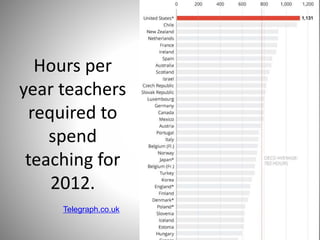
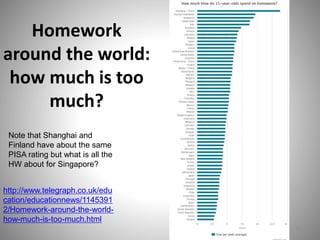
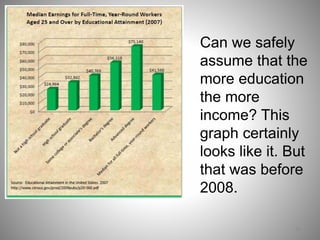
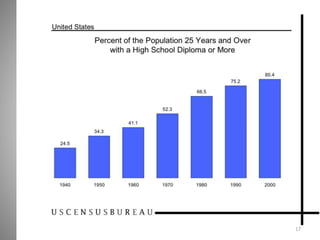
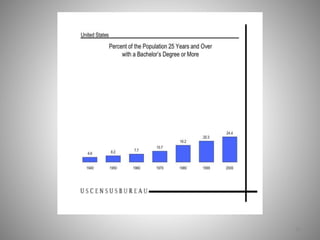
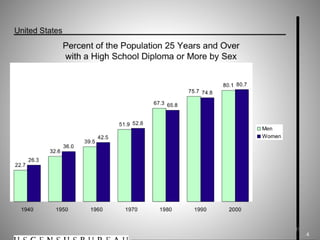
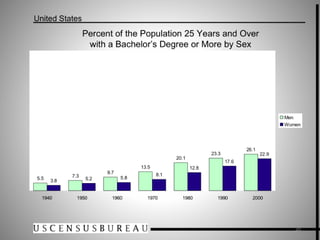
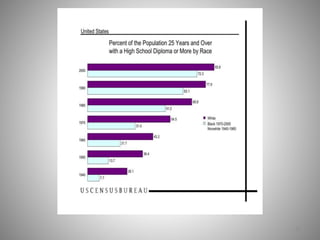
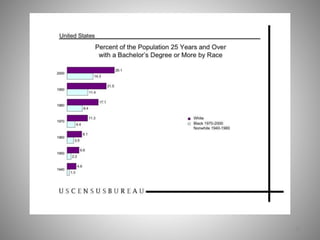
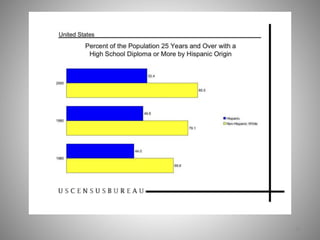
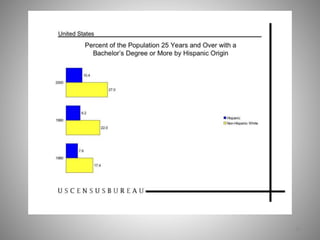
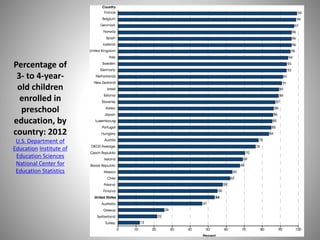
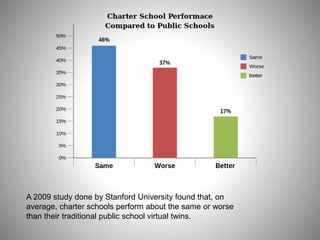
Students go to school for several reasons, including to get a good job, make more money, gain a broader worldview, and better participate in democracy. In school, students learn norms and values of the status quo through the "hidden curriculum," including nationalism, passive learning, and respect for authority. Schools also tend to encourage competition over cooperation. A student's cultural capital, or cultural exposure and worldview gained from family, directly impacts their future socioeconomic status. However, wealthier students generally have more access to educational resources and opportunities. Overall, the document examines factors like socioeconomic status, private interests in education, and inequities in educational opportunities that pose social problems in the U.S. education system.




























![The Governor Ronald Reagan
• Once elected, [1966]Mr. Reagan set the educational tone for
his administration by:
• a. calling for an end to free tuition for state college and
university students,
• b. annually demanding 20% across-the-board cuts in higher
education funding,[2]
• c. repeatedly slashing construction funds for state campuses
• d. engineering the firing of Clark Kerr, the popular President of
the University of California, and
• e. declaring that the state "should not subsidize intellectual
curiosity,[3]”
http://www.newfoundations.com/Clabaugh/CuttingEdge/Reaga
n.html
42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/education4-08-14-160121173008/85/Education-4-08-14-42-320.jpg)
![Further
• Mr. Reagan's denunciations of student protesters were both
frequent and particularly venomous. He called protesting
students "brats," "freaks," and "cowardly fascists." And when
it came to "restoring order" on unruly campuses he observed,
"If it takes a bloodbath, let's get it over with. No more
appeasement!"
• Several days later four Kent State students were shot to death.
In the aftermath of this tragedy Mr. Reagan declared his
remark was only a "figure of speech." He added that anyone
who was upset by it was "neurotic."[4] One wonders if this
reveals him as a demagogue or merely unfeeling.
http://www.newfoundations.com/Clabaugh/CuttingEdge/Reaga
n.html 43](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/education4-08-14-160121173008/85/Education-4-08-14-43-320.jpg)











![Response to The Bell Curve Study
Response: People may be smart in some
respects, in some contexts, and at some
tasks, but not in others. Some may have a
facility for numbers, others for words…The
kind of intelligence facilitating high
performance in one arena does not
necessarily have the same payoff in another.
…[R]anking on a single intelligence
continuum cannot explain much about their
social and economic outcomes.
59](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/education4-08-14-160121173008/85/Education-4-08-14-59-320.jpg)



![Response to The Bell Curve Study
Response: The Bell Curve, according to many
critics, overestimates the genetic basis and
heritability of IQ and underestimates the
influence of the social environment. [..]
While they claim the heritability of IQ may be
as much as 80 percent, other research,
drawing on a wider range of studies, suggests
a much lower figure, somewhere between 30
and 50 percent.
63](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/education4-08-14-160121173008/85/Education-4-08-14-63-320.jpg)


![Icing on the Cake
The ordinary routine of neutral reviewers [peer review]
having a month or two to go over the book with care
did not occur. Another handpicked group was flown to
Washington at the expense of the American Enterprise
Institute and given a weekend-long personal briefing
on the book's contents by Murray himself … just before
publication. The result was what you'd expect: The first
wave of publicity was either credulous or angry, but
short on evidence, because nobody had had time to
digest and evaluate the book carefully.
(The Bell Curve Flattened - Slate Magazine 1997)
66](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/education4-08-14-160121173008/85/Education-4-08-14-66-320.jpg)