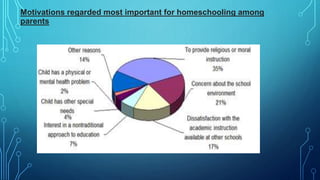
This document discusses and compares established education versus homeschooling. Established education typically involves formal schooling in an institutional setting with uniform curriculum and leads to certificates and degrees. Homeschooling involves education of children at home by family members and tutors, which was a common historical practice. The document outlines the types of education and motivations for homeschooling such as greater parental control, individualized learning, and religious/moral instruction. It also discusses teaching methods, informal learning, and the future of education with trends toward online learning and globalization.