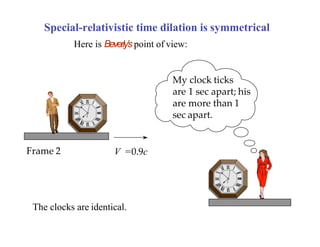
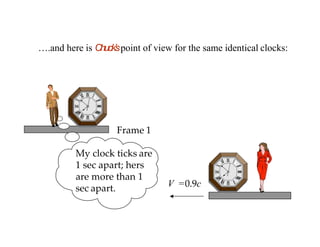
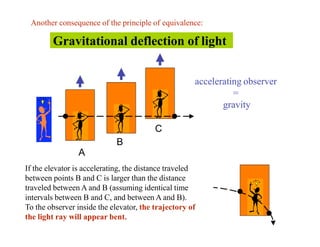
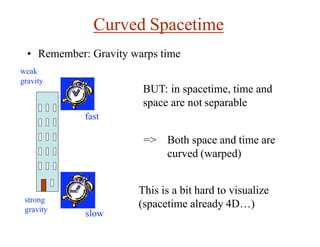
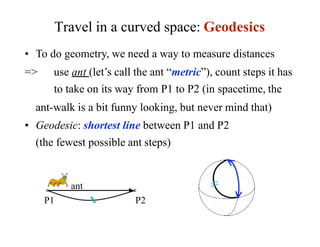
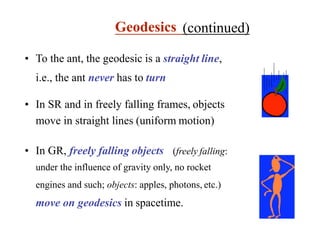
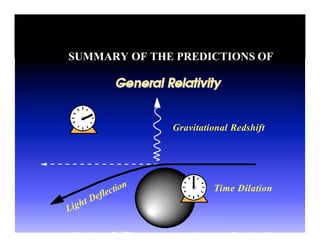
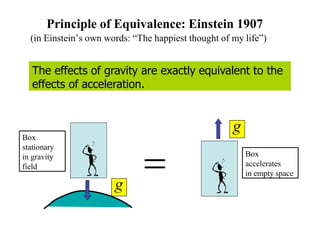
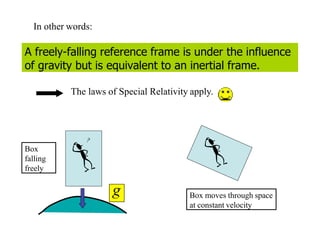
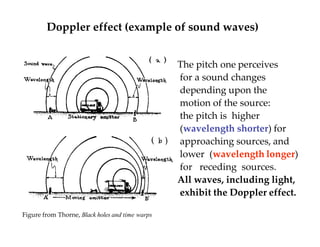
This document discusses Einstein's theory of general relativity and the recent direct detection of gravitational waves. It describes how Einstein predicted that masses curve spacetime and that freely falling objects move along geodesics in curved spacetime. The recent detection by an international collaboration provides direct evidence of Einstein's prediction that changing gravity generates ripples in spacetime called gravitational waves. This confirmation of gravitational waves validates general relativity and opens new opportunities for astronomy.





![Time Dilation in a Gravitational LINES
A thought experiment with flashing
watches shows that time runs slower
at the back of an accelerating space-
ship. The yellow dots represent the
flashes from the watches, and the
spacing between the dots represent
the time between the flashes.
By the equivalence principle,
time must also run slower at
lower altitudes in a gravitational
field.
[Exampleandfiguresfrom“TheCosmicfterspective”,
byBennett et al.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-friday-new-160218172226/85/EINSTEIN-S-GRAVITATIONAL-LINES-9-320.jpg)