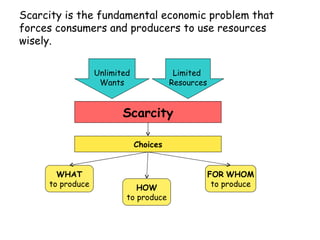
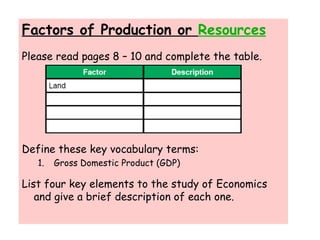
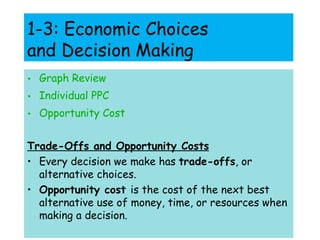
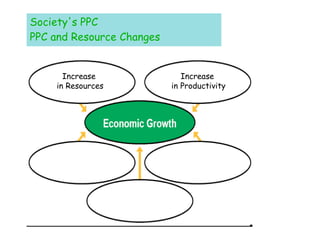
This document provides an overview of the materials and topics that will be covered in Ms. J. Hernandez's Summer Economics class. It includes a list of materials students should bring to each class, as well as materials needed outside of class. The first chapter that will be covered is on the fundamental economic problem of scarcity and the definitions of key economic terms. Students are asked to define terms like scarcity, needs, wants, and TINSTAAFL (there is no such thing as a free lunch). They are also asked questions about the difference between needs and wants and the fundamental economic problem societies face. Subsequent sections will cover factors of production, the circular flow model, productivity and economic growth. Students will learn about concepts like
![Welcome to Summer Economics Ms. J. Hernandez [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/economics1-1-100601200945-phpapp01/75/Economics-1-1-1-2048.jpg)