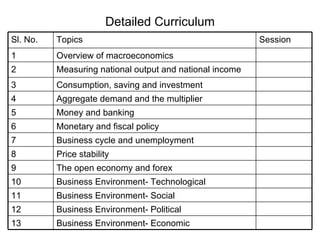
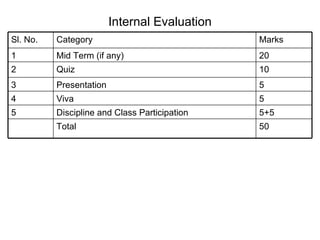
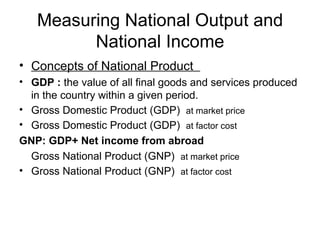
The document provides an overview of topics covered in a macroeconomics and business environment course including national output and income, consumption, investment, aggregate demand, monetary and fiscal policy, and the business environment. It also outlines the internal evaluation process for the course including midterm exams, quizzes, presentations, and participation. Key concepts in macroeconomics are defined such as GDP, GNP, aggregate supply and demand, and how national output and income are measured.