The educational system of South Africa has the following key aspects:
1) It guarantees equal access to basic education according to the constitution, and has principles of equity, quality, relevance, efficiency, and democratic participation.
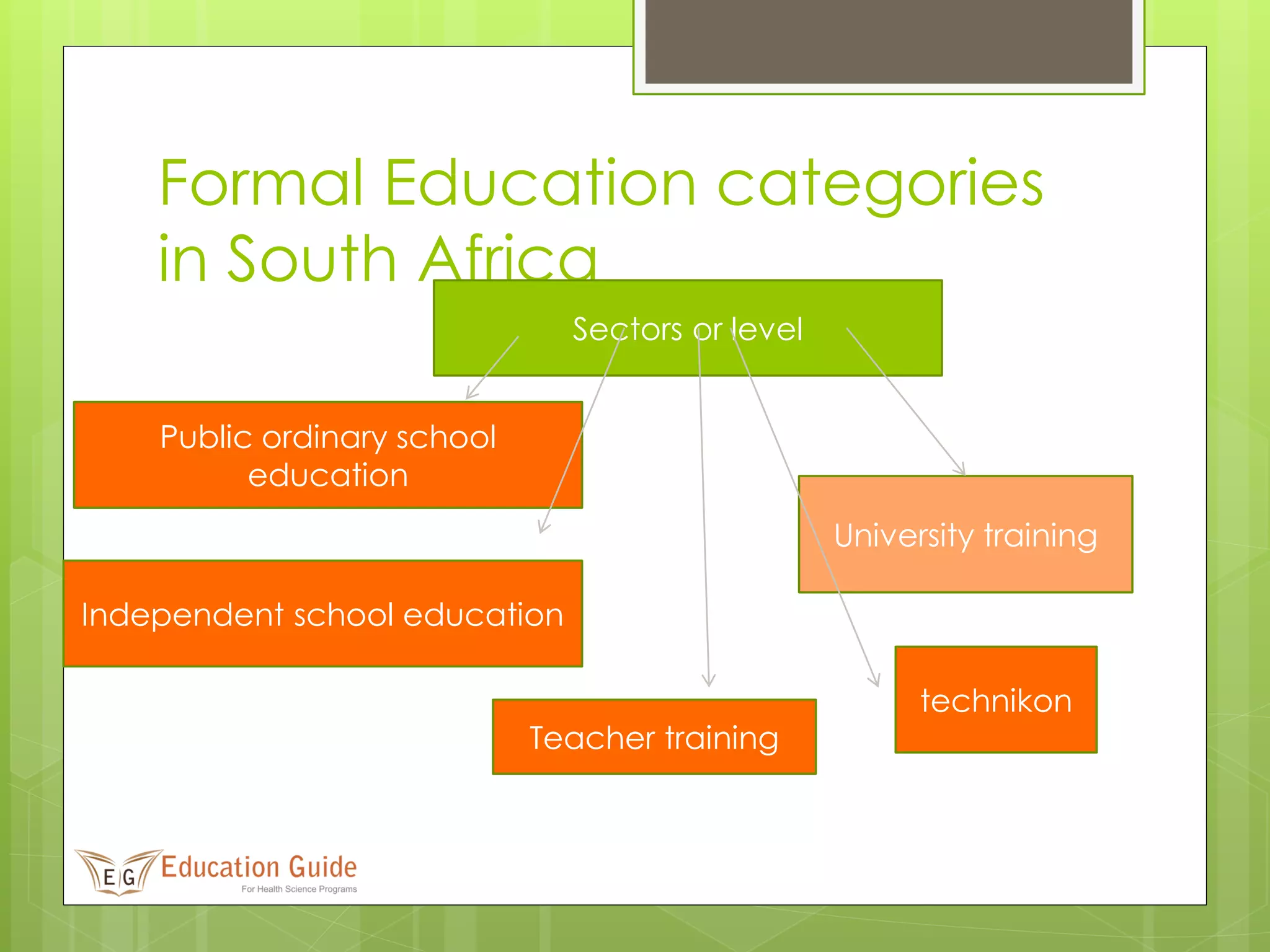
2) It is structured into public ordinary schools, independent schools, teacher training, and universities. Public schools cover pre-primary, primary, secondary, and higher education levels.
3) Compulsory general education and training covers grades R-9 and is divided into foundation, intermediate, and senior phases. Primary education has junior and senior categories, and grade 9 completes compulsory education.