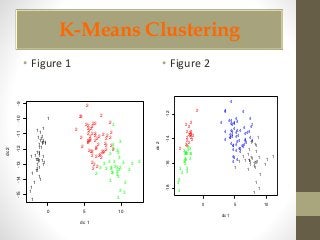
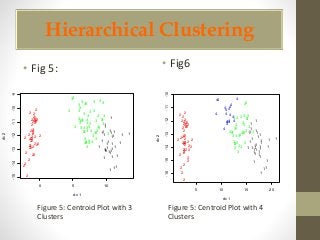
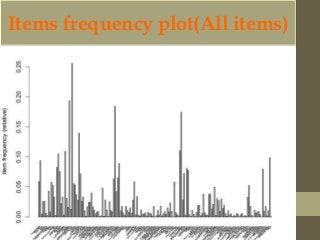
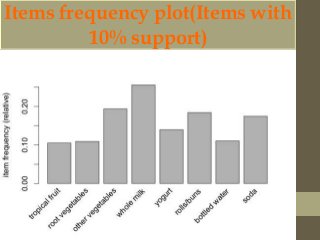
This document discusses clustering and association rule mining techniques. It describes how k-means clustering was used to cluster iris data into pure, slightly impure, and mixed clusters. Hierarchical clustering with Ward's method also grouped the data into clusters. Association rule mining with the Apriori algorithm analyzed transactional grocery data to find relationships between frequently purchased item sets based on support and confidence thresholds.