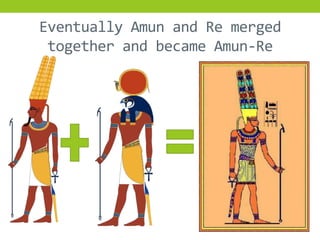
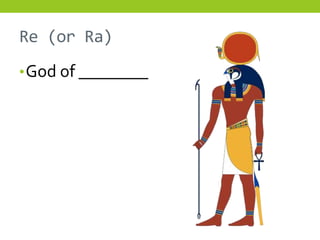
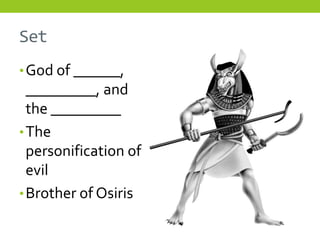
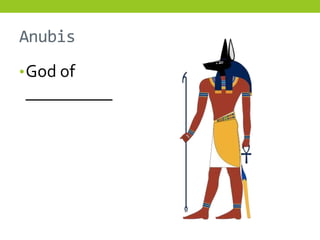
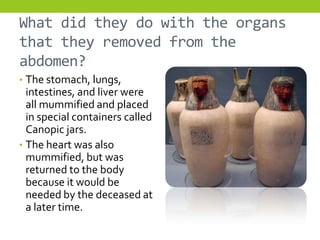
The document provides information about Egyptian religion, including key gods and goddesses like Osiris, Isis, Horus, Re, and Set. It explains major religious practices such as mummification of the dead, which involved removing organs and preserving the body so the soul could use it after death. The Egyptians built pyramids and temples and made offerings to ensure souls could navigate to the afterlife. They also created guides like the Book of the Dead to aid the soul's journey. The document outlines these topics to teach students about Egyptian religious beliefs and rituals.