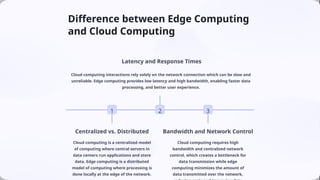
Edge computing is a distributed computing model that processes data closer to the source, enhancing response times and reducing bandwidth costs. Driven by advancements in IoT, real-time analytics, and 5G technology, it supports applications in smart cities, autonomous systems, and industry 4.0. The future of edge computing includes further integration with AI and critical advancements in autonomous technologies.