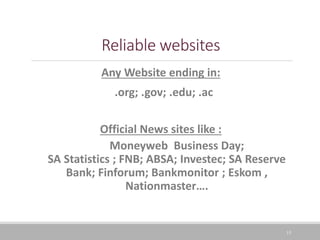
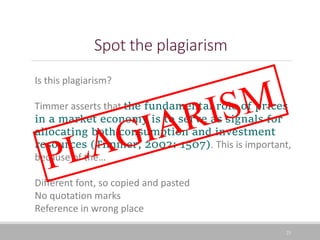
This document outlines a library training session focusing on distinguishing between various sources of information such as books, academic journals, reports, and databases, along with evaluating their reliability and authority. It also covers important concepts such as plagiarism, including its various forms and examples of how it can occur. The session aims to equip participants with the skills to find credible information for their academic assignments and emphasizes the importance of proper referencing.