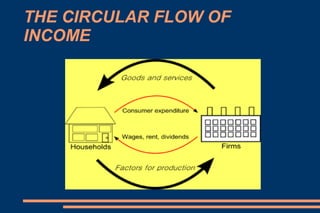
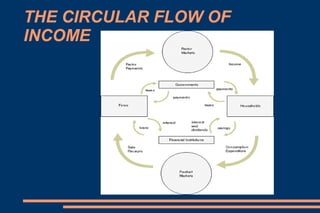
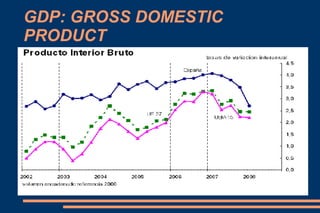
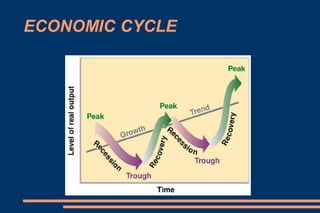
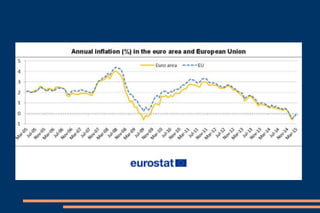
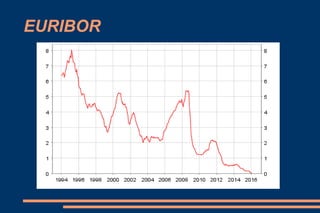
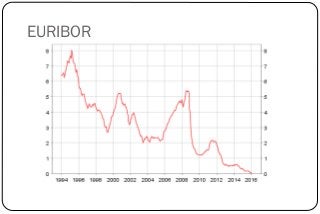
This document discusses key economic concepts including the circular flow of income, GDP, the economic cycle, recession, and economic indicators. It defines the circular flow of income as showing flows of goods and services between households and firms. GDP is defined as the total market value of goods and services produced within a country in a year. The economic cycle and recession refer to periods of decline and growth in economic activity. Economic indicators such as inflation, interest rates, and Euribor are also defined.