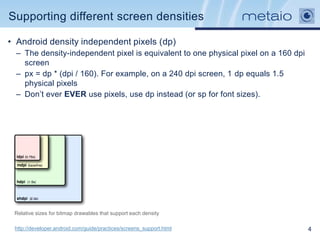
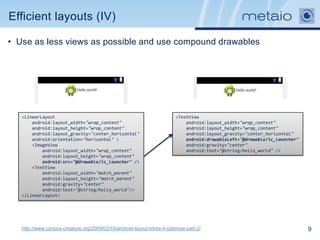
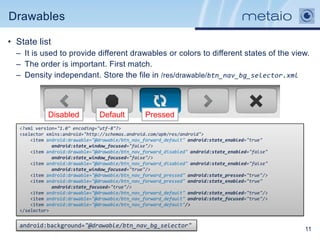
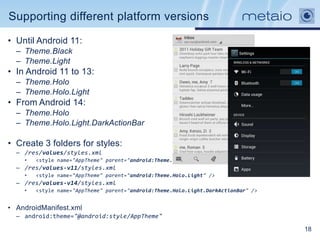
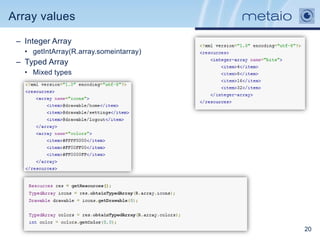
The document provides an overview of efficiently managing Android resources, including resource folders, resource qualifiers, and methods for handling different screen densities and layouts. It covers the use and definition of drawables, animations, styles, and themes, as well as managing values within XML resource files. Additionally, it emphasizes best practices for resource organization to enhance performance and maintainability in Android applications.