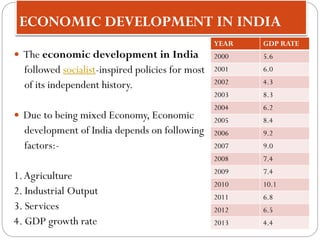
The document outlines a presentation on economic development. It discusses key concepts like economic growth, economic development, sustainable development, and the differences between them. It also examines the main elements, features, conditions and significance of sustainable development. Finally, it identifies the economic and non-economic determinants of economic development, such as natural resources, human resources, physical capital, technology, markets, social factors, political stability, and corruption.