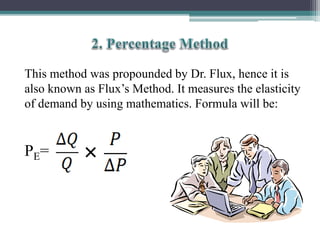
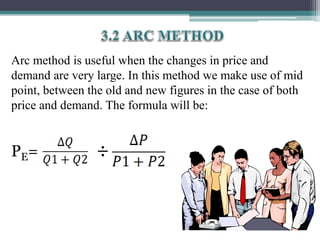
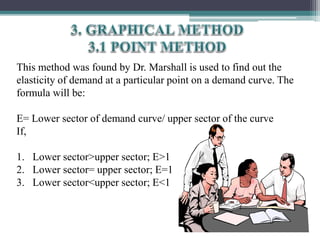
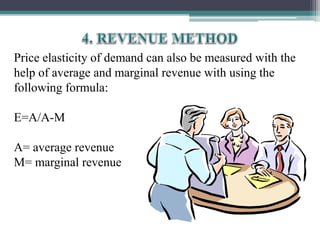
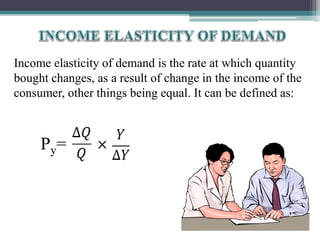
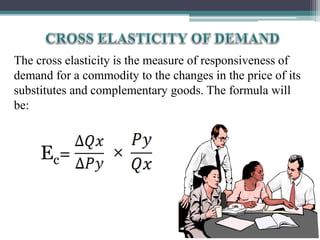
This document discusses different types of elasticity of demand, including price elasticity, income elasticity, and cross elasticity. It defines each type of elasticity using formulas and provides examples of goods that have perfectly elastic, inelastic, or unitary elastic demand. Methods for calculating elasticity are also presented, such as the total expenditure method, percentage method, and arc method. Factors that influence elasticity include the nature and substitutability of the good, uses, prices, habits, budget, and classes of buyers.