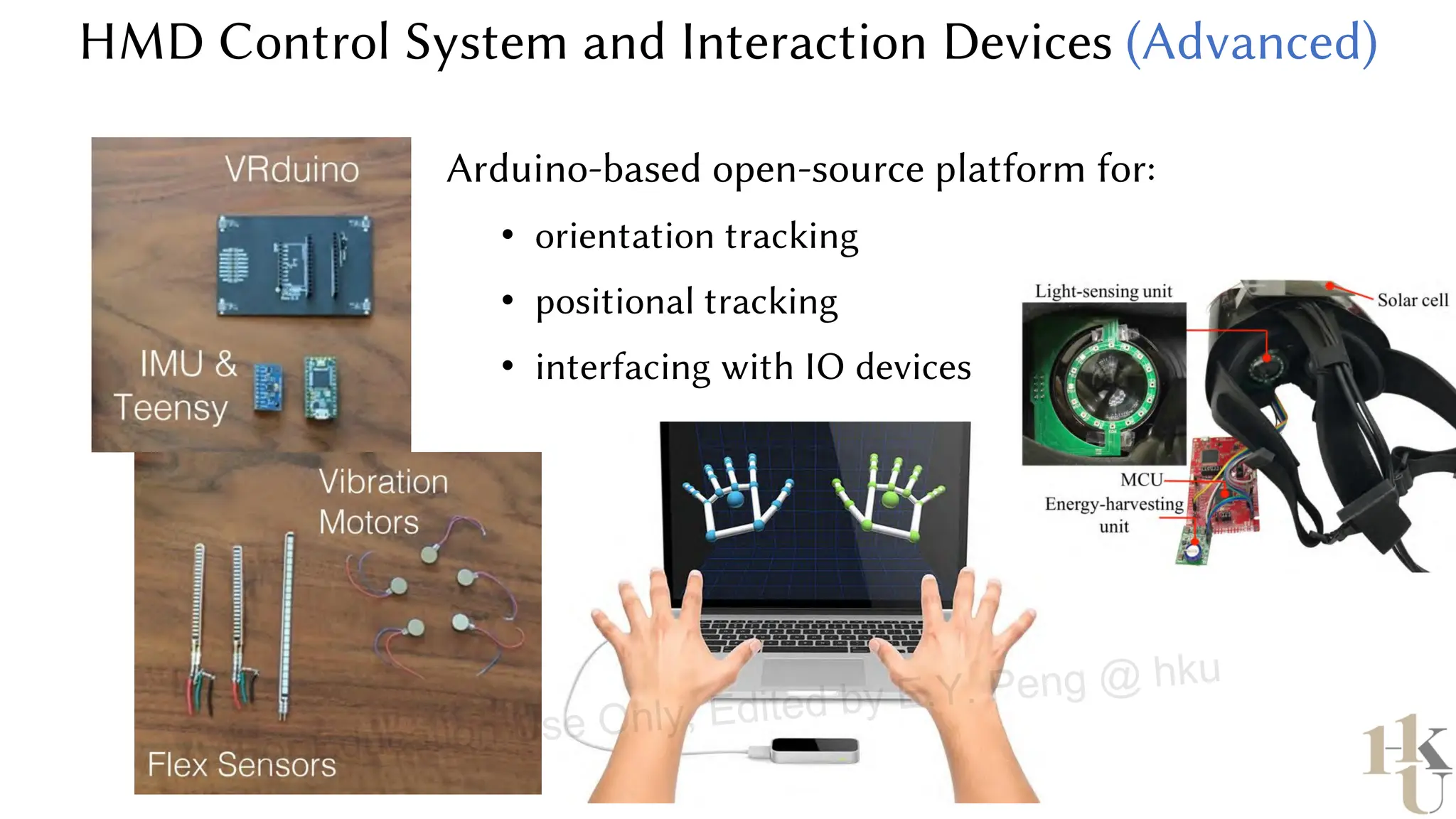
This document provides information about an emerging tech course on VR/AR. It includes the class schedule, assignments, instructor and TAs contact information. It also covers topics like the graphics pipeline, rendering equation, lighting and shading models, texture mapping, OpenGL and WebGL. Foveated rendering and facts about human vision are discussed. It provides documentation on stereo rendering for VR HMDs.
![Class Schedule
Thursday 13:30-16:15 [CPD 258]
Assignment 1 Due
Oct. 13, 2023
Project Proposal Due
Oct. 12, 2023
Late coursework submission would be
unfortunately suffering from penalty of
2% points deduction per day
Instructor
Dr. Evan Y. Peng @ EEExCS
CPD 258
evanpeng@hku.hk
Consultancy
By appointment via emails
Teaching Assistant
Wenbin Zhou @ EEE / CS
zhouwb@connect.hku.hk
Zhenyang Li @ EEE
lizy23@connect.hku.hk
For Education Use Only, Edited by E.Y. Peng @ hku](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/elec4547emergingtechvrarlecture4visionstereorendering2-240109122858-18de6727/75/ELEC4547_EmergingTechVRAR_Lecture_4_vision_stereo_rendering-2-pdf-2-2048.jpg)