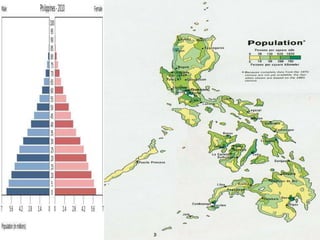
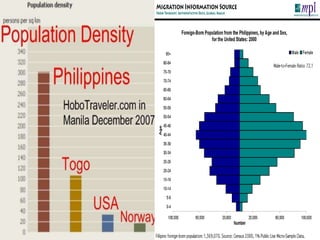
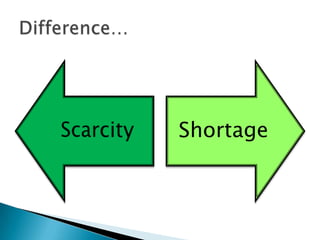
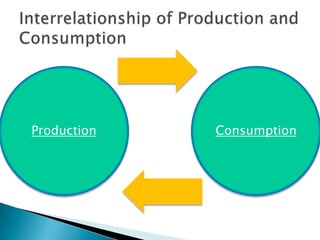
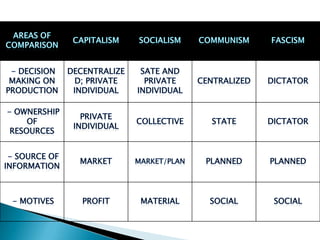
The document discusses the evolution of economic thought from ancient Greek philosophy through the development of various economic theories, including mercantilism, physiocracy, and classical economics, highlighting key figures such as Adam Smith and Karl Marx. It explores the intertwined relationship between economics and other social sciences, emphasizing the practical implications of economic principles in society. Additionally, it provides an overview of the historical context and economic policies affecting the Philippines, detailing the impacts of colonialism, wars, and various presidential administrations on the country's economy.