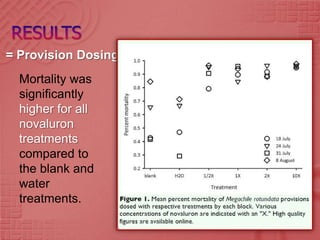
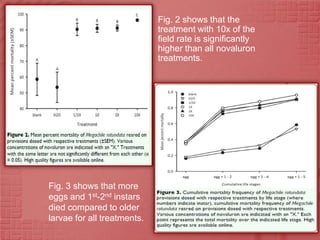
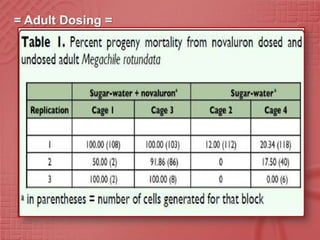
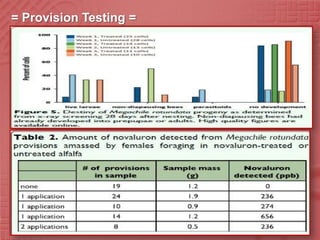
The study evaluated the effects of the insect growth regulator novaluron on immature alfalfa leafcutting bees, Megachile rotundata. In laboratory experiments, various concentrations of novaluron were applied to nectar-pollen provisions and directly to adult bees. Mortality was significantly higher for bee larvae developing in provisions treated with novaluron compared to the untreated controls. The highest mortality occurred at the highest novaluron concentration tested, 10 times the field rate used for Lygus bugs. Younger bee life stages, eggs and early instar larvae, experienced greater mortality than older larvae from novaluron exposure. Novaluron residues were detected in provisions for up to 15 days.