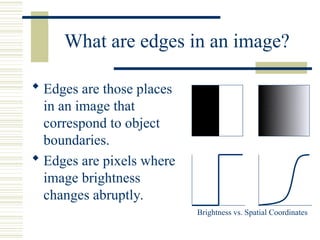
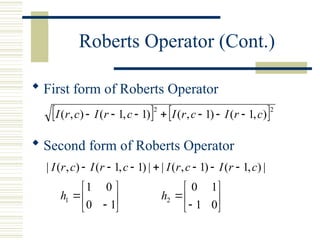
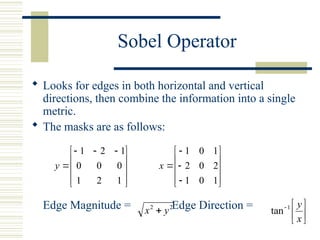
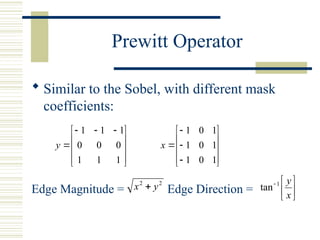
The document discusses edge detection in images, explaining that edges correspond to object boundaries and are characterized by abrupt changes in brightness. It details various edge detection methods and operators, including Roberts, Sobel, Prewitt, Kirsch, Robinson, and Laplacian operators, highlighting their advantages, disadvantages, and performance. The content also mentions the use of MATLAB for implementing these methods and provides a quick note on MATLAB's image processing toolbox for edge detection.