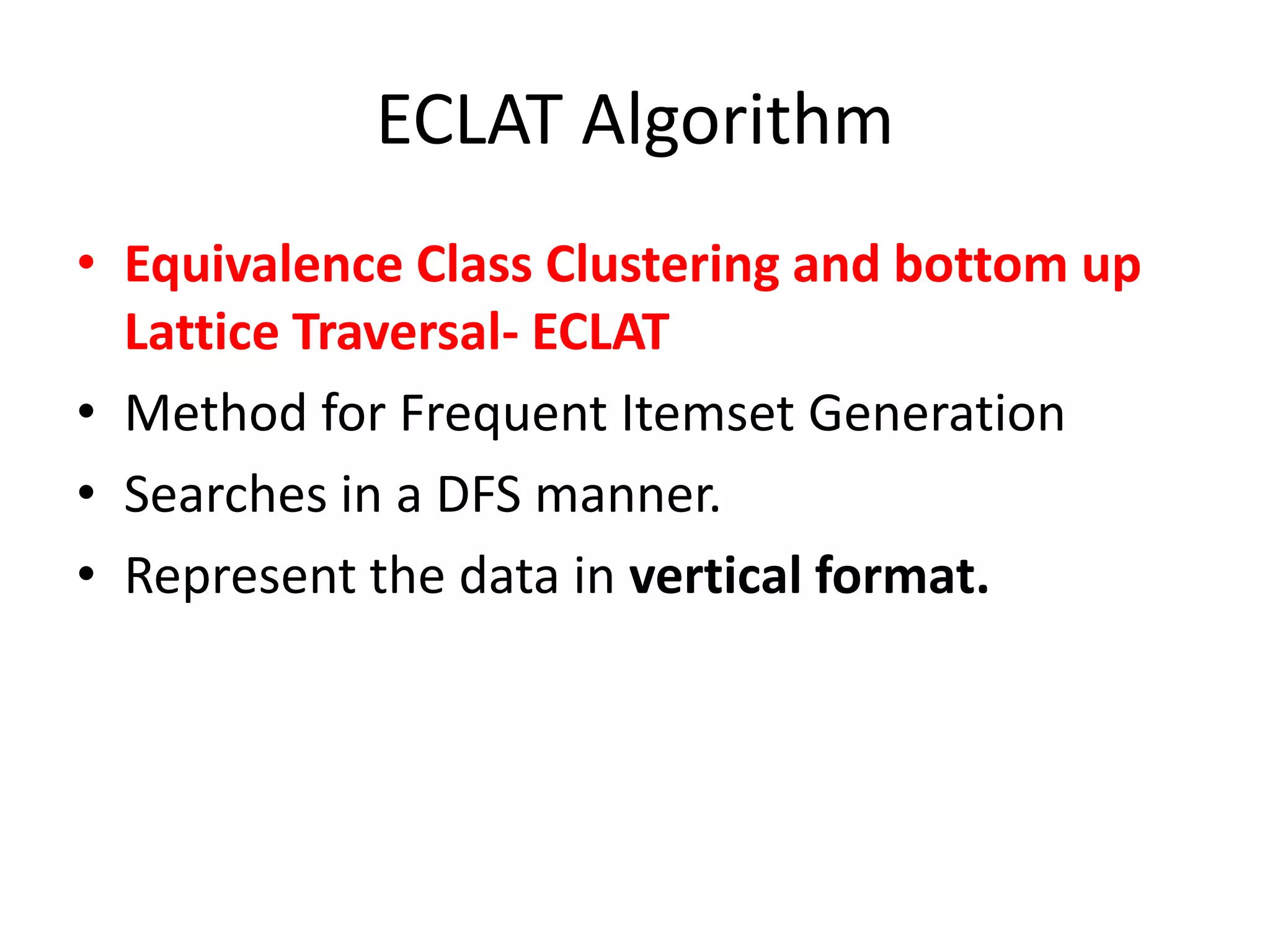
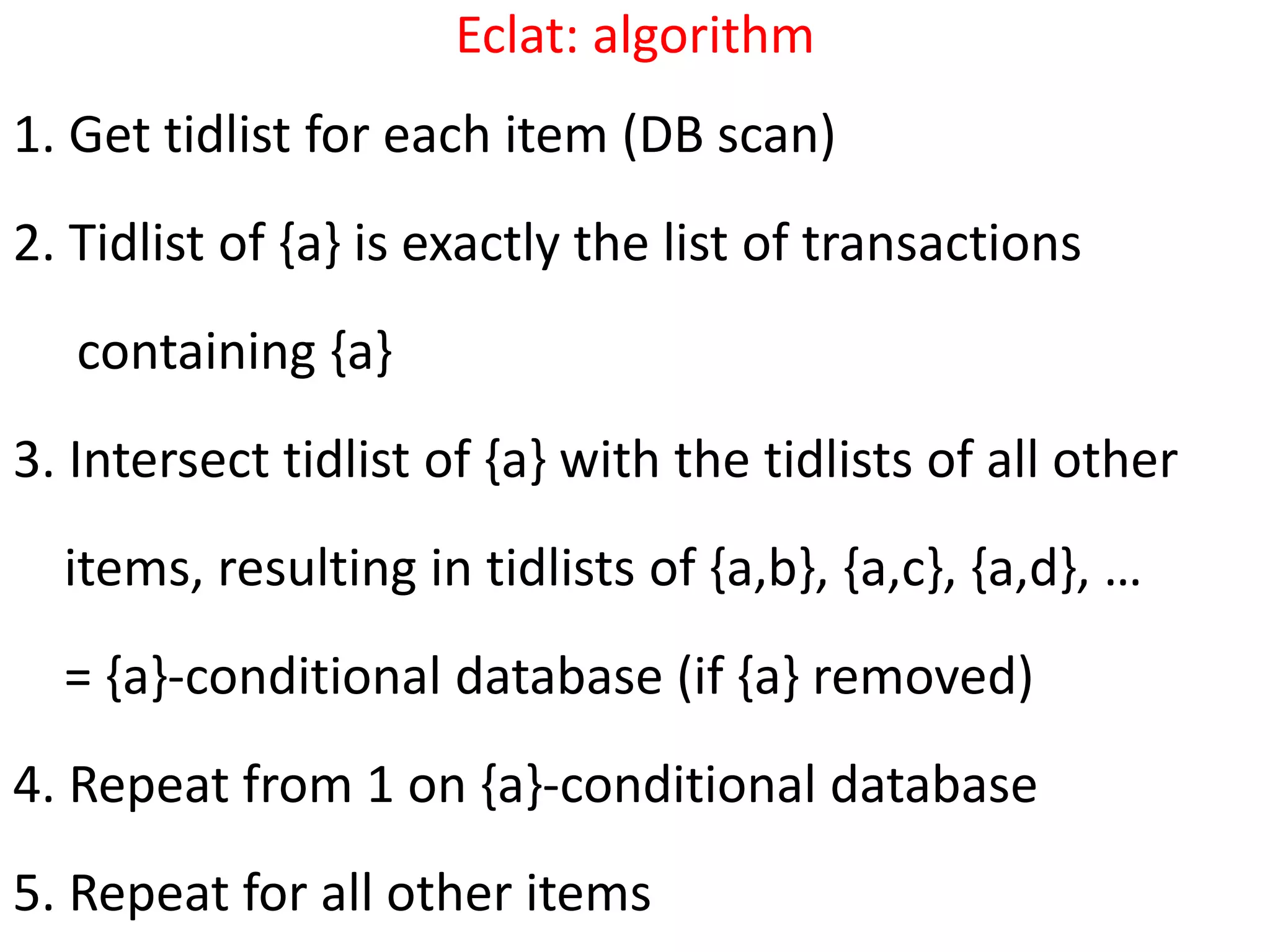
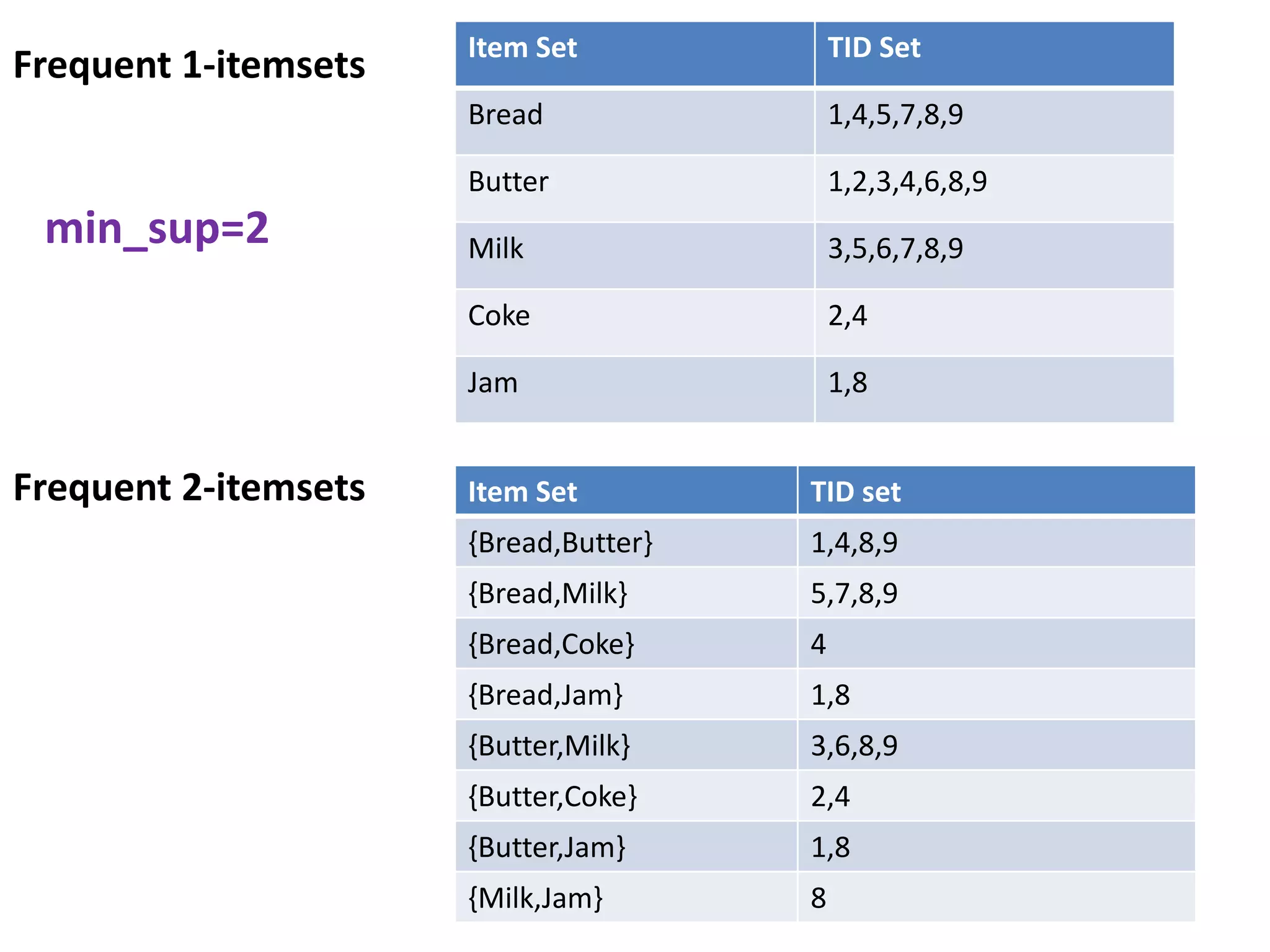
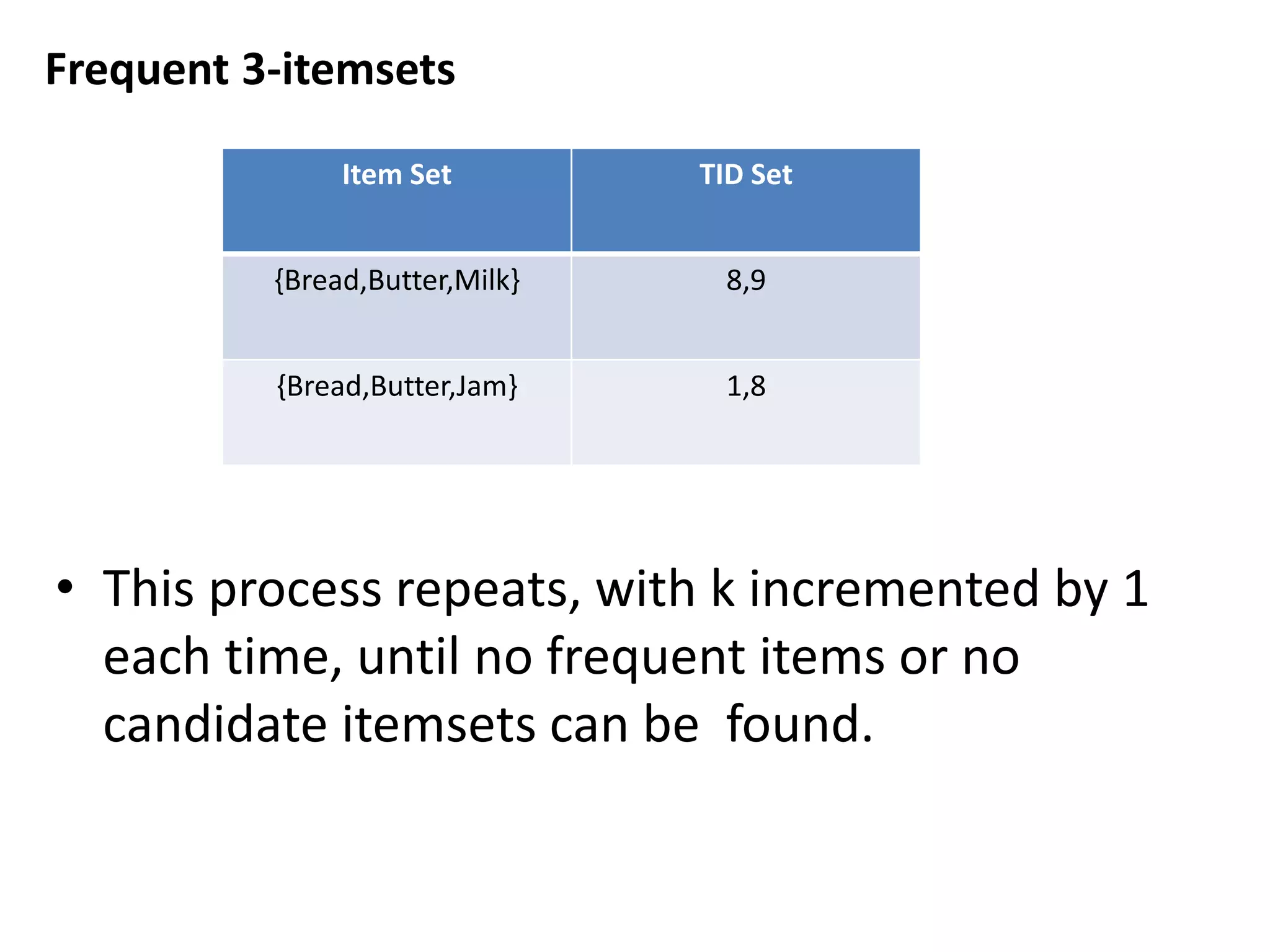
The document discusses the ECLAT algorithm for mining frequent itemsets from transactional data. ECLAT uses an equivalence class clustering approach and bottom-up lattice traversal to efficiently generate frequent itemsets in a depth-first search manner by representing the transaction data in a vertical format of item-tid lists. It improves upon the Apriori algorithm by avoiding multiple database scans and reducing memory usage through its depth-first search approach and representation of the conditional search space without having to remove items.