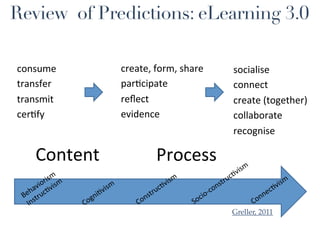
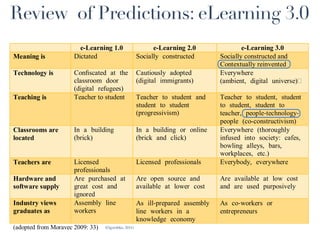
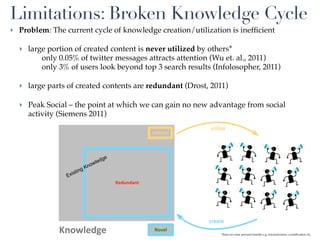
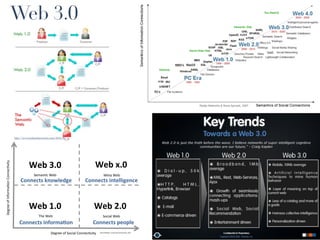
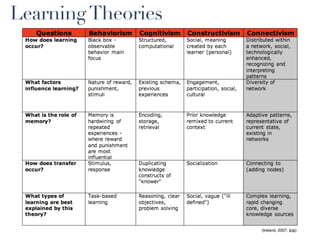
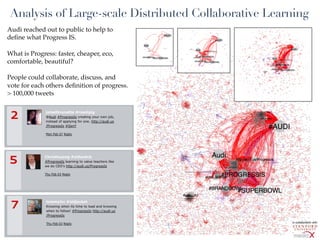
This document discusses the evolution of e-learning and predictions about the future of e-learning, referred to as e-learning 3.0. It begins by reviewing e-learning 1.0 and 2.0, noting how technologies and learning theories have progressed. Predictions for e-learning 3.0 include learning becoming contextual and personalized through intelligent technologies that are integrated everywhere. Challenges with current e-learning models are also discussed, such as information overload and an inefficient knowledge cycle. The document suggests artificial intelligence will play a larger role in e-learning 3.0 by helping address these challenges as data and computing resources increase.